Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are interhalogen compounds?
These are the compounds formed by two halogens. Two or more different halogens combine together due to the difference in electronegativity among halogens and form new chemical species called interhalogen compounds. CIF, ClF3, ClF5, ClF7, BrCl, ICl3, IBr, IF7, etc. are common examples of interhalogen compounds.
A given halogen forms the interhalogen compounds only with that halogen having a lower electropositive character. Since the electropositive character of halogens is in the order F<Cl<Br<I, Fluorine can not form any interhalogen compounds, while iodine has the maximum tendency to form interhalogen compounds. Because F has the lowest electropositive property, all halogens interact with it to form fluorides.
Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens, why?
Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens because interhalogen compounds have a lower value of bond energies than the bond energies of halogens. As we know, the lesser the bond energies of a particular bond, the more easily it breaks and becomes reactive.
You may have questioned why interhalogens have less value in bond energy, right? Since different halogens have different sizes and during the overlap of orbitals, two different sizes of orbitals can not make an effective overlap. This weak overlap of orbital makes the weaker bonds.
Types of interhalogen compounds
Interhalogen compounds can be grouped into the following classes.
- AB Type: ClF, BrF, BrCl, ICl, IBr etc.
- AB3 Type: ClF3, BrF3, IF3, ICl3 etc.
- AB5 Type: ClF5, BrF5, IF5 etc.
- AB7 Type: IF7
The oxidation state of atom A in AB, AB3, AB5, and AB7 molecules is equal to +1, +3, +5, and +7 respectively.
Preparation of interhalogen compound
Preparation of AB type interhalogen
These are prepared by a direct combination of halogens.
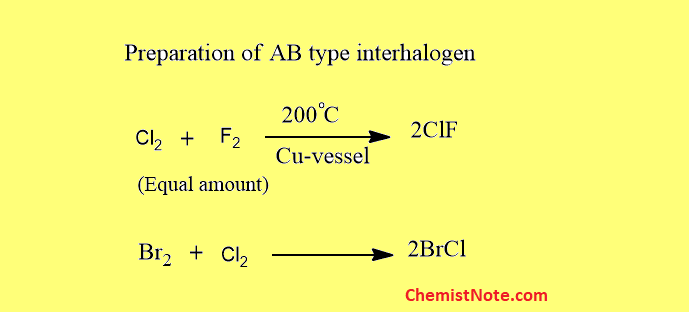
Some are also prepared by other methods.
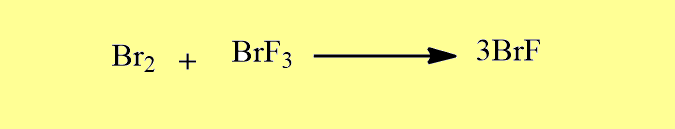
Preparation of AB3 type interhalogen
These are generally prepared by a direct combination of the elements under suitable conditions.
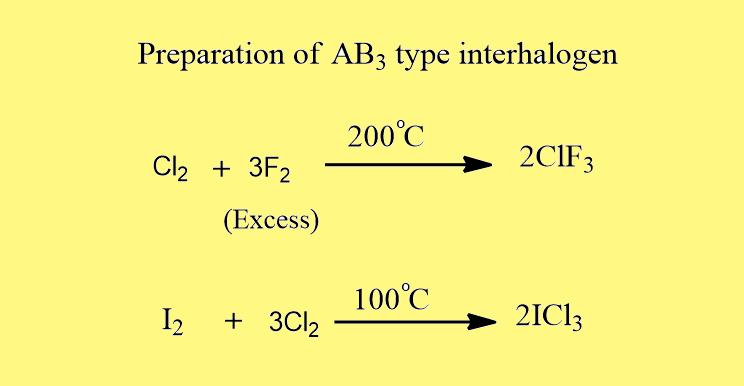
Preparation of AB5 type interhalogen
These are also prepared by a direct method.
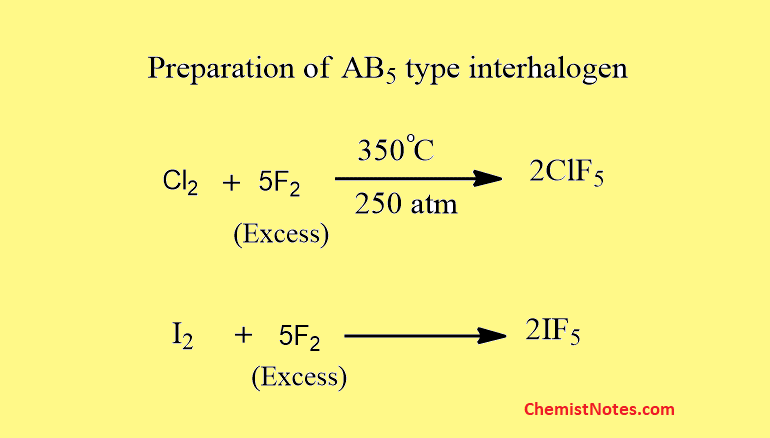
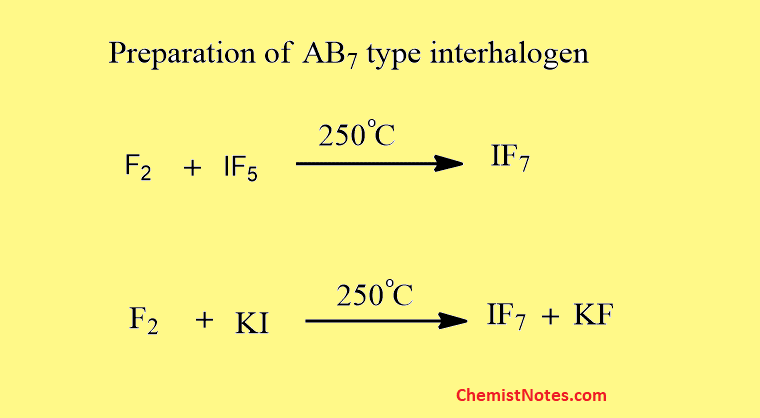
Preparation of AB7 type interhalogen
IF7 is prepared by the action of F2 on IF5 or KI.
Properties of interhalogen compounds
Properties of AB type interhalogen
- These are covalent gases because of the small difference in electronegativity.
- These have different thermal stability. For example, ClF is extremely stable while BrCl decomposes readily. Similarly, BrF and IF are unstable and undergo disproportion rapidly.
These undergo hydrolysis to give oxyacids.
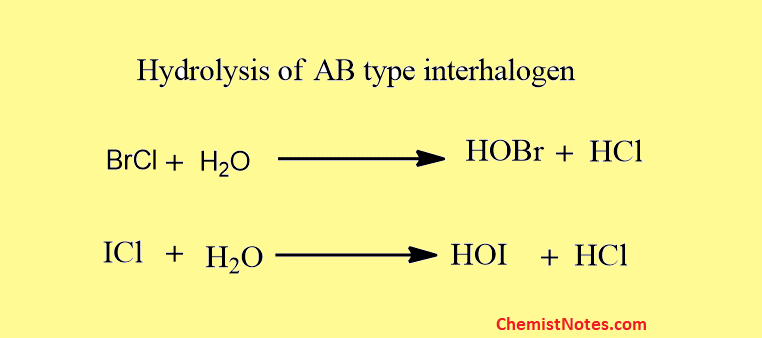
They react with metals to form metal halide.
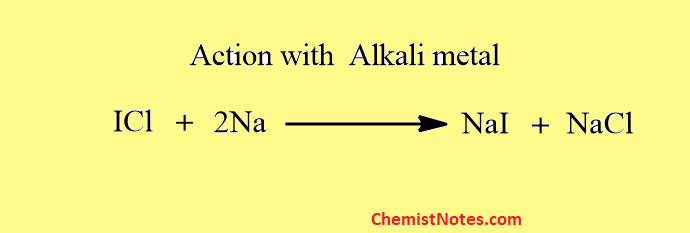
Moreover, these compounds add to olefin at double bond sites.
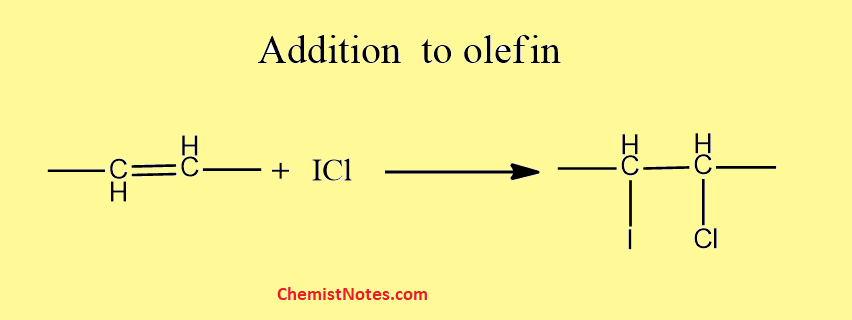
Structure of interhalogen compounds
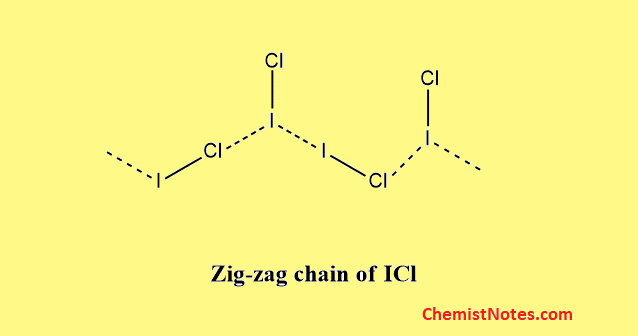
Structure of AB type
All the molecules belonging to this class have linear geometry which arises due to the Sp3 hybridization of the central halogen.
Structure of AB3 type
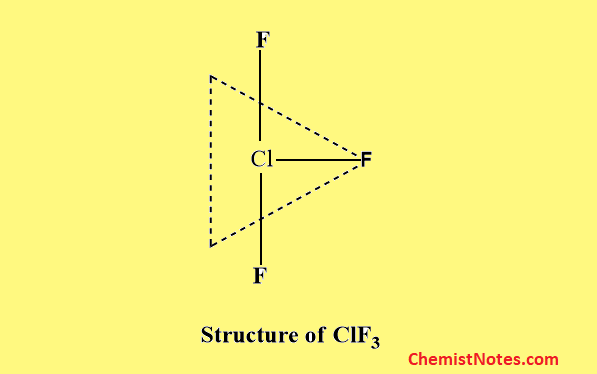
Examples of such compounds are ClF3, BrF3, IF3, etc. All these molecules have a bent T-shaped structure which is due to Sp3d hybridization of the central bigger halogen atom.
Structure of AB5 type
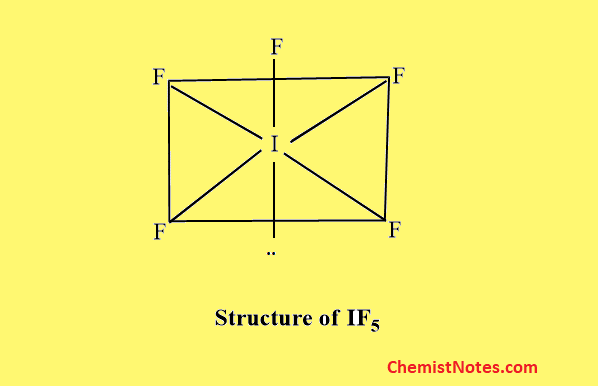
Examples of such compounds are ClF5, BrF5, IF3, etc. All these molecules have distorted octahedral (square pyramidal) structure which arises from the Sp3d2 hybridization of the central larger halogen atom.
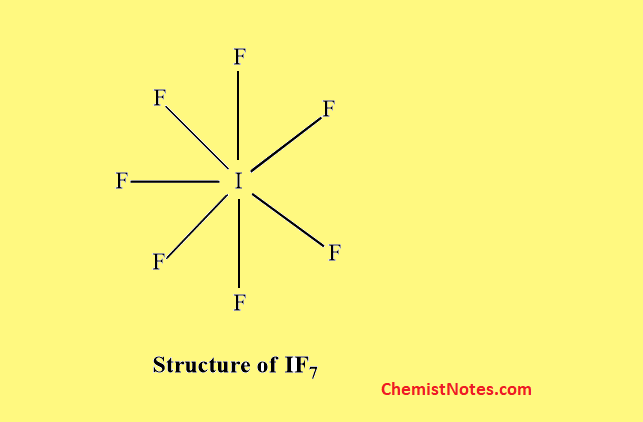
Structure of AB7 type
IF7 is the only interhalogen compound of this type.
Interhalogen compounds uses
- The solution of ICl in glacial acetic acid is used for determining the iodine value of oils.
- ICl can also be used for the preparation of polyhalides.
- ClF3 is used as Fluorinating agent for the preparation of a number of metal fluorides.
- ClF3 is used in cutting oil well tubes.
- ICl is used in medicine as well as in the preparation of polyhalides.
- Acid-base reactions carried out in Liquid BrF3 have been used to prepare a number of complex compounds which are difficult to prepare by other methods.
FAQs/MCQs:
What is interhalogen compound?
The interhalogen compound is a type of compound formed between halogens.
why interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens?
Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens because the bond energy of interhalogen compounds has less value than that of halogens.
Which type of interhalogen compound has t shaped molecular structure?
AB3 type of interhalogen compounds such as ClF3, BrF3, and IF3 has t shaped molecular structure.
Why interhalogen compounds are diamagnetic?
Interhalogen compounds are diamagnetic in nature because they have lone pairs of electrons.