Table of Contents
ToggleFeel good Hormones are the chemical messenger which excites, enhanced your feeling. Have you ever wonder, why there is fluctuating of our feeling, emotions for certain things? What are the reason of such mood swings? It all because of feel good hormones which are responsible for such excitement, feelings.
What are feel good hormones?
Feel good hormones are responsible for elevating your mood depend upon certain circumstances. They are generally named as Endorphins, oxytocin, dopamine, and serotonin. A few easy lifestyle tweaks, such as meditation, exercise, and nutrition, can raise your levels of these hormones and perhaps lift your spirits.
Some hormones can make you feel happy, to get some award, rewards, achievement, some make you feel loved and increase your hormones rush.
Hormones
Hormones are substances that are produced by various glands located throughout your body. They move through the circulation, serving as messengers and contributing to several physiological functions. It is well recognized that several hormones can support the emergence of happy and pleasurable emotions.
A particular class of hormones is known as the “feel-good hormones” due to the positive and occasionally euphoric emotions they elicit. Additionally, they are regarded as neurotransmitters, which indicates that they transfer signals between nerve cells. Which four hormones make you feel good? oxytocin, endorphins, serotonin, and dopamine.
Four Feel good hormones
Generally they are named as:
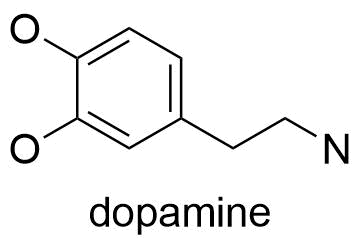
Dopamine: The path to pleasure
The dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is a key component of your brain’s reward system and is also referred to as the “feel-good” hormone. In addition to learning, memory, and other things, it is linked to enjoyable experiences. It is formed by the amino acid, tryrosine which is converted into amino acid called L-Dopa and which undergoes another changes in presence of enzymes and dopamine is formed.
Food high in tyrosine:
- meat product
- dairy product
- avacados
- bananas
- soy
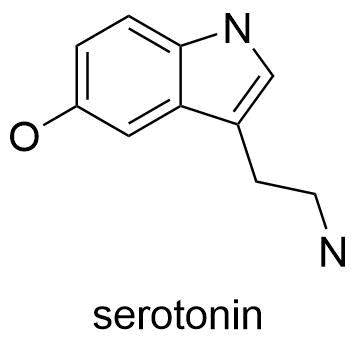
Serotonin: The natural mood booster
This hormone and neurotransmitter aid in mood regulation and also regulates sleep, hunger, digestion, memory, and learning capacity. This hormone is responsible for boosting your mood. An area in the center of brain stem produces serotonin.
Depression and low serotonin levels are related. Serotonin levels in the brain are raised by the most widely used antidepressants, serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Elevating serotonin levels can also be achieved without medication. Exercise is one natural approach to raise serotonin levels. Your body releases more tryptophan, an amino acid that your brain requires to produce serotonin, when you ride a bicycle or exercise weights. This surge in serotonin following a strenuous activity (together with other endorphins and neurotransmitters) is the reason why many experience the euphoric sensation known as a “runner’s high”.
Endorphins: The brain’s natural pain relievers
Neurotransmitters called endorphins are produced in the brain by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. They are natural hormones that have the power to reduce stress, ease pain, elevate mood, and promote overall wellbeing. When you engage in enjoyable activities like eating, exercising, having sex, etc., your body releases endorphins.
When you are in pain or under stress, your brain receives pain signals from your nerves and blocks the nerve cells’ ability to receive them by releasing endorphins. This system functions as a pain-relieving switch, allowing you to carry on with your daily activities even under trying and stressful conditions. Because it is in our natural evolution to seek out pleasure and avoid suffering.
Oxytocin: The love hormones
The posterior pituitary releases oxytocin, a peptide hormone and neuropeptide that is ordinarily synthesized in the hypothalamus. It has been a part of animal evolution since the beginning, and in humans, it affects behavior related to social bonding, reproduction, birthing, and the postpartum period.
In addition to stimulating the uterine muscles to contract, oxytocin also increases prostaglandin synthesis, which in turn causes an increase in uterine contractions. Oxytocin is occasionally administered to women whose labor is progressing slowly in order to accelerate the process. After birth, oxytocin promotes the attachment between mother and child and facilitates the flow of milk from the breast ducts to the nipple.
Additionally, when we become enthused about our spouse or fall in love, our bodies release oxytocin. For this reason, it has been dubbed the “cuddle hormone” and the “love hormone.”
References
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/oxytocin-the-love-hormone
- https://www.healthline.com/health/happy-hormone#sunlight
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/feel-good-hormones