Table of Contents
ToggleThe definition of a hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom that is already covalently joined to a highly electronegative atom, such as N, O, or F in a molecule, and a highly electronegative atom that is present in a molecule of the same substance, present in a molecule of a different substance, or present within the same molecule.
As mentioned already, hydrogen bonding is formed either between the molecules of the same substance or between the molecules of different substances, or between two atoms present in the same molecules. The H-bonding is represented by a dotted line.
Types of Hydrogen bonding
There are two types of H-bonding depending on whether hydrogen bonding is formed between the two molecules or within the same molecules.
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding
- Intramolecular or internal hydrogen bonding
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding
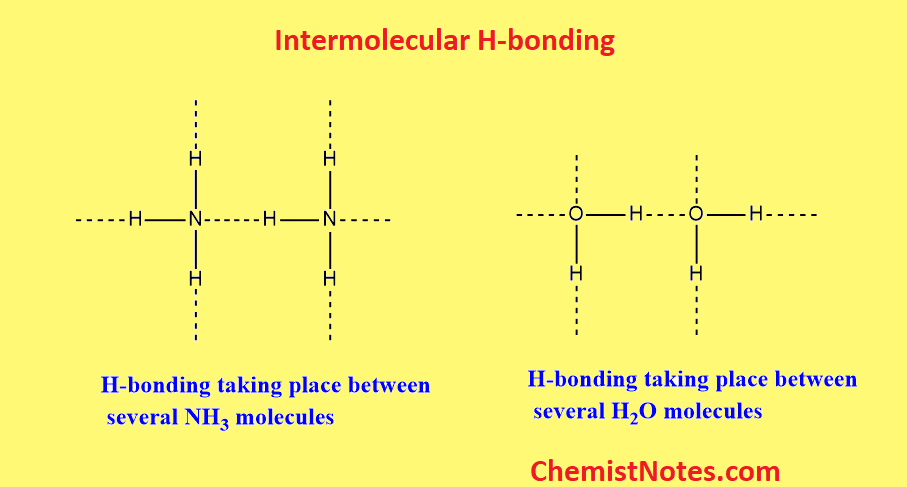
A hydrogen bond between molecules of the same chemical or between molecules of different chemicals is known as an intermolecular hydrogen bond. In this type of H-bonding, two or more molecules of the same substances or different substances get polymerized or associated and form a large cluster. The formation of a cluster is called association or polymerization.
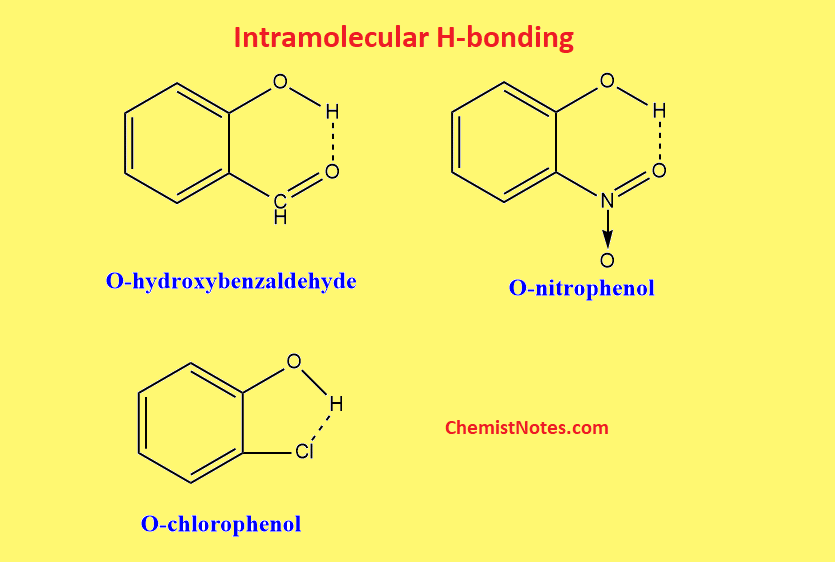
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding
The hydrogen bonds between two atoms within the same molecule are known as intramolecular hydrogen bonds. In this type of H-bonding, a planar 5-membered or 6-membered chelate ring is obtained. Moreover, the interacting atoms should be placed in such a way that there is minimum strain during the formation of the ring.
How is a hydrogen bond formed?
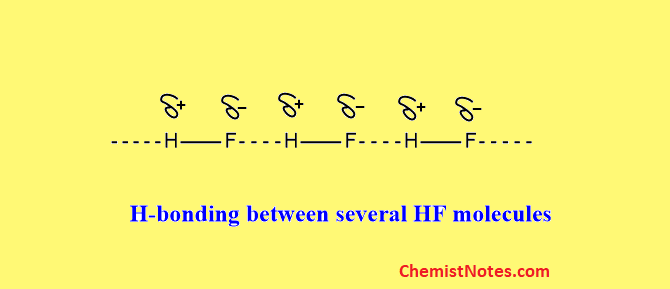
Let us take an example of the formation of hydrogen bonds in HF molecules. Due to the high electronegativity and the small size of the F-atom, the H-F bond in HF is a polar covalent bond, which can be represented as shown below:
Therefore, HF molecules behave as a dipole. When many HF molecules come closer, H-atom having a partial positive charge in one H-F dipole is attracted towards the F-atom having a partial negative charge of another H-F dipole by the electrostatic force of attraction which is known as the hydrogen bond.
A large cluster of molecules is created as a result of hydrogen bonding that develops between many HF molecules.
We may conclude from the preceding discussion that hydrogen bonding is just dipole-dipole attraction. However, hydrogen bonding is more powerful than other dipole-dipole attractions.
Conditions for the formation of hydrogen bond
The major conditions which must be fulfilled for the formation of hydrogen bonding in compounds are given below:
- Presence of high electronegative atom: A strongly electronegative atom, such as N, O, or F, should be directly connected to a hydrogen atom by a covalent bond in molecules.
- Presence of the atom with small size: The highly electronegative atom must be of small size so that the A-H (A=N, O, F) may be highly polar and a strong interaction between several dipoles may occur.
Strength of Hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bonding is not considered a chemical bond but it is just an electrostatic force of attraction between dipoles. Therefore, H-bond is a weak bond.
What are the factors that affect the strength of hydrogen bonds? One of the major factors is the electronegativity of the atom attached to the hydrogen atom by a covalent bond. The strength of the hydrogen bond increases with the increase of the electronegativity of the atoms attached to a hydrogen atom. For example; the strength of the H-bond in NH3 molecules is weaker than the HF molecule since the electronegativity of N, O, and F is in the order of N<O<F.
A hydrogen bond is much stronger than Van der Waal’s forces but weaker than a covalent bond and ionic bond. The order of strength is Van der Waal’s< H-bond< Covalent bond< Ionic bond.
Are hydrogen bonds stronger than dipole-dipole?
Yes, hydrogen bonds are stronger than dipole-dipole interaction. When hydrogen is bonded with strongly electronegative elements such as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen, hydrogen bonding occurs. Because of the large electronegative difference, the atoms are pulled together more tightly, resulting in a stronger bond.
On the other hand, Dipole-dipole interaction occurs when a partially negative charged ion interacts with a partially positive charged ion. Thus, the bond formed between the atoms is significantly weaker as a result of electrostatic attraction.
Does hydrogen bonding increase boiling point?
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding increases the force of attraction between the molecules. Thus, the compound requires more energy to separate these molecules. Therefore, intermolecular hydrogen bonding increases the boiling point of the compounds.
Does hexanol have hydrogen bonding?
Hexanol can form hydrogen bonding with water as well as with other molecules of hexanol. Since it has a hydrogen atom attached to the highly electronegative oxygen atom, it can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds as shown in the figure.
Does HF have hydrogen bonding?
HF can form intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water as well as with other HF molecules. It has active hydrogen directly attached to the highly electronegative Fluorine atom, it has the capability to form hydrogen bonding.
Does HCl have hydrogen bonding?
As we have already explained the criteria for the formation of hydrogen bonds, the size of the electronegative atom must be small. Due to the large size of the chlorine atom, it can not form hydrogen bonds effectively because the smaller the size of atoms, the stronger the interaction. Thus, HCl does not have hydrogen bonding.
Does NH3 have hydrogen bonding?
Yes, the NH3 molecule has hydrogen bonding or it can form intermolecular hydrogen bonding due to the presence of hydrogen atoms directly linked with highly electronegative nitrogen atoms.
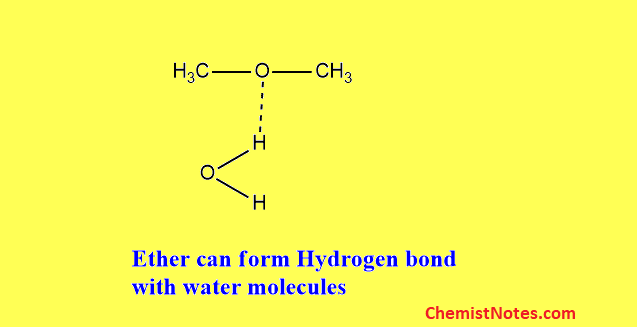
Does dimethyl ether have hydrogen bonding?
An oxygen atom is connected to two carbon atoms on either side of dimethyl ether. Dimethyl ether molecules cannot establish hydrogen bonds with one another because the oxygen atoms are not linked to the hydrogen atoms.
But, Ethers can form hydrogen bonds to water because the oxygen atom is attracted to the partially-positive hydrogens in water molecules, making them more soluble in water than alkanes.
Are hydrogen bonds stronger than van der waals?
Yes, hydrogen bonds are stronger than Van der Waal’s force. Van der Waal’s force is the force of interaction between dipole-dipole while the hydrogen bond is a strong electrostatic attraction between molecules.
FAQs/MCQs:
How many hydrogen bonds can a single water molecule form?
A single water molecule can form four hydrogen bonds.
Is hydrogen bonding stronger than dipole-dipole?
Yes, hydrogen bonding is stronger than dipole-dipole interaction.
Does acetone have hydrogen bonding?
Acetone lacks hydrogen bonding because no hydrogens are linked directly to oxygen.
How many hydrogen bonds are between adenine and thymine?
There are two hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine.
Where are hydrogen bonds found in DNA?
Hydrogen bonds are found between nitrogen bases of two complementary strands of DNA.
Which enzyme breaks the hydrogen bonds during replication?
The helicase enzyme breaks the hydrogen bonds during replication.
Does CH3OH have hydrogen bonding?
Yes, CH3OH has three hydrogen bonds, two as proton acceptors and one as a proton donor.
How many water molecules could hydrogen bond directly to glucose?
17 water molecules could hydrogen bond directly to glucose.
Does formyl chloride have hydrogen bonding with water?
Yes, formyl chloride has hydrogen bonding with water.
Which amino acid cannot participate in hydrogen bonding?
Alanine, cysteine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, and valine can not participate in hydrogen bonding.