Table of Contents
ToggleDefinition: The polarization of one bond caused by the polarization of an adjacent bond is known as an inductive effect. Inductive effect is a permanent effect. The presence of a more electronegative atom attached to one of the carbon atoms will lead to bond polarization.
The electron-withdrawing nature of groups or atoms is called a negative inductive effect. It is indicated by -I.
NH3+ > NO2 > CN > SO3H > CHO > CO > COOH > COCl > CONH2 > F > Cl > Br > I > OH > OR > NH2 > C6H5 > H
And the electron-releasing nature of atoms or groups is called the +I effect.
C(CH3)3 > CH(CH3)2 > CH2CH3 > CH3 > H
Inductive effect examples
For example, the C-C bond in chloroethane is polarized by the presence of the electronegative chlorine atom.
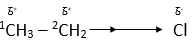
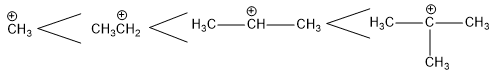
Stability of carbocation
Alkyl group attached to the positively charged carbon atom of carbocation tends to release electrons to the positively charged carbon by +I effect. This results in dispersal of positive charge on it and hence increases the stability of carbocation. Greater the number of alkyl groups, greater is the dispersal of the positive charge and greater is the stability of carbocation.
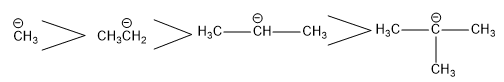
Stability of Carbanion
Electron releasing alkyl group tend to intensify the negative charge and hence destabilize the carbanion. Therefore stability of carbanion decreases with increase in alkyl group.
Difference between Inductive effect and Mesomeric effect
| Inductive effect | Mesomeric Effect |
| The polarization of one bond caused by the polarization of an adjacent bond is known as an inductive effect. | The mesomeric effect arises due to the substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound, and it is represented by the letter M. |
| The electronegativity difference between the two atoms in the bond directly affects on the inductive effect. | The mesomeric effect is a permanent effect which depends on the substituents or the functional groups in a chemical compound. |
| The electron-withdrawing nature of groups or atoms is called a negative inductive effect. It is indicated by -I. | When the substituent is an electron-withdrawing group, the mesomeric effect is negative -M. |
| The electron-releasing nature of groups or atoms is called a positive inductive effect. It is indicated by +I. | When the substituent can be considered as an electron releasing group based on the resonance structures, the effect is positive +M. |
FAQs
What is inductive effect?
The polarization of one bond caused by the polarization of an adjacent bond is known as an inductive effect.






