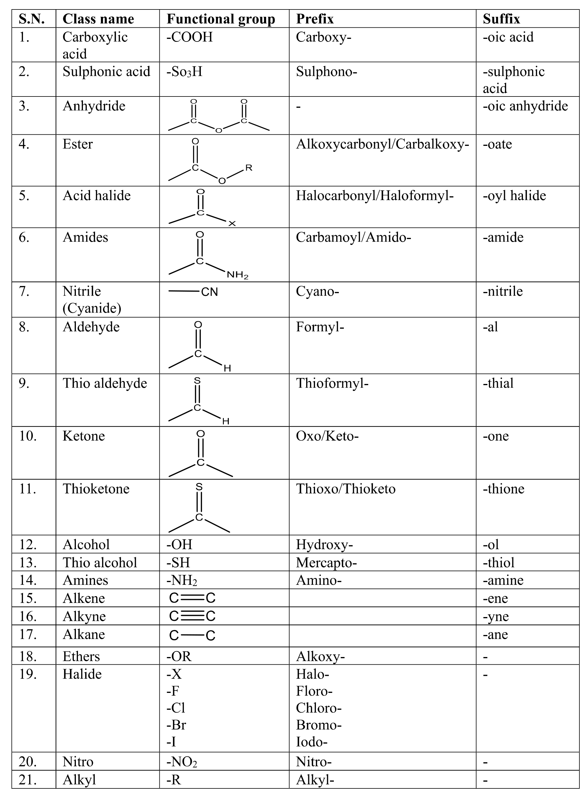
Table of Contents
ToggleOrganic chemists developed and utilized the IUPAC nomenclature system of organic compounds to solve the problems caused by common/arbitrary nomenclature systems. The comprehensive and systematic set of logical rules for the nomenclature of organic compounds was prepared by IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) in 1979 and was upgraded in 1993.
IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds
Before going to the rules of the IUPAC nomenclature system of organic compounds, let’s discuss some terms involved in it.
IUPAC Name= Prefix + Word root + Primary suffix + Secondary suffix
Prefix: The word prefix means the substituents or groups written before the word root. Side chains, substituents, and low-priority functional groups are written as prefixes. All the atoms or groups except the principal functional group present in the parent chain are written before the word root and called substituents or prefixes.
Word root: The word root indicates the total number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain, also known as the parent chain. The word root of the organic compound denotes the name of alkanes and cycloalkanes.
| No. of Carbon atoms | Word root | No. of Carbon atoms | Word root |
| C1 | Meth- | C20 | Eicos- |
| C2 | Eth- | C30 | Triacont- |
| C3 | Prop- | C40 | Tetracont- |
| C4 | But- | C50 | Pentacont- |
| C5 | Pent- | C60 | Hexacont- |
| C6 | Hex- | C70 | Heptacont- |
| C7 | Hept/Sept- | C80 | Octacont- |
| C8 | Oct- | C90 | Nonacont- |
| C9 | Non- | C100 | Hect- |
| C10 | Dec- |
Primary Suffix: Primary suffix indicates the type of carbon-carbon bond present or the saturated or unsaturated nature of the longest chain or parent chain.
| Nature/Type of C-C bond | Primary Suffix |
| C-C | -ane |
| C=C | -ene |
| C≡C | -yne |
If more than one carbon-carbon double bond or triple bond is present in the parent chain the di- is used for 2, tri- for three, tetra- for four, and so on is written before the primary suffix along with their positions.
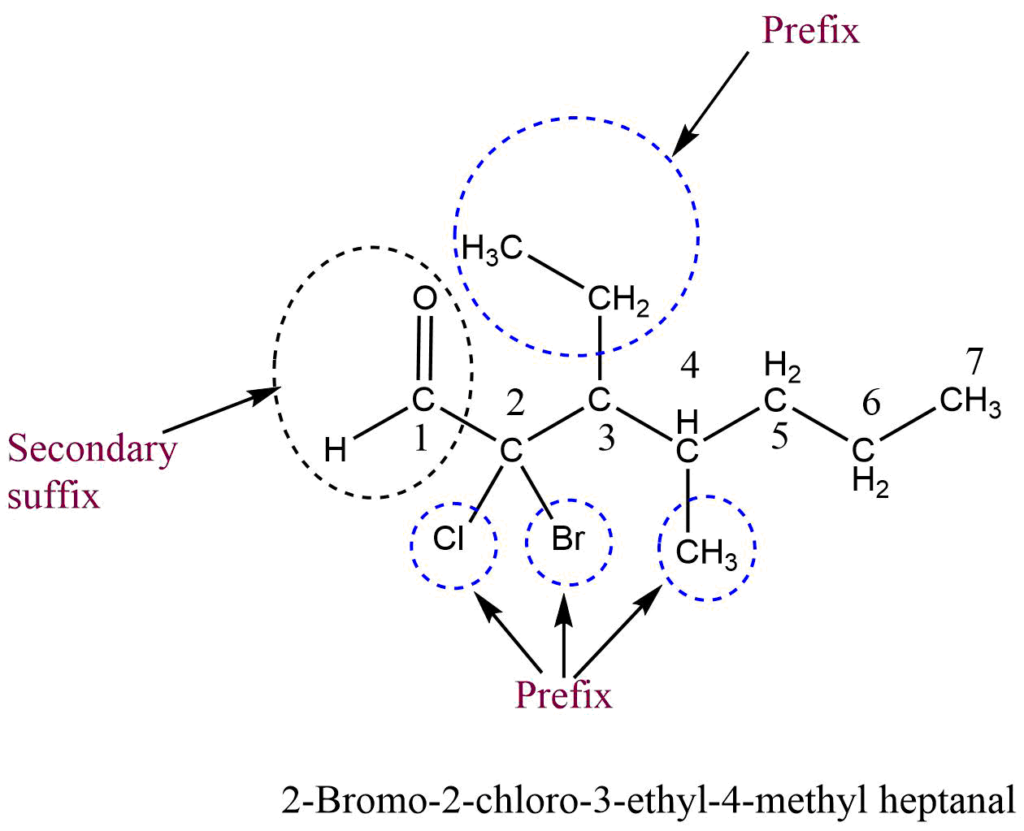
Secondary Suffix: The secondary suffix indicates the principal functional group present in the parent chain and is written immediately after the primary suffix. If the secondary suffix starts with a vowel letter then the ‘e’ of the primary suffix is replaced by the secondary suffix.
Rules of IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC has proposed some rules for the nomenclature of organic compounds which are as follows:
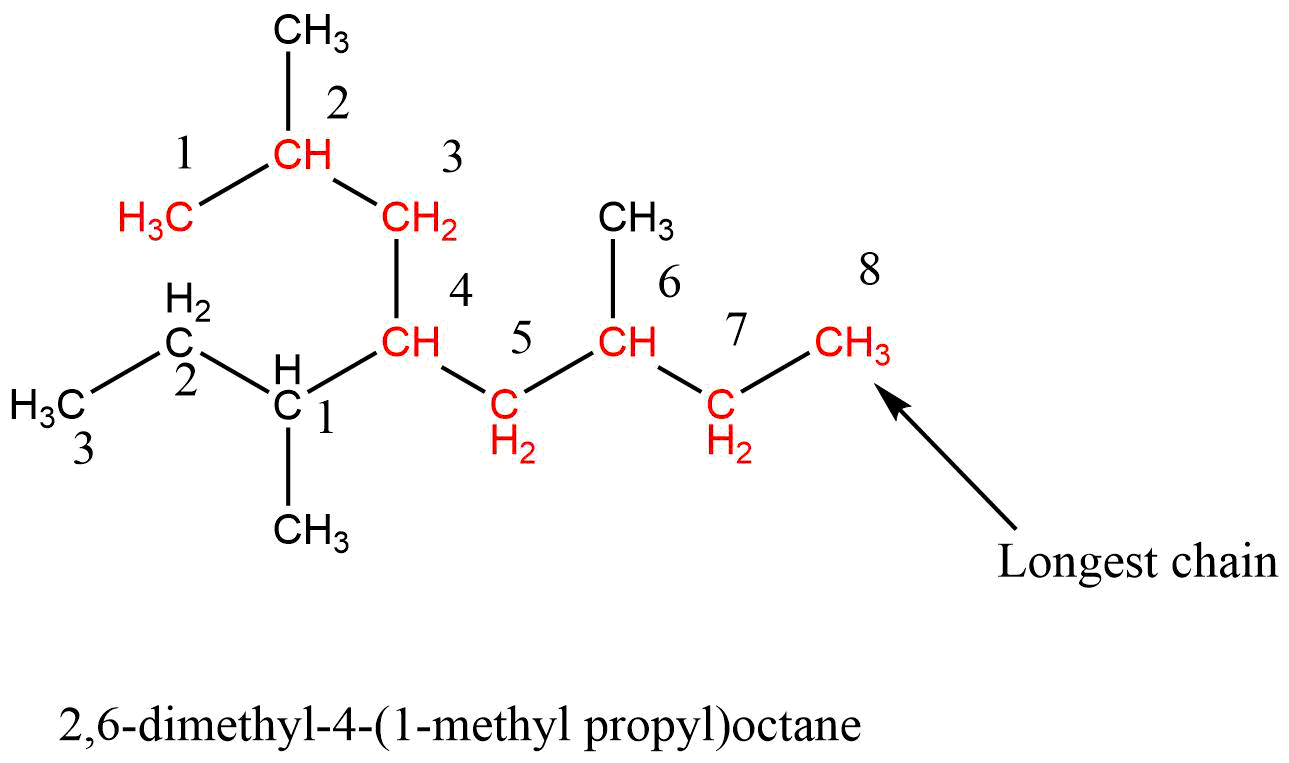
1. Longest chain rule (selection of longest continuous carbon chain)
Always select the longest possible continuous carbon chain which determines the word root and primary suffix.
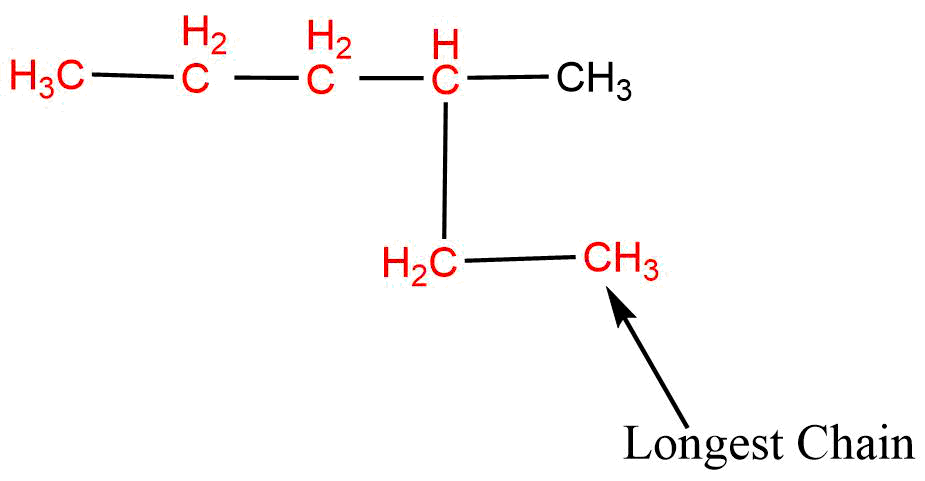
If two or more equal long chains are possible then that chain is selected which has more numbers of side chains or prefixes.
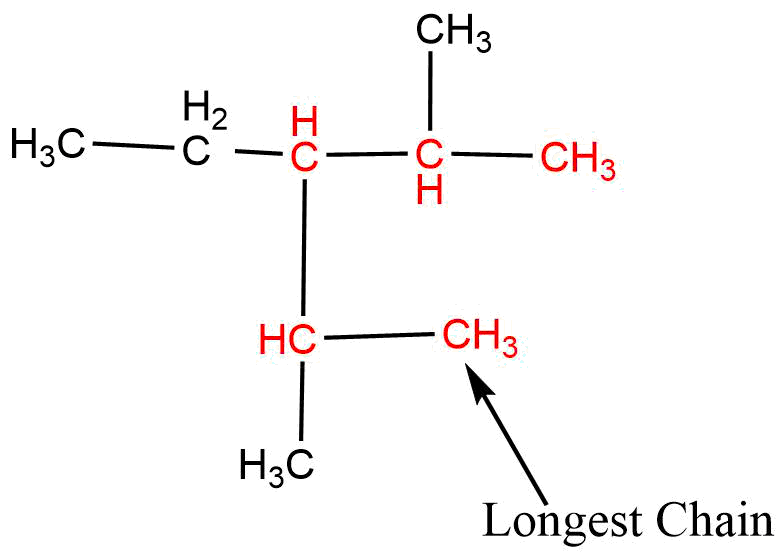
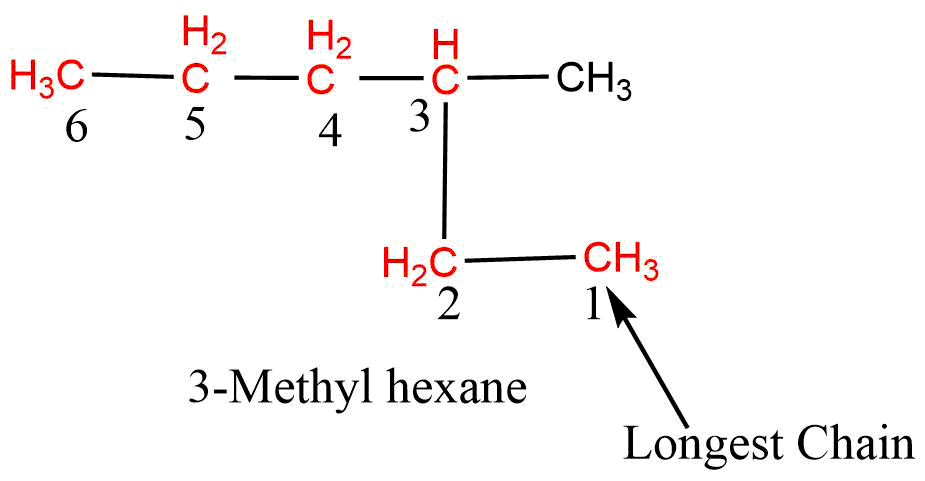
2. Lowest Number rule
This rule is applied only when only one substituent is present in the parent chain (longest chain). The numbering is started from that end which gives the lowest number to the substituent attached to the parent chain, i.e., the numbering should be started from the close end of the substituent.
Alkyl groups attached to the longest chain are called substituents and are written as prefixes.
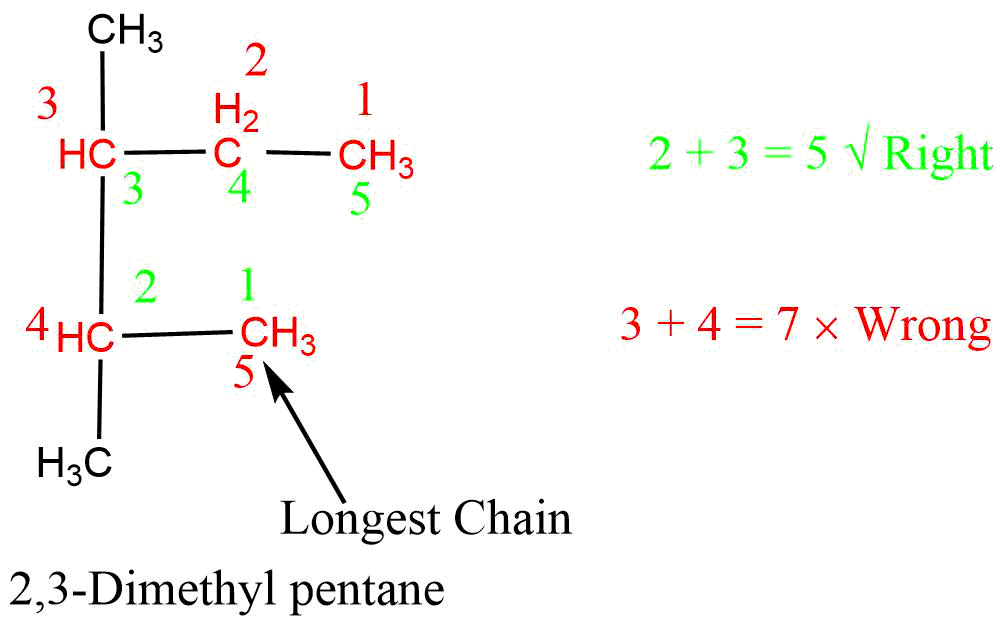
3. Lowest sum rule
If more than one same substituent is present in the parent chain the number should be started from that end which gives the lowest sum of numbers assigned to substituents attached to the parent chain.
4. Alphabetical order rule (Naming of substituents)
When two or more different substituents are present in the parent chain, then the substituents must be written in alphabetical order. Substituents are written as prefix and their positions are indicated by separate numbers.
- If two or more same substituents are present in the parent chain then di-, tri-, tetra-, etc. are used and their positions are separated by a comma, (,). For comparison in alphabetical order prefixes, di-, tri- etc. are not considered.
- If different substituents/prefixes are present on the parent chain then they are arranged in alphabetical order and two different substituents are separated by hyphen (-) along with their position.
- Name and positions of substituents are separated by a hyphen (-).
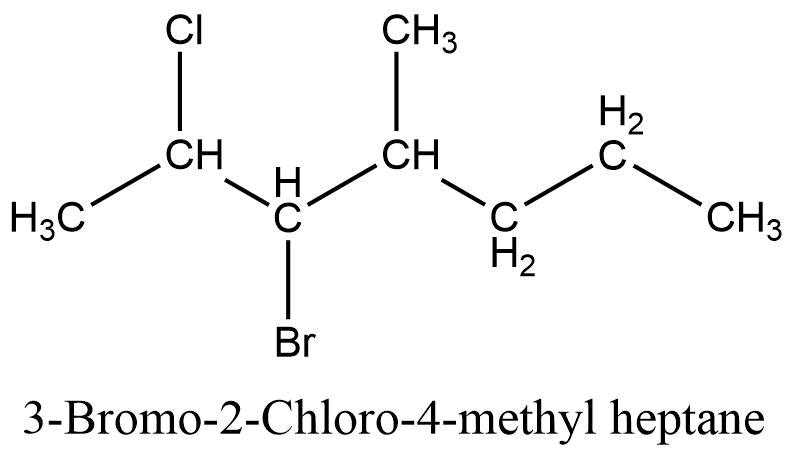
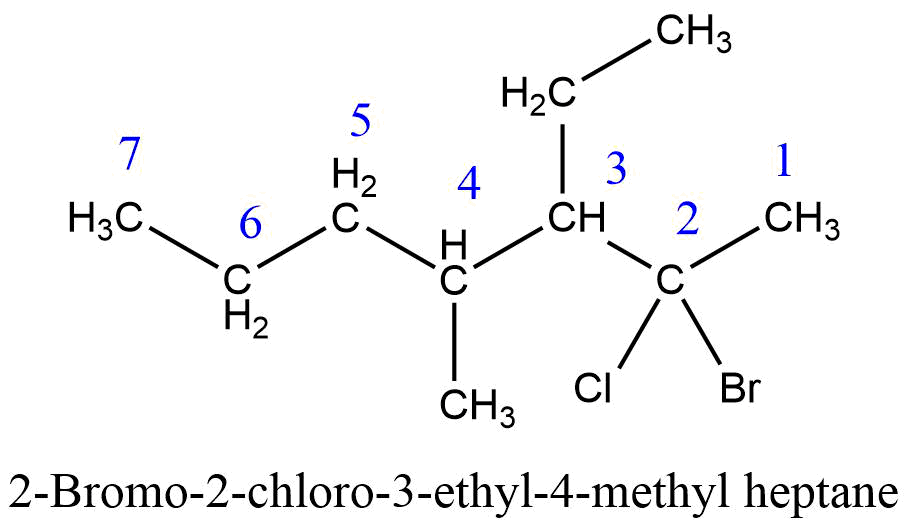
5. Complex alkyl substituent rule
If the alkyl substituent is further branched then it is named as substituent alkyl group. In this case, the alkyl group is separately numbered in such a way that the carbon atom that is directly attached to the parent chain is given the number 1 and the name is enclosed in the bracket.
6. Multiple functional group rule
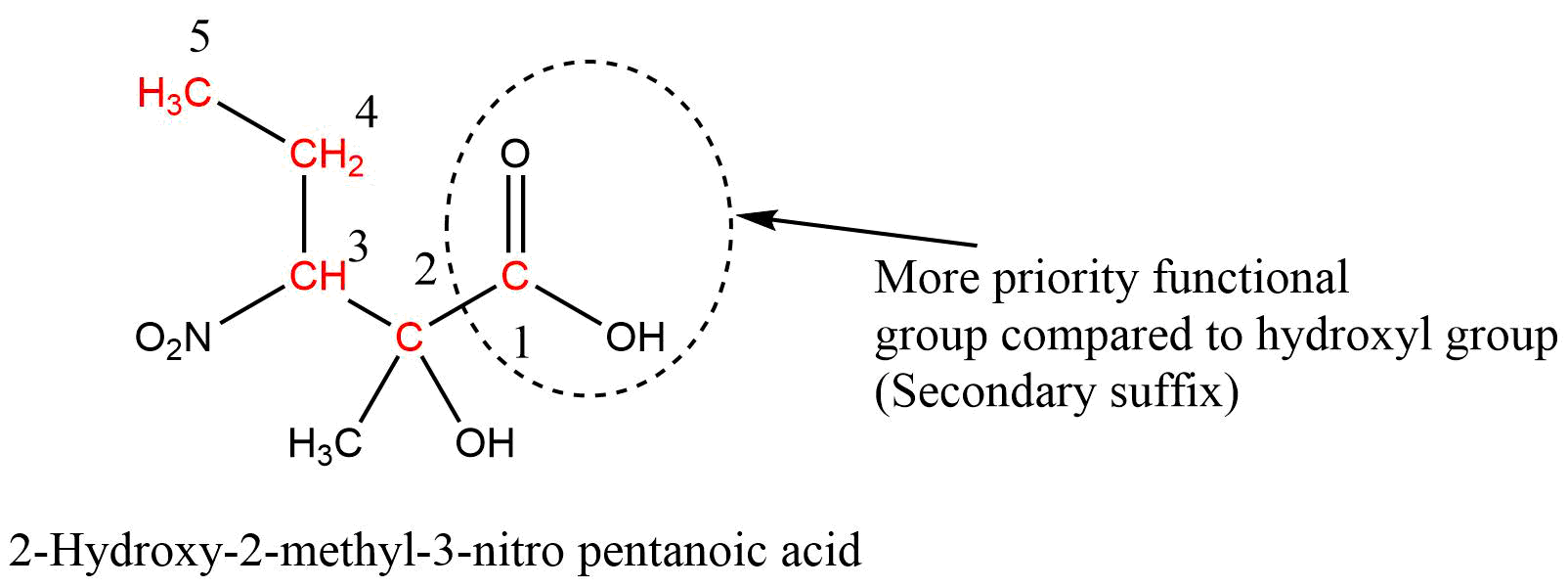
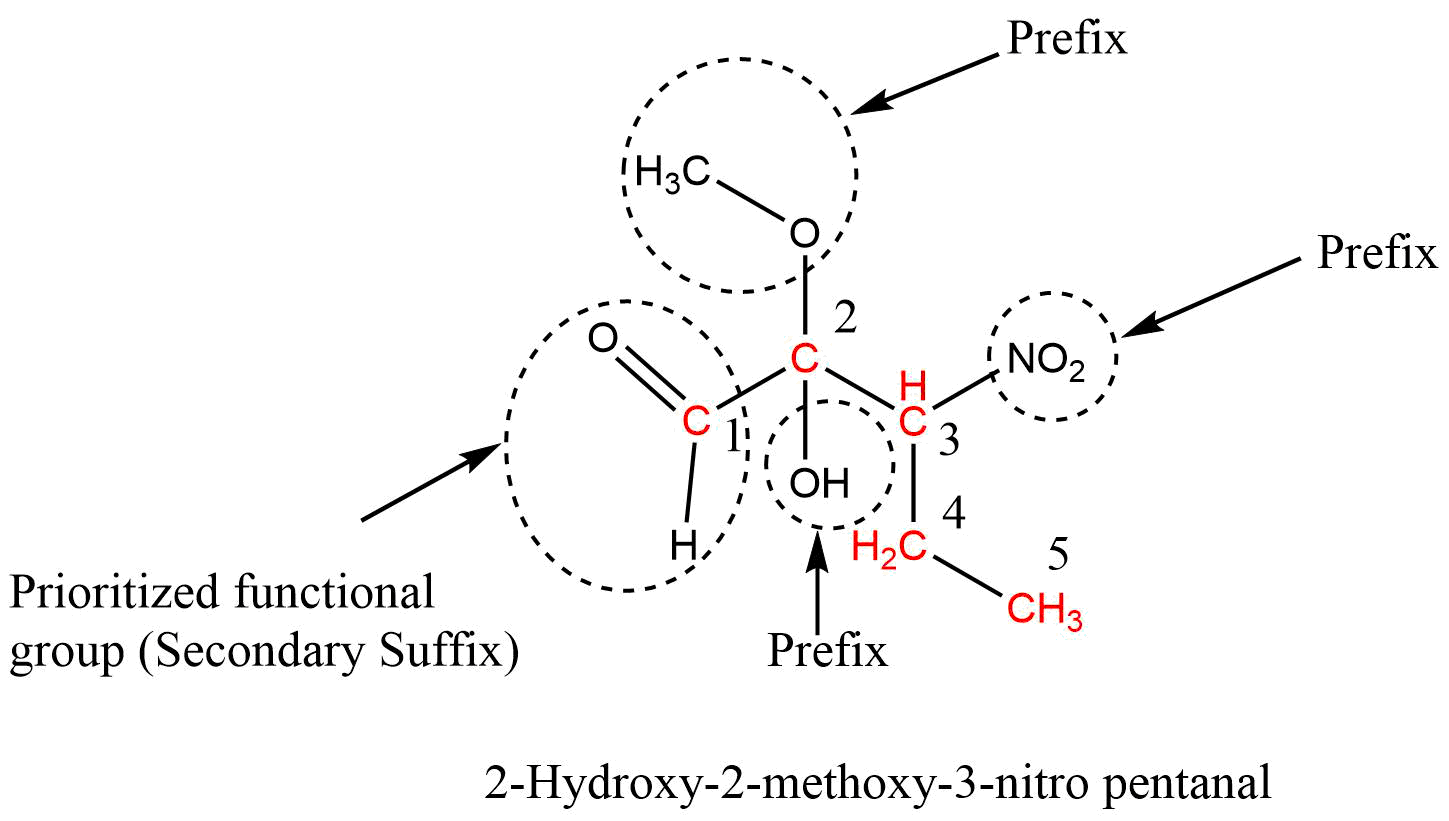
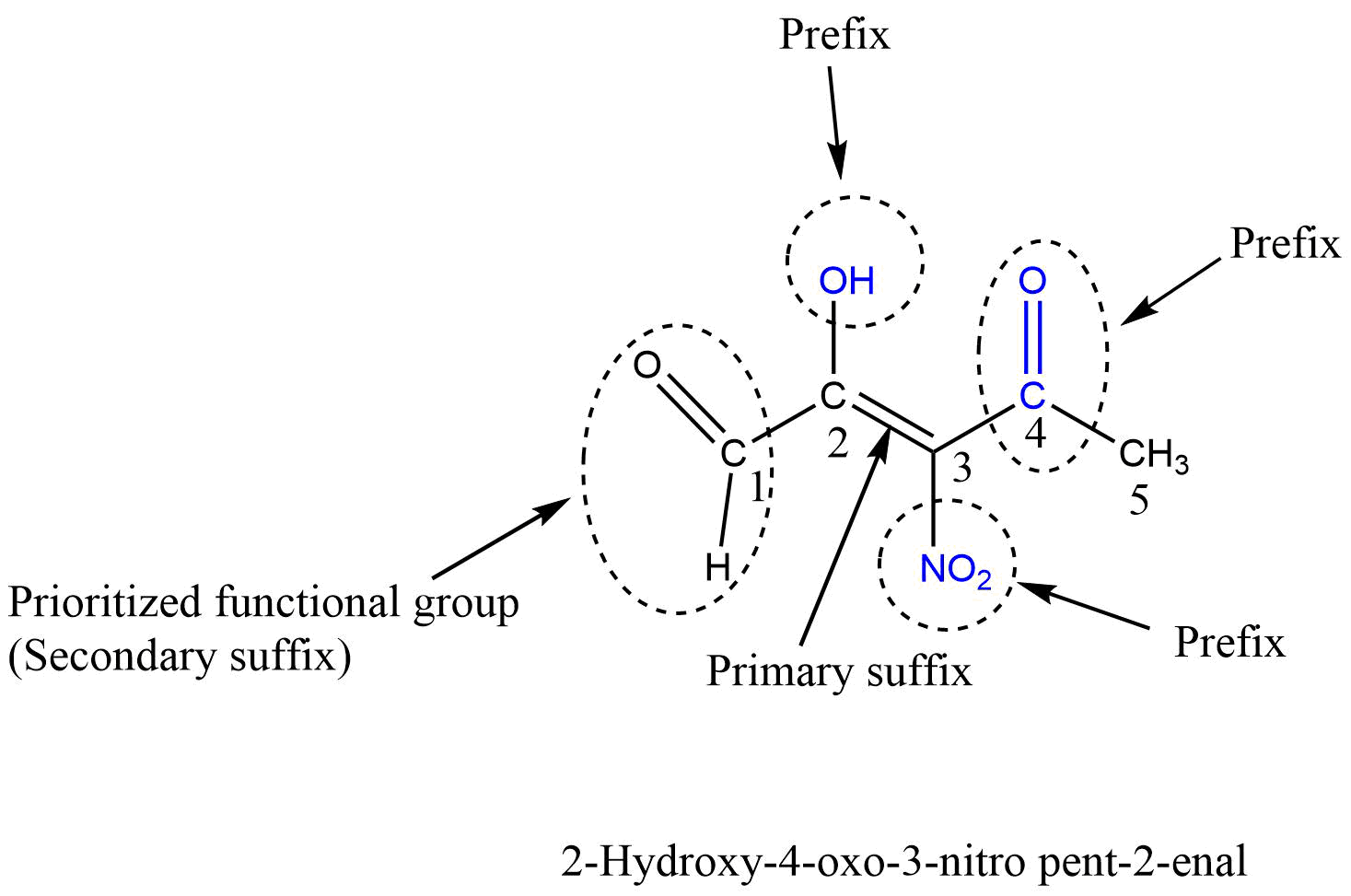
When a parent chain contains two or more functional groups, only one functional group is regarded as the principal functional group, and other functional groups are considered prefixes and written in front of word roots in alphabetical order along with their position. In this case, IUPAC naming takes place on the basis of the principal functional group. That is, the numbering of carbon atoms is done from that end which gives a lower number to the principal functional group.
Priority order of functional groups in IUPAC nomenclature
The following priority order of the functional group is used for selecting the principal functional group.
Carboxylic acid > Sulphonic acid > Acid anhydrides > Esters > Acid halides > Amides > Cyanide (Nitrile) > Aldehydes > Thio aldehydes > Ketones > Thio ketones > Alcohol > Thio alcohol > Amines
If the functional group-containing carbon atoms like -COOH, -CHO, -COOR, -COCl, -CN, etc. are present in the parent chain, then the carbon atom of the functional group gets always number 1 during the numbering of carbon in the parent chain.
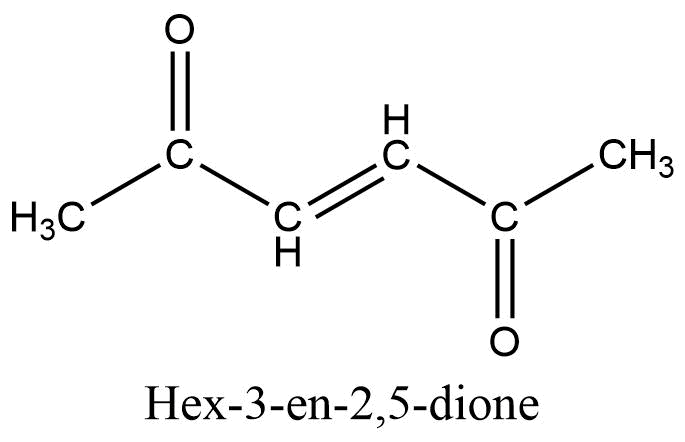
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
Answer:
- 2-Chloro-4,4-dimethylhexane
- 3-Methyl but-1-ene
- 2-Methyl but-1-ene
- 3-(n-Propyl) hex-1-ene
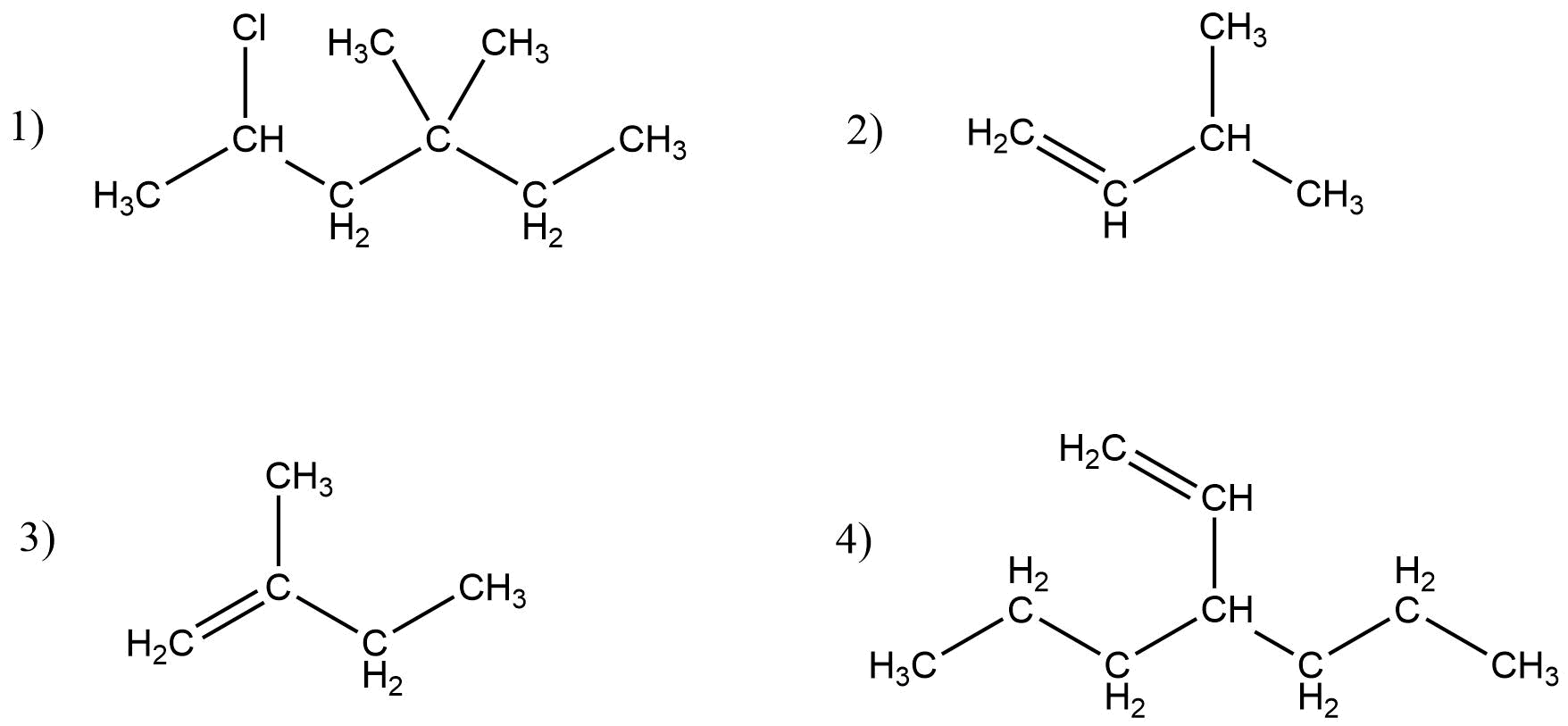
Give IUPAC name for the following compound
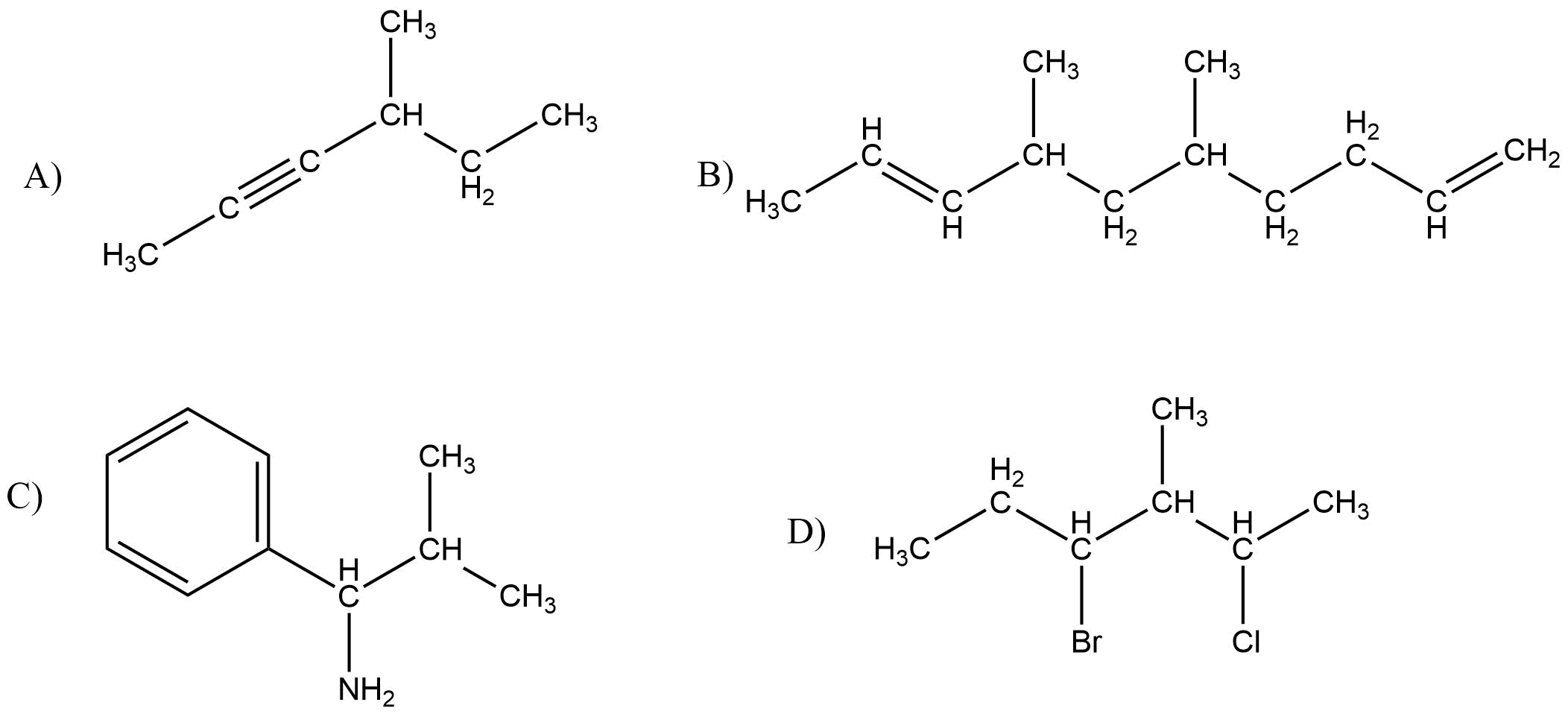
Answer:
A) 4-Methyl hex-2-yne
B) 5,7-Dimethyl deca-18-diene
C) 2-Methyl-1-phenyl propanamine
D) 4-Bromo-2-chloro-3-methyl hexane
Give the IUPAC name for the following compounds
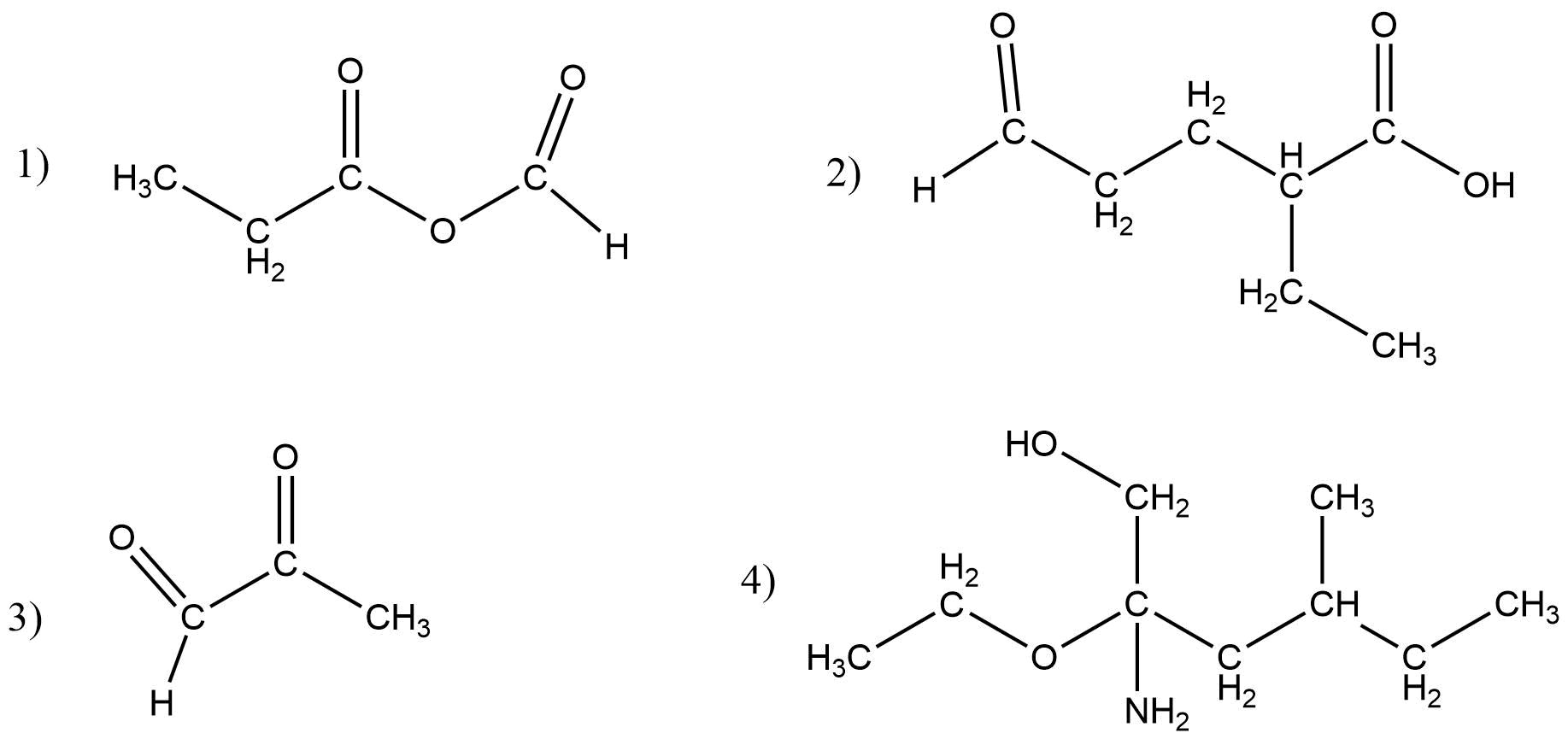
Answer:
- Methanoic propanoic anhydride
- 2-Ethyl-4-formyl butanoic acid
- 2-Oxo propanal
- 2-Amino-2-ethoxy-4-methyl hexanol
FAQs/MCQs:
What is the full form of IUPAC?
The full form of IUPAC is the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
Write the priority order of functional groups in multifunctional organic compounds.
Carboxylic acid > Sulphonic acid > Acid anhydrides > Esters > Acid halides > Amides > Cyanide (Nitrile) > Aldehydes > Thio aldehydes > Ketones > Thio ketones > Alcohol > Thio alcohol > Amines
What is the prefix of thioalcohol?
The prefix of thioalcohol is mercapto.
What are the suffix and prefix of ester?
The suffix and prefix of ester are -oate and carbalkoxy- respectively.
Published by: Siddha Raj Upadhyaya (Gurudev)
Naming of organic compounds video
References:
- A.M. Patterson and C.E. Curran, A system of organic nomenclature, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 39, 1623-1638 (1917).
- A Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds, Recommendations 1993, Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1993.
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Sections A and B, 1st edition, 1958; 2nd edition, 1966; 3rd edition (combined with section C), 1971; 4th edition (combined with sections C, D, E, F and H), 1979.






