Table of Contents
ToggleOrtho hydrogen and para hydrogen are two forms of hydrogen molecules. Let’s discuss some background before explaining these forms of hydrogen.
Two H-atoms combine to form a hydrogen molecule. Each H-atom has one proton in the nucleus and one electron revolving around the nucleus. The two protons present in the nucleus of both H-atoms may spin either in the same direction (i.e., parallel direction) or in the opposite direction (i.e., antiparallel direction).
On the basis of the direction of spin of two protons in the nucleus, hydrogen molecules are of two types.
- Orthohydrogen molecule
- Para hydrogen molecule
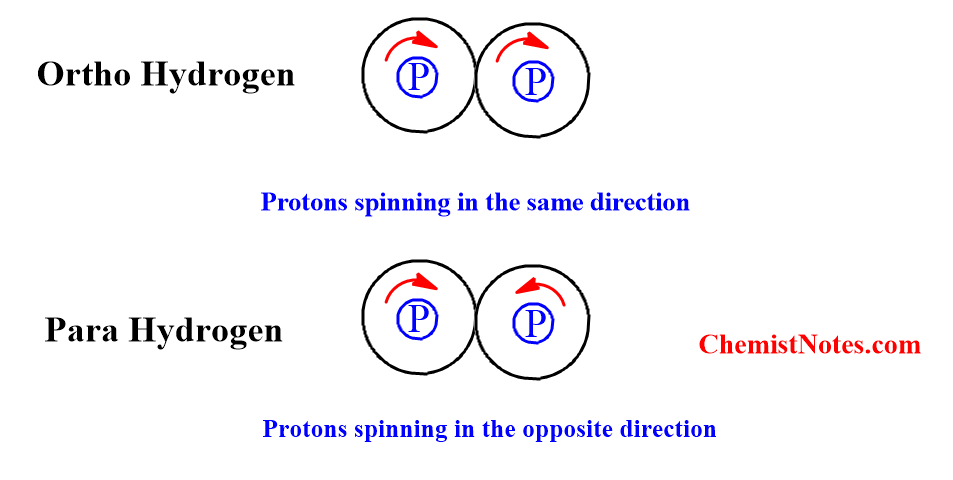
Ortho hydrogen
If both protons in the nucleus of both H-atoms of hydrogen molecules spin in the same direction, i.e., in a parallel direction, such a hydrogen molecule is called an orthohydrogen molecule. Due to spin in the same direction, the net/resultant spin is one.
Para hydrogen
If both protons in the nuclei of both H-atoms in a hydrogen molecule spin in the opposite directions, i.e. antiparallel direction, such a hydrogen molecule is called a parahydrogen molecule. Due to the opposite spin of the protons, the resultant nuclear spin is zero.
However, two electrons in the ortho as well as parahydrogen molecule always spin in the opposite direction.
Difference between ortho and para hydrogen molecule
In an ortho hydrogen molecule, the spins of the protons are in the same direction (Parallel), while the spins are in the opposite direction (antiparallel) in the case of a para hydrogen molecule. This is the major difference between ortho and para hydrogen molecules. The other differences are listed below:
- The internal molecular energy is higher in the case of ortho than parahydrogen. This may be due to the fact that the spin of the two protons being in the same direction, increases the energy of the orthoform. Since one spin of the proton cancels that of the other in para, there is a decrease in the internal molecular energy.
- There are different bond spectrums for both hydrogen forms. This can be used to demonstrate the existence of ortho and para hydrogens.
- There are differences in physical properties such as melting points, boiling points, and specific heat between the two hydrogen forms.
- The magnetic spin of para hydrogen is zero due to the cancellation of nuclear spin.
Although these two forms of hydrogen have different physical properties, their chemical properties are the same.
Ortho-para hydrogen conversion
Parahydrogen is less stable than orthohydrogen. Thus, less stable parahydrogen is converted to stable orthohydrogen.
The conversion of Para hydrogen to ortho hydrogen can be achieved by the following process.
- By heating to 800 degrees Celsius or above.
- By passing electric arc
- By treatment with catalysts, usually Platinum
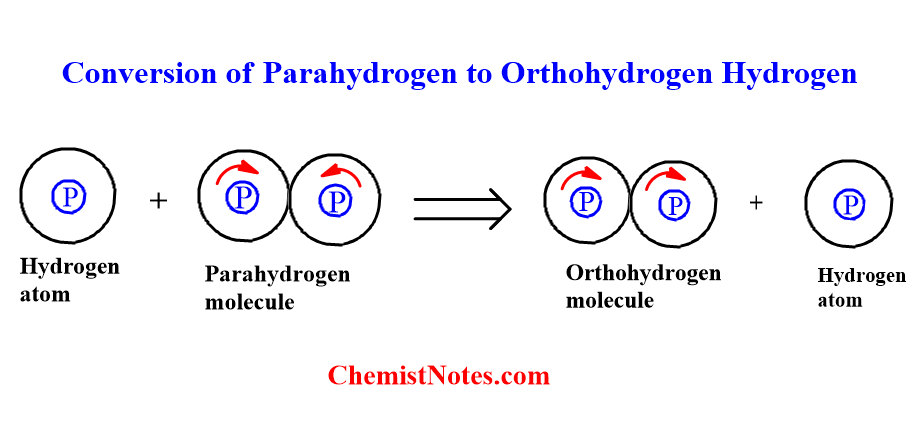
- By mixing with atomic hydrogen
When a parahydrogen molecule collides with atomic hydrogen, the parahydrogen molecule is converted into ortho molecules.
Separation of ortho and para hydrogen from ordinary hydrogen
We know, the ordinary molecular hydrogen at room temperature consists of para and ortho hydrogens in 1:3 ratio.
To separate, paraform from ordinary hydrogen, the ordinary hydrogen is passed through a tube packed with activated charcoal and cooled in liquid air or liquid hydrogen for about 3–4 hours. Another method of separation is by using Gas Chromatographic technique.
Effects of temperature on relative proportion of Ortho and Para hydrogen
It has been found that there is effect of temperature on relative proportion of ortho and para hydrogens.
- At absolute zero temperature, only the form exists. The ratio of ortho and para is 0:1.
- As the temperature increases, the proportion of ortho form increases and that of para form decreases.
- At temperature of liquefaction of air, the ratio of ortho and para forms is 1:1
- At room temperature and at elevated temperatures, this ratio of ortho and para hydrogen is 3:1
FAQs/MCQs:
how do you convert para hydrogen into ortho hydrogen?
Para hydrogen can be converted into ortho hydrogen simply by heating para hydrogen to 800 degree Celsius or by using electric arc.
is ortho hydrogen an isotope of hydrogen?
No. Ortho hydrogen is not an isotope of hydrogen. It is just one form of hydrogen, classified based on nuclear spins.
write the difference between ortho and para hydrogen?
The major difference between ortho and para hydrogen is the difference in orientation of the proton spin.