Table of Contents
ToggleNutrient Agar is a type of solid media for the growth of a variety of non-fibrous organisms, which is a general-purpose media. Due to its ability to promote the growth of several kinds of bacteria and fungi as well as the fact that it contains many of the nutrients required for bacterial growth, nutrient agar is widely used. Prior to biochemical or serological testing, nutrient agar can also be used to check the quality and purity. Peptone, beef extract, and agar are the ingredients in nutrient agar.
Nutrient Agar definition
Nutrient Agar is a straightforward formulation that still offers the nutrients required for the growth of numerous easily reproducible bacteria. Water-soluble chemicals are found in the beef extract (carbohydrates, vitamins, nitrogen compounds, and salts). In particular, amino acids and long-chain peptides found in peptones serve as the primary sources of organic nitrogen. The American Public Health Association originally released nutrient agar formula in 1917.
Nutrient Agar plate
Generally, nutrient agar plates are used for culturing bacteria. They are also available in ready-made for wrapping with plastic and should be stored at 4 degrees. They are found in a pack of 10 plates. These plates cost approx about AU$18.70 and should avoid contamination.

Principle of procedures
Beef extract, peptone, and agar help compensate for Nutrient Agar. The nutrients required for the replication of a large number of non-overly fussy microorganisms are provided by this comparatively straightforward formulation. Salts, organic nitrogen molecules, vitamins, and carbohydrates are among the water-soluble chemicals found in beef extract. The main sources of organic nitrogen, especially amino acids, and long-chain peptides, are peptones. The solidifying agent is agar.

Composition of Nutrient agar
It contains all the ingredients required for the growth of bacteria. Peptone, beef extract, and agar are the ingredients in nutrient agar. This comparatively straightforward formulation offers the nutrients required for the growth of many non-overly fussy bacteria. Similar in composition but devoid of agar is the nutrient broth.
| Name of the ingredients | amounts(gm) |
| Beef extract | 3.0 |
| peptone | 5.05 |
| agar | 20.0 |
| NaCl | 0.5 |
| distilled water | 1000mL |
How to make Nutrient agar? Recipe
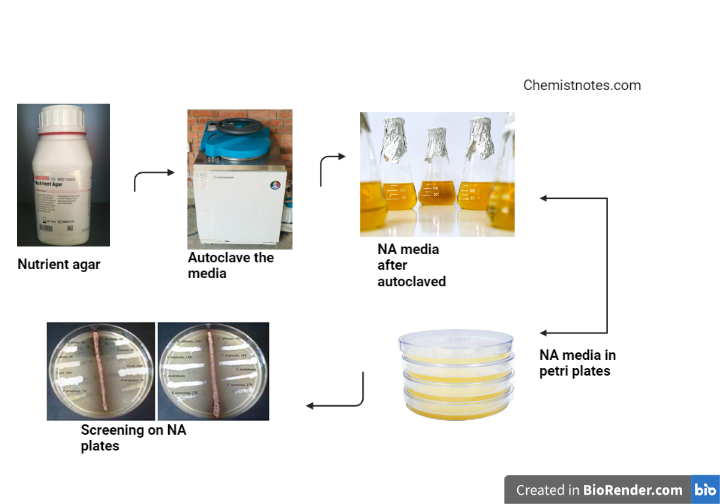
Like other media, it is also easy to prepare with NA powder and distilled water. The powder components are mixed together, boiled for about a minute to ensure thorough mixing, and then sterilized using an autoclave, typically at 121 °C (250 °F) for 15 minutes. They are immediately covered in Petri dishes after being chilled to around 50 °C (122 °F). When the dishes contain solidified agar, they are kept in the refrigerator or stored upside down until they are used. Inoculation is performed on warm plates rather than cool ones; if the dishes were previously chilled for storage, they must be reheated to room temperature before being used for inoculation.
Differences between NA agar and NA broth
Microorganisms can be grown on nutrition agar and nutrient broth, respectively. Nutrient broth is a liquid media, whereas nutritional agar is solid, and this is the fundamental distinction between the two. Example of nutrient agar in a petri dish. Example of nutrient broth in a culture bottle. When 13g of nutrient broth powder (CM0001B) is added to 1L of distilled water, it is thoroughly mixed and dissolved before being poured into the final containers (eg. conical flask) By autoclaving for 15 minutes at 121 °C and sterilized.

Nutrient agar selective or differential medium
Because numerous bacteria can grow in nutrient-rich medium, NA media is non-selective and isolation presents a high risk of contamination. It cannot be utilized as a selective growth medium for picky organisms with specific nutrient needs.
The growth of a diverse spectrum of non-fibrous organisms is supported by the general-purpose medium known as nutrient agar. Because it promotes the growth of different kinds of bacteria and fungi and contains many of the nutrients required for bacterial growth, nutritional agar is widely used. Prior to biochemical or serological testing, nutrient agar can also be employed for quality control and purity verification.
Peptone, beef extract, and agar make up nutrient agar. Although it is a straightforward composition, it offers the nutrients required for the growth of numerous easily replicated bacteria. The beef extract includes water-soluble ingredients (carbohydrates, vitamins, nitrogen compounds, and salts). The most significant supply of organic nitrogen comes from peptones, particularly through amino acids and long-chain peptides.
Uses of Nutrient Agar
Nutrient Agar is a fundamental culture medium that is used to maintain organisms or to verify the purity of subcultures from isolation plates in advance of biochemical or serological assays. The medium is used to retain control organisms in semi-solid form as agar butts or slopes.
For the culture of bacteria and the counting of organisms in water, sewage, feces, and other materials, nutrient agar is utilized.