Table of Contents
ToggleEsters are derivatives of carboxylic acids in which the -OH group of the carboxylic acid has been replaced by the -OR group (where R may be alkyl or aryl group). These are the most important class of acid derivatives and are widely distributed in nature in plants, fruits, and flowers.
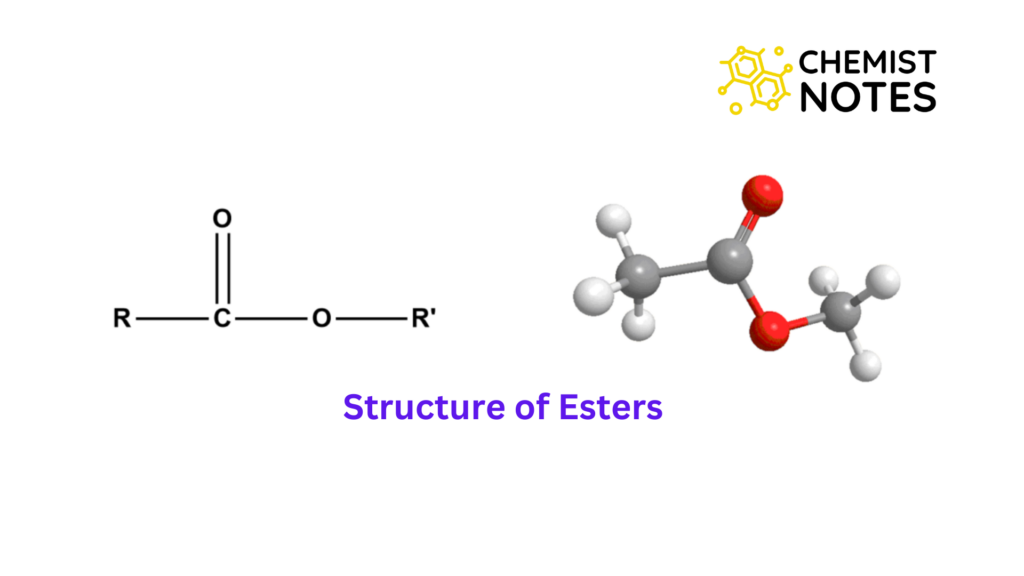
Structure of Esters
Ester has a double carbon-oxygen bond that is additionally singly linked to a second oxygen atom. The oxygen atom is also linked to an aryl or alkyl group.
Nomenclature of Ester
Esters are named by replacing the suffix —ic acid of the IUPAC or common name of parent acid with ‘—ate’ and adding the name of the alkyl group before it. For example,

| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| HCOOC2H5 | Ethyl formate | Ethyl methanoate |
| CH3COOC2H5 | Ethyl acetate | Ethyl ethanoate |
| CH3CH2COOC2H5 | Ethyl propionate | Ethyl propanoate |
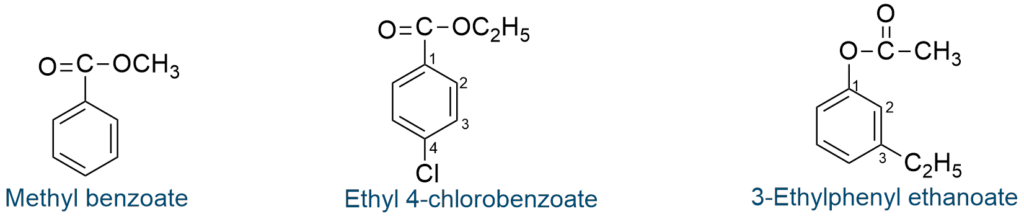
The name of some aromatic ester are given below:
Preparation of Ester
Esterification reaction
Ester can be prepared by the reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols in the presence of conc. sulphuric acid. This reaction is called the esterification reaction. The esterification process is one of the major methods of preparation of ester. Through an esterification reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, this chemical reaction produces at least one ester product.
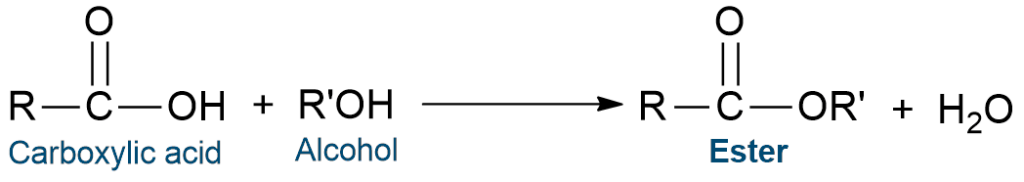
The esterification reaction is reversible in nature.
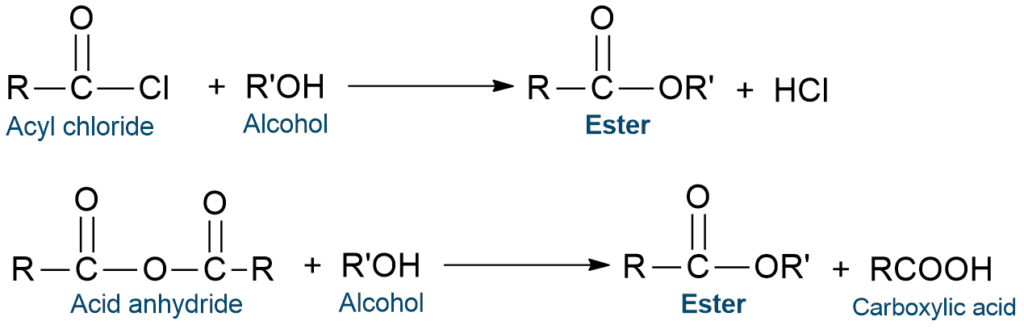
From acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides
Esters are also prepared by the reaction of acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides with alcohols.
From Haloalkane
Esters can be prepared by heating haloalkanes with silver salts of carboxylic acids.

Properties of Esters
Physical Properties
State: Esters are colorless liquids or solids with a characteristic fruity smell. The pleasant smell of most of the flowers and fruits is due to the ester present in them. The characteristics taste and odors of different ester find applications in the manufacture of artificial flavoring and perfuming agents. The flavors of some of the ester are given below.
| Esters | Flavour |
| n-Pentyl ethanoate | Banana |
| benzyl ethanoate | Jasmine |
| Isobutyl methanoate | Raspberry |
| Octyl ethanoate | Orange |
| Ethyl butanoate | Pineapple |
| Amyl butyrate | Apricot |
Solubility: Ester’s are sparingly soluble in water but are miscible in organic solvents like alcohols and ether. In fact, most of the esters are themselves very good solvents for plastics and nitrocellulose.
Boiling points: The boiling points of ester are always less than the corresponding carboxylic acids because esters do not form intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Uses of Esters
- They are used as plasticizers for plastics and resins.
- They are used as artificial fruit flavors for making essences.
- These are used as industrial solvents for lacquers, oils, fats, varnishes, etc.
- Ester with aromatic odors are utilized in fragrances, essential oils, food flavorings, cosmetics, and other products.
FAQs
What is ester used for?
Ester is used in synthetic flavlours, cosmetics, fragrances and other industrial solvents.
How is an ester formed?
The reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols in the presence of conc. sulphuric acid formed ester which is called esterification reaction.
What is an ester in chemistry?
Ester are derivatives of carboxylic acids in which the -OH group of the carboxylic acid has been replaced by the -OR group (where R may be alkyl or aryl group).






