Table of Contents
ToggleDifferent atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are known as isotopes. Hydrogen has three isotopic forms ( Protium, Deuterium, and Tritium): with mass numbers 1,2, and 3. Because the amount of neutrons in each isotope varies, the mass number of the isotopes varies as well. Isotopes have different mass numbers due to the difference in neutron numbers.
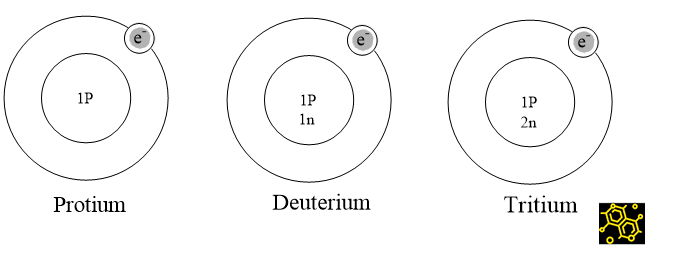
The most abundant and stable isotope is protium (11H) or ordinary hydrogen.
A stable isotope is a deuterium (12H or D), also called heavy hydrogen.
The third isotope is radioactive (t1/2 = 13.33yrs) in nature which is tritium (13H or T) Tritium is a β-particle emitter.
Comparative study of 3 isotopes
| Name | Hydrogen(Protium) | Deuterium | Tritium |
| Symbol | 11H or H | 12H or D | 13H or T |
| Atomic number (Z) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Mass number (A) | 1.00799 | 2.0147 | 3.0170 |
| Number of protons (P) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Number of electrons (e) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Number of neutrons (n) | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Relative abundance | 99.985% | 0.015% | 10-15% |
| Nature | Non-radiative | Non-radioactive | |
| Nuclear spin | 1/2 | 1 | 1 |
| Molecular formula | H2 | D2 | T2 |
All the three isotopes of hydrogen have the same electronic configuration (1s1). So, all three isotopes give similar chemical properties. However, due to different mass numbers, they are different in their physical properties and in the rates of a chemical reaction. For example, electrolysis of ordinary water occurs more rapidly than in heavy water. This difference in properties due to the difference in mass number is called the isotope effect. Hence ordinary hydrogen undergoes reactions faster than deuterium due to the isotopes effect.
| Physical constants | H2 | D2 | T2 |
| Molecular mass (g mol-1) | 2.016 | 4.028 | 6.03 |
| Melting point (K) | 13.8 | 18.7 | 20.63 |
| Boiling point (k) | 20.4 | 23.9 | 25.0 |
| Bond energy (KJ mol-1at 298L) | 435.9 | 443.4 | 446.9 |
| Heat oof vaporization KJ mol-1 | 0.904 | 1.226 | 1.393 |
Applications of Isotopes of Hydrogen
Protium
- Used to produce oxy-hydrogen flame for welding
- Used in filling balloons
- Used in Haber’s process of ammonia synthesis
- used in the manufacture of vanaspati ghee.
- Used in reducing agents in metallurgical process.
Deuterium
- Used in the transformation of nuclear reaction as deuteron projectile.
- deuterium and its compounds are used as tracers to study reaction mechanisms.
- Used in nuclear fusion reactions.
Tritium
- Used in nuclear reaction to liberate large amount of heat which is used in a hydrogen bomb.
- It is a radioactive isotope used as a radioactive tracer in water absorption by plant roots.
FAQs
Isotopes of hydrogen with 2 neutrons is called…
Tritium has 2 neutrons.
What are the three isotopes of hydrogen?
The three isotopes of hydrogen protium, deuterium, and tritium.
How do isotopes of hydrogen differ from one another?
In isotopes of hydrogen, the amount of neutrons and the mass number varies from one another.
How many isotopes of hydrogen are known?
3 types of hydrogen are known.
Heavy isotopes of hydrogen?
Deuterium is a heavy isotope of hydrogen.