Table of Contents
ToggleResonance effect is withdrawal or releasing of electrons associated to a particular substituent through the delocalization of pi-electrons, which can be demonstrated by various canonical structures. The phenomena in which two or more structures can be written for true structure of a molecule but none of them alone can explain all the properties of the molecule is called as resonance effect.
There can be resonance only between structures that contain the same number of odd electrons. The individual structure is called a resonance form or a canonical form.
The phenomena of resonance is shown by a double-headed arrow which is written in between the cannonical forms. The resonance hybrid is more stable than any of the canonical forms contributing to the resonance.
Resonance Effect examples
In the case of Benzene:
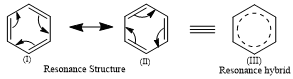
Structure (I) and (II) has two types of carbon and carbon bonds, three C-C single bonds with a bond length of 1.54 Å and three C=C double bonds with a bond length of 1.34 Å. But experimentally, it is found that all 6 bonds of carbon and carbon are similar and found intermediate of C-C and C+C bond of length 1.39 Å.
The low reactivity of halogen in vinyl bromide can be explained on account of the phenomenon of resonance.
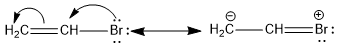
Application of Resonance Effect
The great usefulness, and hence the great value, of the resonance theory lies in fact that it retains the simple crude type of structural representation.
Stability of Carbocation
It has been discovered that the carbocation in which the positive charge is conjugated with a double bond is more stable. Delocalization of π-electrons of conjugated double bonds results in resonant structures, which increase stability. For Example, An allylic carbocation is more stable than the corresponding alkyl cation due to the resonance.
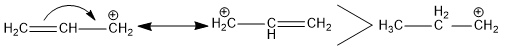
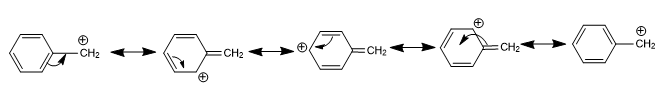
Stability of Carbanion
Due to resonance, the presence of double bonds or an aromatic ring near to a negatively charged carbon atom increases the stability of the anion. The negative charge on benzyl carbanion dispersed over other carbon atom due to resonance hence benzyl carbanion is more stable than ethyl carbanion.
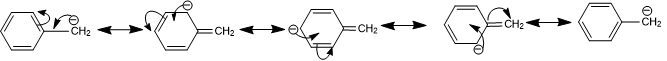
Stability of Free Radical
Simple alkyl radicals are less stable than allylic and benzylic types of free radicals due to the delocalization of the unpaired electrons over the π system.
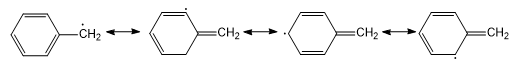
Mesomeric Effect Vs Resonance Effect
- The phenomena in which two or more structures can be written for true structure of a molecule but none of them alone can explain all the properties of the molecule is called resonance effect . The mesomeric effect arises due to the substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound, and it is represented by the letter M.
- The mesomeric effect and resonance effect is a permanent effect in which mesomeric effect depends on the substituents or the functional groups in a chemical compound.Resonance refers to delocalization of electrons in a given system.
- The group which shows +R effect (electron releasing) is equivalent to +M effect and the group shows –R effect (electron attracting) is equivalent to –M effect.
Difference Between Resonance and Inductive Effect
- The polarization of one bond caused by the polarization of an adjacent bond is known as an inductive effect. The phenomena in which two or more structures can be written for true structure of a molecule but none of them alone can explain all the properties of the molecule is called Resonance Effcet.
- The electronegativity difference between the two atoms in the bond directly affects on the inductive effect while Number of Resonating structure effect the stability.
FAQs
What is resonance effect in organic chemistry?
The phenomena in which two or more structures can be written for true structure of a molecule but none of them alone can explain all the properties of the molecule is called as resonance.
What is resonance effect?
The phenomena in which two or more structures can be written for the true structure of a molecule but none of them alone can explain all the properties of the molecule is called as resonance effect.
What is the difference between resonance and mesomeric effect?
The phenomena in which two or more structures can be written for the true structure of a molecule but none of them alone can explain all the properties of the molecule is called the resonance effect. The mesomeric effect arises due to the substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound, and it is represented by the letter M.







2 Responses
The stability of free radical part diagram is abit wrong
Thank you Aakanksha. We will update it soon