Table of Contents
ToggleA carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom that possesses two bond pairs and two unshared electrons. Carbenes are short-lived reaction intermediates formed during the course of reactions.
The general formula of carbene is R-(C:)-R’ or R=C:.
Examples:
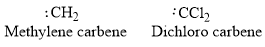
Types of carbene
Depending upon whether the two non-bonded electrons on carbene are paired or unpaired, a carbene is classified into two types viz. singlet and triplet carbene.
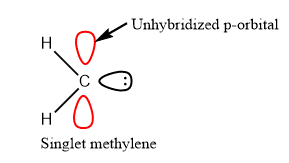
Singlet Carbene
- The unshared electrons are paired in singlet carbene and represented as follows:
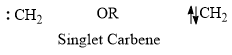
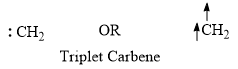
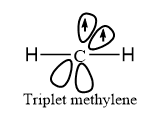
Triplet carbene
- The unshared electrons are unpaired in triplet carbene and represented as follows:
Structure of Carbene
Hybridization of Singlet Carbene
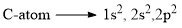
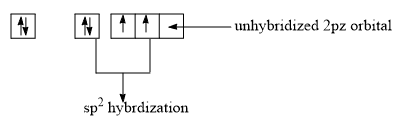
Singlet carbenes have their carbon in a sp2 hybridized state. Of the three sp2 hybrid orbitals, two are used in forming two single bonds with monovalent atoms or groups attached to the carbon. The unshared pair of electrons are present in the third sp2 hybrid orbital and the unhybridized p-orbital is empty.
Hybridization of Triplet carbene
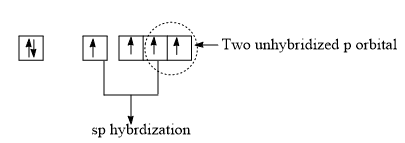
Triplet carbene has its carbon in a sp hybridized state. The two sp hybrid orbitals form two bonds with monovalent atoms or groups attached to the carbon. The two unhybridized p-orbitals contain one electron each.
Stable carbenes
Two non-bonded electrons are present in the same orbitals in singlet carbene. As a result, electronic repulsion takes place. Triplet carbene is lower in energy and more stable.
Carbene Reactions
- Addition Reaction
Carbene adds to an alkene to produce cyclopropane derivatives. The addition of singlet carbene to an alkene is stereospecific.
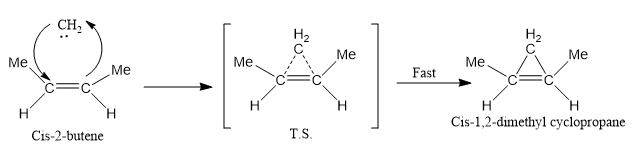
- Insertion Reaction
The most reactive species, singlet carbene can insert itself between the carbon and hydrogen bond. For example, the insertion of (:CH2) into propane would result into a mixture of n-butane and iso-butane.
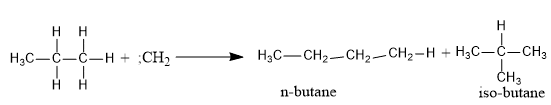
- Rearrangement Reaction
Carbene may undergo rearrangement with the migration of alkyl or hydrogen to form stable molecules.
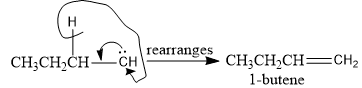
Carbene and Nitrene
Nitrenes are electron-deficient and reactive intermediates, in which the structure of nitrene reveals that there are six electrons around nitrogen. These are nitrogen analogs of carbene and hence something referred to as azo carbene.
Carbene video
FAQs
What is carbene?
A carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom that possesses two bond pairs and two unshared electrons.
What are carbenes? give examples
carbenes are molecules containing a neutral carbon atom that possesses two bond pairs and two unshared electrons.






