Table of Contents
ToggleHydrazine (H2N-NH2) is an anhydrous, clear, colorless, fuming, oily liquid with an ammonia-like odor. It is a high volumetric energy density liquid fuel with a hydrogen content of 12.6% by volume, which is also used as rocket fuel. Hydrazine is a highly reactive base, and the reducing agent is employed in a variety of industrial and medical processes. It is highly toxic when inhaled or absorbed through the skin.
Structure of Hydrazine
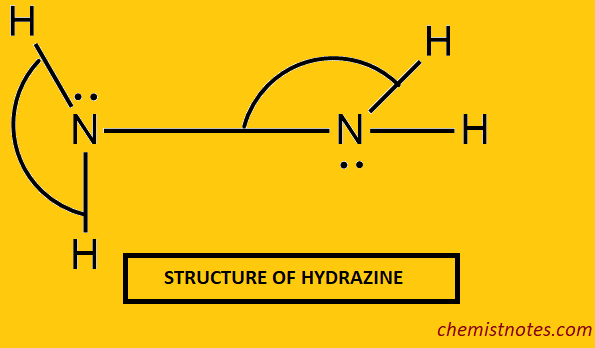
It is assumed that each nitrogen atom in sp3 hybridized, it follows that there are two lone pairs of electrons in the N2H4 molecule, one on each of the two nitrogen atoms.
- N-N bond distance = 1.47 + or – 0.02 Ao
- N-H bond distance = 1.04 Ao
- NNH and NHN bond angles are 110o
Preparation of Hydrazine
Hydrazine is prepared by boiling aqueous ammonia with sodium hypochlorite.
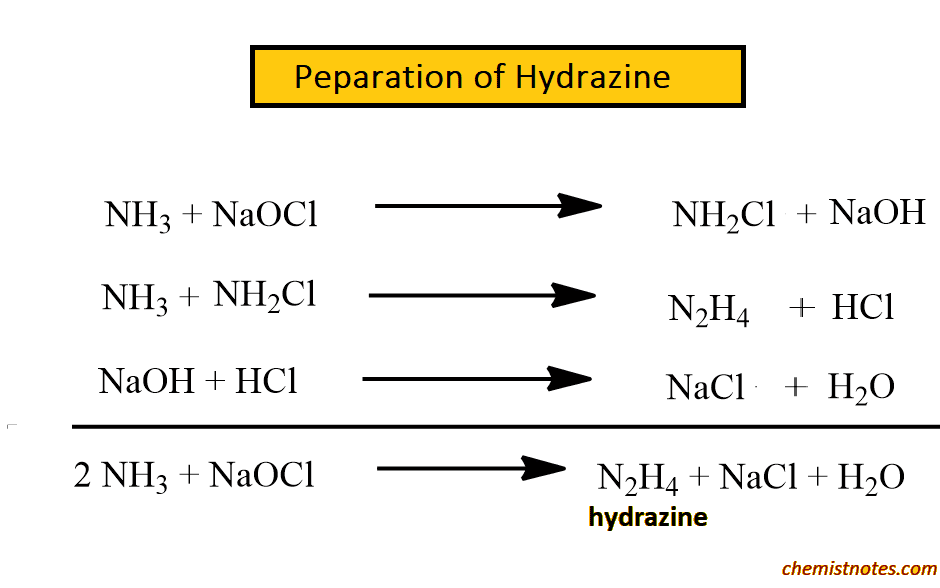
A side reaction between chloramine and hydrazine may destroy some or all of the product which is difficult during preparation.
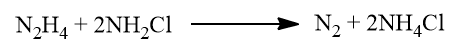
This reaction is catalyzed by traces of heavy metal ions. This is surprised by the addition of glue or gelatine which form complexes with the metal ion. So an excess of ammonia and glue gelatination as a demasking agent is used to reduce possible side reactions.
Properties of Hydrazine
The basic property of hydrazine
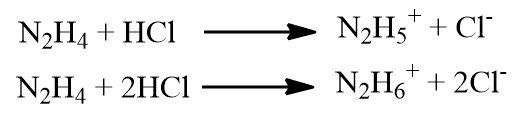
Hydrazine is a diacidbase and can form salts with one or two equivalents of acids. It reacts with acids, forming two series of salts, which are white ionic crystalline solids and are soluble in water.
Like NH3, it can also form a coordinate complex with both lewis acids and metal ions, it is because nitrogen atoms have a lone pair of electrons.
Hydrazine acts as the reducing agent
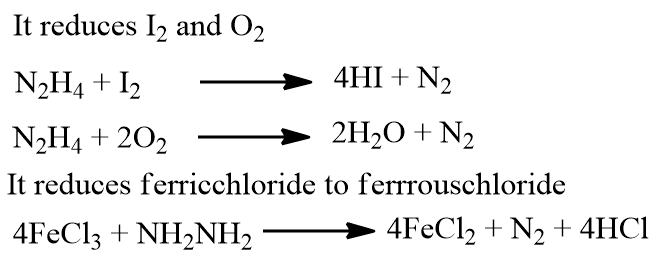
In acidic solution, hydrazine usually behaves as a mild reducing agent, through powerful reducing agents can reduce N2H4 to NH3 thus causing N2H4 to be oxidized.

Hydrazine may acts as electron donor. The N atoms have a lone pair of electron, which can form coordinate bonds to metal ion such as Ni++ and Co++.
Uses of Hydrazine
- The methyl derivatives MeNHNH2 are mixed with N2O4 and used as a rocket fuel in space shuttle, in guided missiles and in the appolo lunar modulus.
- To prepare hydrazine derivative in organic chemistry.
- Used as reducing agent
- Used in medicine as a constituent and anti-tubercular drugs.
- They used to produced silver and copper mirror.
FAQs
What is hydrazine?
Hydrazine (H2N-NH2) is an anhydrous, clear, colorless, fuming, oily liquid with an ammonia-like odor.
What is hydrazine used for?
Hydrazine is a highly reactive base, and the reducing agent is employed in a variety of industrial and medical processes and also used as rocket fuel.
How dangerous is hydrazine?
Hydrazine is highly toxic when inhaled or absorbed through the skin.