Table of Contents
ToggleThe electron affinity of an element is defined as the energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom to form a gaseous anion, or negative ion. Usually, only one electron is added, forming a uninegative ion. Since energy is evolved, these terms have a negative sign. Electron affinities depend on the size and effective nuclear charge.
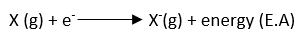
The larger value of electron affinity indicates the greater tendency of an atom to accept the electron.
Electron Affinity Trends Periodic Table
Electron affinity doesn’t show perfectly regular trends along a period or a group because of a number of expectations. But, in general, the electron affinity decreases along with the group and increases along the period.
Variation along a group
Both atomic size and nuclear charge increase along with the group, although the effect of atomic size increase is considerably more pronounced than nuclear charge increase. As the atomic size grows, the incoming electron experiences less nucleus attraction, and electron affinity decreases along with the group.
Electron affinity of Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium
| Element | Electron affinity(KJ/mol-1) |
| Li | -59.8 |
| Na | -53 |
| K | -48.9 |
| Rb | -46.9 |
Variation along a period
The atomic size reduces as we move through a period, but the nuclear charge increases. The combined effect of these two causes increases the force of attraction for the electron, so electron affinity increases in the period from left to right.
Electron affinity of Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne
| Element | Electron affinity(KJ/mol-1) |
| Li | -59.8 |
| Be | -0 |
| B | -23.0 |
| C | -122 |
| N | -20.1 |
| O | -140.9 |
| F | -327.9 |
| Ne | 0 |
Electron Affinity Trends
- Halogens (gr. VIIA) have the highest electron affinity.
- The electron affinity of fluorine is however, unexpectedly lower than chlorine.
- The electron affinities of elements having exactly half-filled and completely filled orbitals are essentially zero.
- The electron affinities of alkaline earth metals (gr. IIA), i.e. Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, etc, are also zero.
- Nitrogen and phosphorous have low electron affinity values.
Born-Haber Cycle
The cycle, devised by Max Born and Fritz Haber in 1919, relates the lattice energy of a crystal to other thermochemical data. The energy terms required in forming a crystal lattice, such as sodium chloride, may be divided into a series. The elements are first turned into gaseous atoms, then into ions, and ultimately into ions, before being packed into the crystal lattice.
Since energy is supplied to the system, because the enthalpies of sublimation and dissociation, as well as the ionization energy, are all positive. Energy is evolved in these processes because the electron affinity and lattice energy are negative.
Hess’s law states that the overall energy change in a process is completely determined by the energy of the initial and final states, not by the path used.
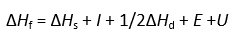
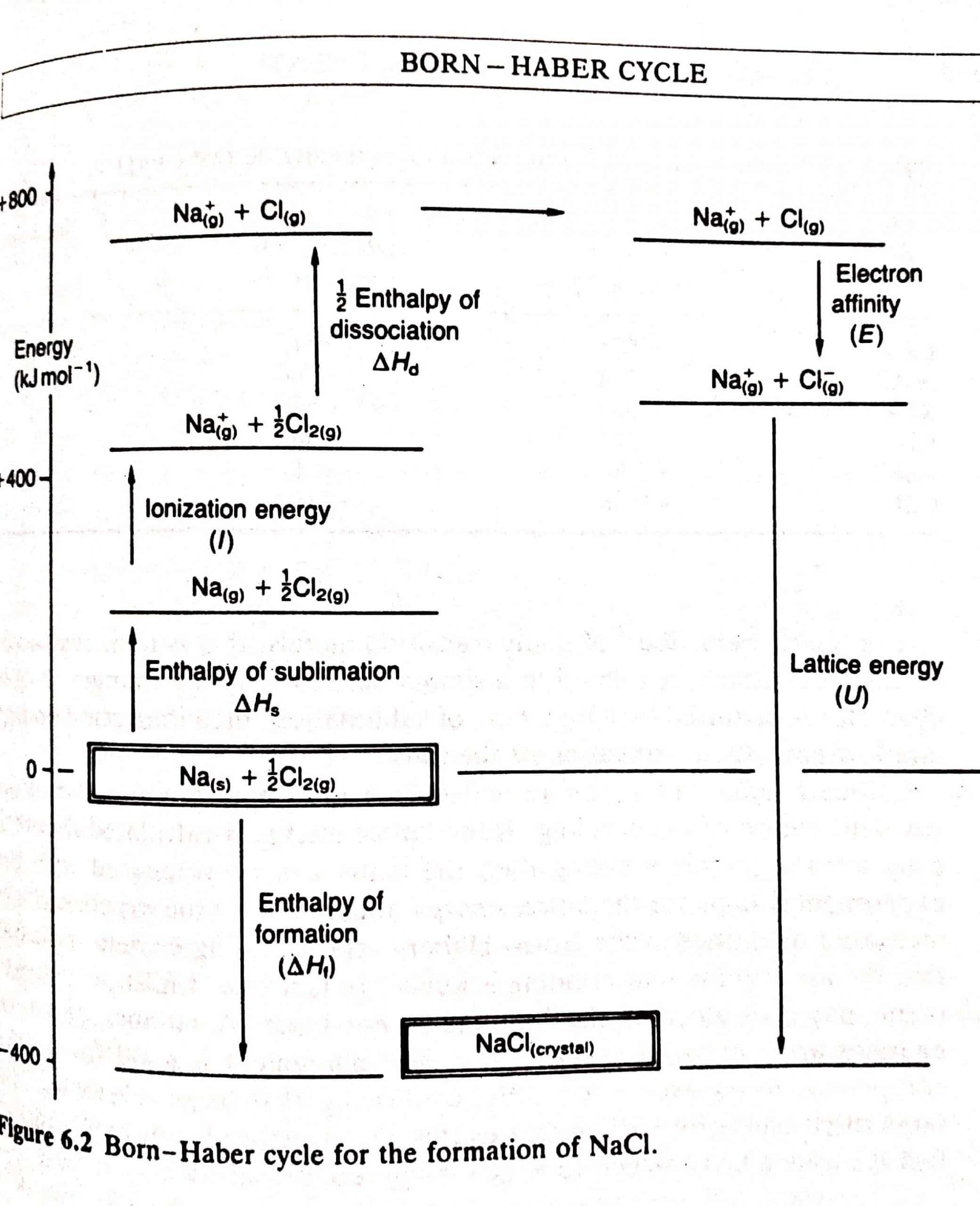
All the terms except the lattice energy and electron affinity can be measured.
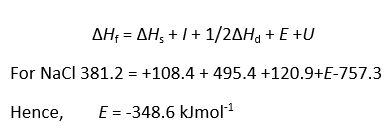
Ionization energy and Electron affinity
| Ionization energy | Electron affinity |
| Ionization energy is defined as the amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from an isolated gaseous atom in its ground state to produce a cation. | The electron affinity of an element is defined as the energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom to form a gaseous anion, or negative ion. |
| when we move from left to right in a period, the ionization energy increases with increasing atomic numbers. | electron affinity increases in period from left to right. |
| The ionization energy decreases in a group from top to bottom in a group. | electron affinity decreases along with the group. |
FAQs and MCQs
Which element has the highest most negative electron affinity?
Halogens (gr. VIIA) elements are the highest electron affinity.
How to calculate electron affinity?
Electron affinity calculate using the Born-Haber cycle.
What is electron affinity?
The electron affinity of an element is defined as the energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom to form a gaseous anion, or negative ion.
Why does electron affinity increase across a period?
The atomic size reduces as we move through a period, but the nuclear charge increases.