Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are function groups?
In organic chemistry, functional groups are one of the most reactive parts of organic compounds and determine the major characteristic of compounds. An organic complex has a backbone (skeleton) of carbon-carbon single bonds with different groupings of atoms, known as functional groups, connected at various locations. C=C, C≡C, and polar bonds from carbon to heteroatoms are more reactive than C-C or C–H bonds, and this is where the chemistry occurs. An organic complex has a backbone (skeleton) of carbon-carbon single bonds with different groupings of atoms, known as functional groups, connected at various locations.
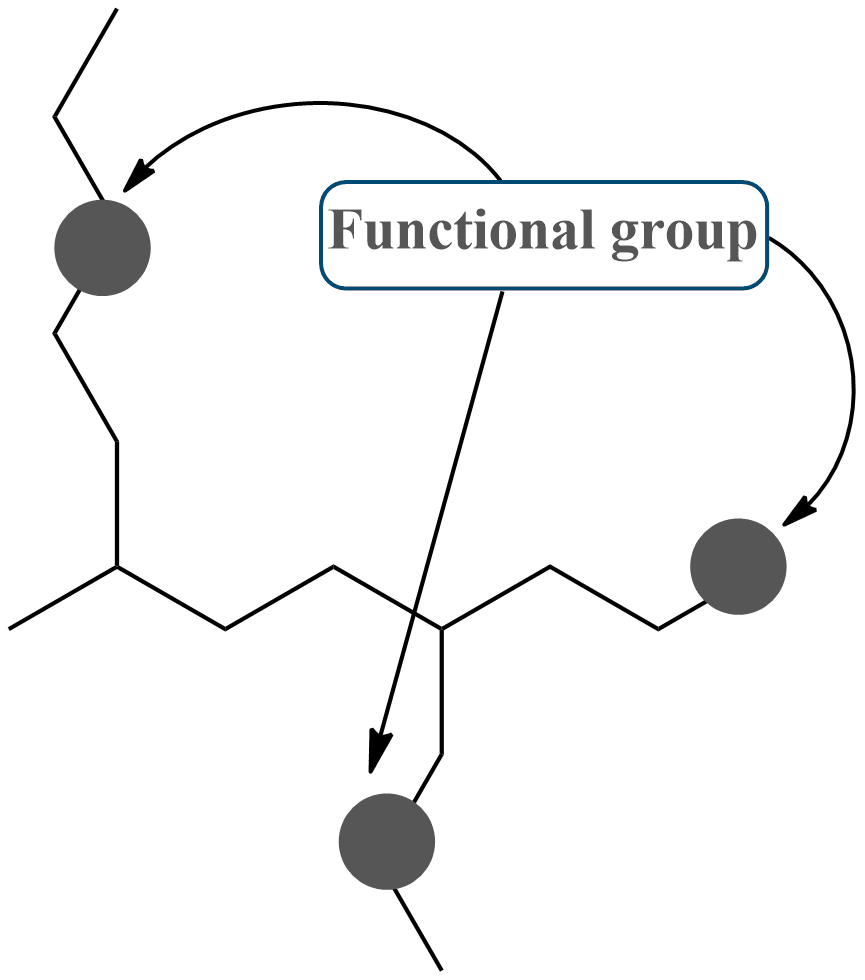
Examples of the Functional groups
The presence of certain functional groups in a molecule has a significant impact on its behavior, reactivity, and interactions with other molecules, resulting in a large diversity of organic compounds found in nature and produced for different purposes. Understanding functional groups is crucial for predicting the characteristics and behavior of organic molecules, as well as designing new chemical procedures and medications. Here are some common functional groups.
Alkanes
Alkanes are the simplest and most stable class of hydrocarbons. They contain only carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds.
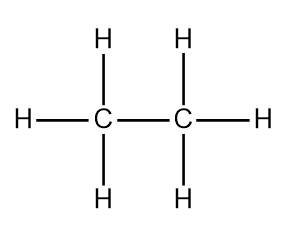
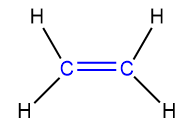
Alkenes
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons, they contain a carbon-carbon double bond. The presence of the carbon-carbon double bond makes alkene more reactive than alkanes.
Alkynes
Alkynes are the most reactive among alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes due to the presence of a carbon-carbon triple bond.
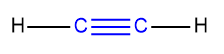
Arenes
Arenes, also known as aromatic hydrocarbons, contain a ring of carbon atoms with alternating single and double bonds i.e. Benzene.
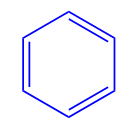
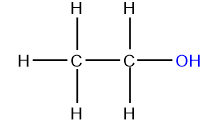
Alcohols
Alcohols are compounds obtained by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of aliphatic hydrocarbons with the corresponding number of hydroxyl groups (–OH).
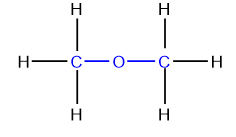
Ethers
Ethers are a class of compounds whose molecules have an oxygen atom bonded to two organic groups. The bivalent oxygen (–O–) is the functional group of ethers.
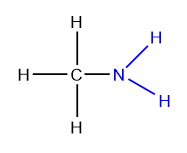
Amines
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds which may be considered as derivatives of ammonia in which hydrogen atoms have been replaced by alkyl or aryl groups.
Aldehydes and Ketones
Aldehydes and ketones form two important classes of organic compounds containing the carbonyl (>C=O) group.
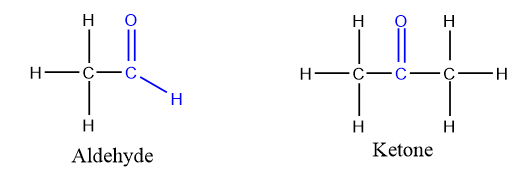
Carboxylic Acids
Organic compounds containing carboxyl group (–COOH) possess sufficient acidic character and are called carboxylic acids. The carboxyl group is made up of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups.
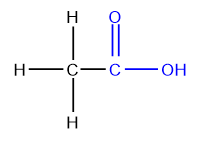
Amides
Amides contain a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a nitrogen atom(N).
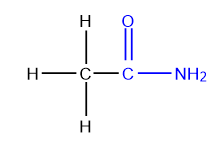
Nitriles
Nitriles contain a cyano group, which consists of a carbon tom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom (C≡N). Nitriles are also known as cyanides.
Nomenclature of Functional Groups
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) created a set of rules for the naming of functional groups in organic chemistry. This rule support in the standardization of organic compound nomenclature, making it simpler to discuss and understand their structures and characteristics.
| Class | General Molecular Formula | Example | IUPAC Name | Common name |
| Alkanes | R–H | H3C–CH3 | Ethane | Ethane |
| Alkenes | RR’C=CR”R”‘ | H2C=CH2 | Ethene | Ethylene |
| Alkynes | RC≡CR’ | HC≡CH | Ethyne | Acetylene |
| Arenes | Ar–H | C6H6 | Benzene | Benzene |
| Alkyl halides | R–X | CH3CH2Cl | Chloroethane | Ethyl chloride |
| Aryl halides | Ar–X | C6H5Cl | Chlorobenzene | Chlorobenzene |
| Alcohols | ROH | CH3CH2OH | Ethanol | Ethyl alcohol |
| Phenols | ArOH | C6H5OH | Phenol | Phenol |
| Ethers | ROR’ | H3CH2COCH2CH3 | Diethyl ether | Diethyl ether |
| Aldehydes | RCHO | CH3CHO | Ethanal | Acetaldehyde |
| Ketones | RR’C=O | CH3COCH3 | 2-propanone | Acetone |
| Carboxylic acids | RCO2H | CH3COOH | Ethanoic acid | Acetic acid |
| Esters | RCO2R’ | CH3COCH3 | Methyl ethanoate | Methyl acetate |
| Amides | RCONHR’ | CH3CONHCH3 | N-methylacetamide | N-methylacetamide |
| Amines | RNH2, RNHR’, RNR’R” | CH3CH2NH2 | Ethylamine | Ethylamine |
| Nitriles | RC≡N | H3CC≡N | Acetonitrile | Acetonitrile |
| Nitro Compound | ArNO2 | C6H5NO2 | Nitrobenzene | Nitrobenzene |
FAQs
What is a functional group?
functional groups are one of the most reactive parts of organic compounds and determine the major characteristic of compounds.
what are the examples of functional groups?
Some examples of the functional group include hydroxyl, ketone, amide, ether, etc.
What is a functional group in biology?
Some of the most important functional groups in biological compounds include hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and thiol groups.
Is alkene a functional group?
A carbon-carbon double bond present in the alkene group is functional group.
How do you identify a functional group?
Functional groups are atom groups that are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds.






