Table of Contents
ToggleIn 1912, Moseley, an English physicist, observed that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are determined by atomic number rather than atomic weight. Modern periodic table rules state that “The physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.”
Elements are grouped into four different blocks, in ascending order of atomic number, and thus the positions of alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, inert gases, and other elements are separated in the modern Periodic Table. So it is superior to Mendeleev’s periodic table.
The features of Modern Periodic Table are:
- Some elements, such as Argon and Potassium, Cobalt and Nickel, were reorganized based on their atomic number.
- Isotopes of the same element can be placed within the same group due to the same atomic number.
- The controversy of Hydrogen was clarified.
- Elements have been classified into 4 different blocks.
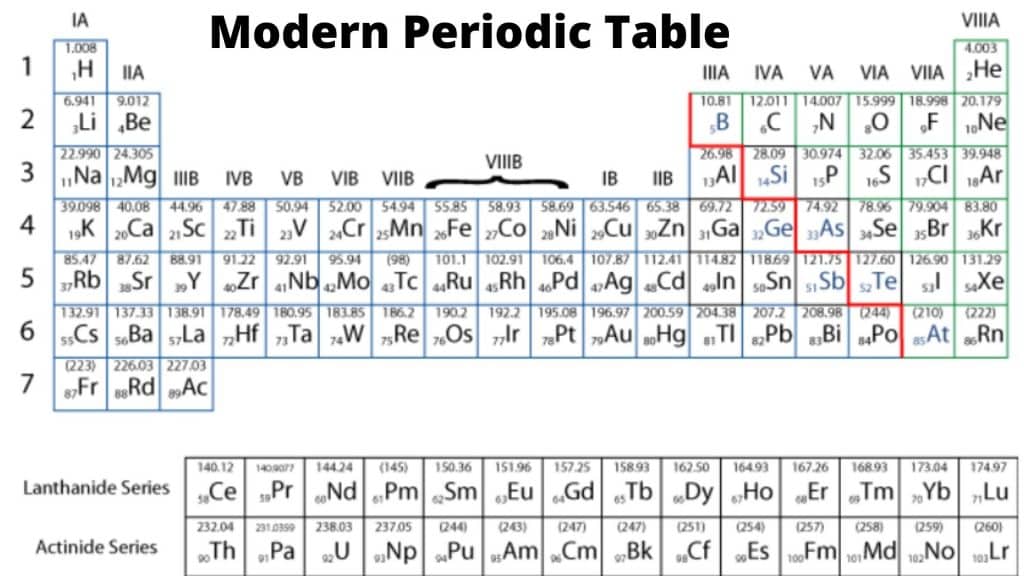
Periods are the horizontal rows of elements in the periodic table. There are seven periods.
Bohr (1920) constructed a periodic table known as the long form periodic table.
Depending on the number of incomplete shells in the atom, the elements in the periodic table can be classified into four different types of elements.
Representative elements
Two groups on the left (IA &IIA) and five groups on left (IIA, IVA, VA, VIA, VIIA) of Subgroup A are representative elements.
Inert gases
Elements of zero group or (18) column are called inert gases.
Transitional elements
Elements constituting subgroup B (IB, IIB, IIIB, IVB, VB, VIB, VIIB) and VIII are called transition elements.
Inner transitional elements
Lanthanides(4f-series) and Actinides(5f-series) are separated rows at the bottom of periodic table, these elements are called Inner transitional elements.
Characteristics of periods
The number of electrons in the valance shell increases as we move from the left to right.
- The valency of the electron increases from 1 to 4 then decreases to 0.
- Atomic size of an atom decreases from left to right due to increase in nuclear charge as extra electron is added.
- Ionization energy and electro positivity decreases as we move from left to right in periodic table.
- Electronegativity and metallic character increases as we move from left to right.
- Groups are the vertical columns of elements in periodic table. There are 18 groups arranged vertically.
Characteristics of groups
- Atoms of the element in the group have the same number of the electron in the outermost shell.
- Elements in the group have same valency except for the group 0, which do not take part in the chemical reaction.ar
- Atomic size increases as we move down as one new shell is added.
- Ionization increases as we move down the group.
- Metallic character, chemical reactivity of metals increases but not metallic character and chemical reactivity decreases as we move down the group.
Sub-shells
Each shell consists of a number of sub-shells in which electrons are distributed.
s-block
They are very soft metals with low melting and boiling points. It includes alkali and alkali earth metals. They are good reducing agents since they are highly electropositive and form positive ions by losing one or two electrons from their outermost shells. eg Ca, Mg. Most elements of this block impart characteristics of clour to the flame.
p-block
The elements in which the last electron enters into any of the p-orbitals of the outermost shell are called p-block elements. It includes metals, metalloids, nonmetals, and inert gases. They have 1-6 valence electrons in the outermost shells. The completely filled p-orbital are noble gases.
d-block
The elements in which the last electrons enter any one of the five d-orbitals of their respective penultimate shell are d-block elements. It includes the transition element, which lies in between the s and p block elements. E.g., Ag The valance electron lies in the d sub-shells.
f- block
It includes the elements lanthanide and actinide. They have a high melting and boiling point. They form coloured salts and show variable oxidation states, commonly a +3 state.
Aufbau principle
This principle explains how the atoms are arranged in the orbitals. According to this principle, the sub-shells of the lowest energy are filled first, then the higher energy levels are filled, and so on.

Valency
The total number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, either shared or gained or lost in a chemical combination is called valency. The outermost electron determines the chemical reactivity of the element. eg sodium has one valence electron that it transfers to the shell of another atom and becomes positively charged. so the valency of sodium is 1.
FAQs
How many groups are in the modern periodic table?
There are 18 groups in the modern periodic table.
How is the modern periodic table arranged?
The physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
How are the elements arranged in the modern periodic table
The elements in modern periodic table are organized by atomic numbers.
The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing
The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers.