Table of Contents
ToggleTetracycline, a member of the tetracyclines family, is an oral antibiotic used to treat a variety of illnesses, including cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. Vomiting, diarrhea, dermatitis, and appetite loss are typical adverse reactions. The terms acne and pimple frequently get confused. However, there is a straightforward distinction to make: a pimple is an external skin eruption, whereas an acne outbreak is an internal one.
Antibiotics are used to fight against bacterial infections, not viral ones. However, colds, the flu, and other viral diseases cannot be treated with antibiotics like tetracycline. Antibiotic overuse increases your risk of developing a subsequent infection that is resistant to antibiotic therapy.
Moreover, Tetracycline can be used for animals too. It is used to treat specific bacterial infections and inflammatory skin diseases in dogs under the trade names Achromycin®, Medicycline®, Sumycin®, and Tetracyn® (such as lupus).
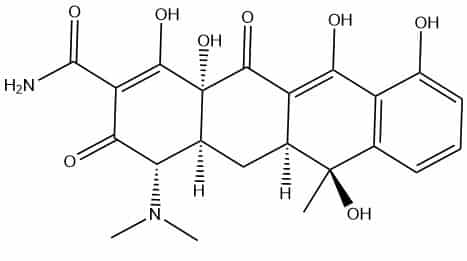
Tetracycline examples
Some of the examples of tetracycline in the form of their brand names are:
- Adoxa
- Adoxa CK
- Adoxa Pak
- Brodspec
- Cleeravue-M
- Declomycin
- Doryx
- Dynacin
- Minocin
- Nuzyra
- Seysara
- Sumycin
- Vibramycin Calcium
These drugs are available in the following forms:
- Tablet
- Powder for Suspension
- Capsule
- Capsule, Extended Release
- Syrup
- Tablet, Delayed Release
- Tablet, Extended Release
Mechanism of action of Tetracycline
Similar to other antibiotics, it works through the inhibition of protein synthesis, cell wall formation, and so on. Tetracycline, a fast-acting antibiotic, stops bacterial growth by inhibiting translation. Due to its association with the 30S ribosomal subunit, the amino-acyl tRNA is unable to bind to the ribosome’s A site. It also partially binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit. The nature of this bond is reversible. Tetracycline may also have an impact on the cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria, which could result in the leakage of intracellular components like nucleotides.
Absorption of Tetracycline
When injected intramuscularly, bioavailability is less than 40%; intravenously, it is 100%; and orally, it is between 60 and 80 percent (fasting adults). Tetracycline oral formulations have a 50% or more reduction in GI absorption when consumed with food or milk.
Route of elimination of Tetracycline
They are biologically active and condensed by the liver into bile, which is then expelled in large amounts in the urine and feces.
Toxicity of Tetracycline
LD50=808mg/kg (orally in mice).
How does tetracycline work on acne?
The mechanism of action of tetracycline is to inhibit the development of acne-causing bacteria. It also has anti-inflammatory properties, reducing inflammation and swelling in acne. This antibiotic is used to treat moderate to severe acne, despite the fact that it is occasionally used for mild inflammatory acne that is extremely difficult to treat.
Direction to use tetracycline
Tetracycline is available in oral pill form. It is typically consumed twice or four times a day. Tetracycline should be taken empty-handed at least one hour before or two hours after meals or snacks. To avoid irritating the esophagus (tube between the throat and stomach), tetracyclines should be taken with a full glass (8 ounces) of water.
Working duration of tetracycline
Within four to six weeks, some individuals might see an improvement in their acne. However, after using this medication for 6 to 8 weeks, if your acne does not improve or if it worsens, consult a medical practitioner. Before the condition completely improves after acne therapy, it may take up to 8 to 12 weeks.
Dosages of Tetracycline
250 to 500 milligrams (mg) every six hours for adults and teenagers. The dose is dependent on body weight for children older than 8 years old. 6.25 to 12.5 mg per kilogram (kg) (2.8 to 5.7 mg per pound) of body weight is typically administered every six hours.
Overdoses of tetracycline antibiotics
It is possible for bacteria to adapt to the point where antibiotics no longer work against them when taken too frequently or under improper conditions. Bacterial resistance or antibiotic resistance is what is referred to as this. Even the most potent medications are now ineffective against some germs. There is a rising issue with antibiotic resistance which is also known as multidrug resistance. The side effects may be severe nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, jaundice, azotemia, acidosis, stupor, and shock.
Difference between tetracycline and Doxycycline
Tetracyclines are broad-spectrum antibiotics that are frequently prescribed to treat pelvic, urethral, chest, and skin infections. Syphilis, Lyme disease, Q fever, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and plague is just a few of the illnesses for which doxycycline is prescribed. The prevention of malaria is another common application of it.
Why is Doxycycline preferred over tetracycline?
Since Doxycycline is potentially less hepatotoxic than tetracycline, it is preferred.
Tetracycline Video
FAQs
What should not be taken while using tetracycline?
Answer: Antacids containing magnesium, aluminum, calcium, or sodium bicarbonate, calcium supplements, zinc products, iron products, and laxatives containing magnesium will interfere with tetracycline and make it less effective.
Are tetracycline and Doxycycline the same?
Answer: Doxycycline is the class of tetracycline antibiotics.
Is tetracycline used for acne?
Answer: Tetracycline can be effective for treating acne.
Side effects of tetracycline
Answer: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, mouth sores, black hairy tongue, sore throat, dizziness, headache, or rectal discomfort.
What is the relation between tetracycline and dairy products?
Answer: Taking dairy products or other high-calcium foods together with Tetracycline, can decrease the effectiveness of Tetracycline to treat an infection.
Why do dairy products decrease the effectiveness of tetracycline?
When consumed concurrently with tetracycline derivatives, milk, and other dairy products, antacids containing polyvalent cations, as well as other iron salts, may reduce absorption by up to 90%.