Table of Contents
ToggleFree radical is defined as any atom or group of atoms that contain unpaired or odd electrons. In other words, free radicals are atoms or groups of atoms with unpaired electrons in outer shell configuration. When a neutral molecule undergoes homolytic fission, each of the bonded atoms retains one electron from the shared pair, and hence free radicals are produced.
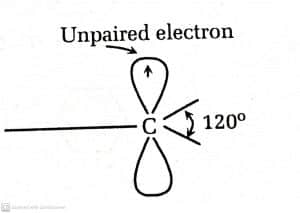
Some of the features of free radicals are:
- sp2 hybridization
- Geometry of carbon atom is planar, and have bond angles of 120o
- Highly reactive i.e. less stable
- Free radical shows paramagnetic behaviour due to spin of the odd electron
- Behave as oxidant or reductant as it has tendency to accept or donate electrons
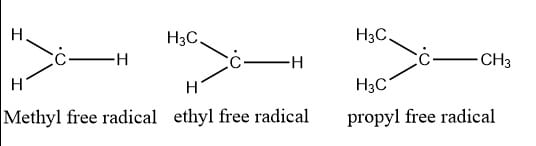
Examples of free radicals
Some of the examples of free radicals are
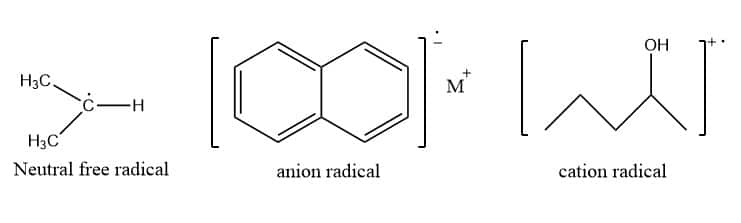
Types of free radical
Mostly there are two types of free radicals. They are neutral free radical and Charged (cation/anion) free radical.
Sources of free radicals
- Environmental pollution
- Radiations
- Ozone layer
- Mitochondria
- Peroxisomes
Free radical formation
Some of the major ways of generation of free radicals include:
Homolytic cleavage:
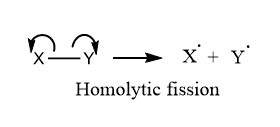
Photocatalytic cleavage:
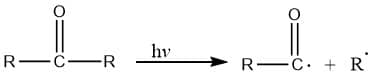
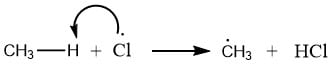
Abstraction of atom:
Free radical stability:
Free radical stability order: Methyl free radical < primary free radical < secondary free radical < tertiary free radical
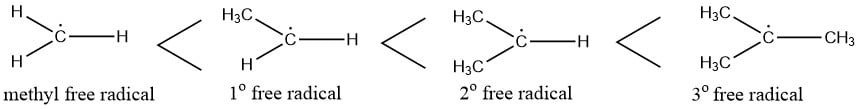
Stability of free radical
- Greater the number of hyperconjugating structures of species, greater is the stability of free radical. Thus the increasing order of stability of free radical is 1o < 2o < 3o free radical
- Stability of free radical increases by the resonance effect
FAQs
What are free radicals?
Free radicals are any atom or group of atoms that contain unpaired or odd electrons.
Free radical polymerization
Free radical polymerization is the process of formation of the polymer by the addition of free radicals unit or block.
free radical bromination
The photochemical reaction in which bromine is substituted for Hydrogen on an alkane is called free radical halogenation.
free radical halogenation
The photochemical reaction in which chlorine or bromine is substituted for Hydrogen on an alkane is called free radical halogenation.
free radical scavenger
Those substances that help in the protection of cells from being damaged by free radicals are called free radical scavengers.
What causes free radicals?
The cleavage like homolytic cleavage, photolytic cleavage, abstraction of an atom of species, etc. causes free radical formation.
Is O3 a free radical?
No, O3 is not a free radical.
Which free radical would be most stable?
Depending on the number of carbon groups attached to the carbon atom containing unpaired electrons, tertiary free radical is the most stable.






