Table of Contents
ToggleAntibiotics, popularly known as antibacterials are used to treat or prevent some types of bacterial infections. However, it doesn’t work for viral infections like cold and flu, sore throat, etc. Penicillin, the first ever accidentally discovered antibiotic brings a new revolution to the field of medicine. Various types of antibiotics classes are:
- Penicillin
- Cephalosporins
- Aminoglycosides
- Glycopeptides
- Tetracyclines
- Macrolide etc
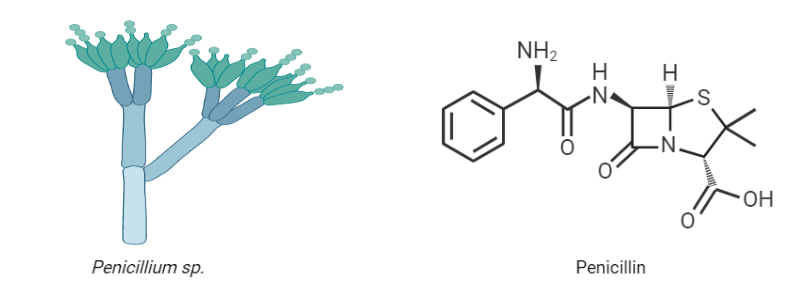
Among all the classes of antibiotics, penicillin was the first discovered accidentally in the lab by British Scientists Alexander Fleming in 1928 London at the department of St. Mary’s Hospital along with Dr. Eb chain and Sir Howard Florey. The discovery happened when Fleming unintentionally left a dish of staphylococcus germs exposed for a few days. When he came back, the dish was covered in bacterial growth, with the exception of one spot where mold had begun to form. He noticed that fungus (mold) Penicillium notatum had contaminated a culture plate of Staphylococcus bacteria he had accidentally left uncovered (project on natural germ killing).
A class of antibiotics known as penicillin is frequently used to treat various gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial infections. Because of the location of the beta-lactam ring, these medications are also known as beta-lactam antibiotics. Three major structural requirements are:
- Fused beta-lactam and thiazolidine ring
- A free carboxylic acid group
- One or more substituted amino acid side chains.
Mechanism of action of Antibiotics
Generally, antibiotics work by different methods by inhibiting protein synthesis and inhibiting cell wall synthesis. It works by attacking the peptidoglycans, which create strong linkages that provide the bacterial cell strength and prevent leaking from the cytoplasm. This causes the bacteria to bristle as a result of the inhibition of bacterial cell wall formation.
In general words, bacteria treat certain infections either by stopping bacteria from reproducing or destroying them.
Working duration of antibiotics
As soon as we start taking antibiotics, they start to work. Additionally, it is based on the kind of infection we are treating.
What happened when we didn’t complete our dosages?
The majority of antibiotics need to be taken for 7–14 days. Despite the fact that we might feel better after a few days of therapy. The doctor’s recommended dosages must be followed to the letter or multi-drug resistance may develop.
Do antibiotics make us tired or fatigued?
On consuming antibiotics as prescribed, we may experience tiredness and lethargy. It’s possible that this is a sign of the infection being treated with antibiotics or that it’s a severe (rare) side effect of taking antibiotics.
Side effects of antibiotics
Some of the major side effects of antibiotics are:
- Nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- black hairy tongue
- fever
- muscle pain
- headache.
Despite the fact that antibiotics have revolutionized modern medicine and are beneficial to humanity, multidrug-resistant bacteria are also on the rise, so it is important to use antibiotics carefully. These drugs should only be taken on a prescription, never be used to treat common infections, and their recommended dosages must be followed to the letter.
Published by: Pratiksha Chaudhary (Chemikshya)
Antibiotics Video
FAQs
1. Penicillin was discovered by
Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming.
2. Penicillin is obtained from
Penicillin is obtained from Penicillium notatum.
3. sar of penicillin
Broad-spectrum antibacterial action is produced by the thiazolidine ring’s sulfur when combined with O, CH, and CH-β-CH3.
4. Examples of antibiotics
Amoxicillin, cefadroxil, tetracycline, gentamicin, etc are a few examples of antibiotics.
5. macrolide antibiotics
A class of antibiotics known as macrolide antibiotics is frequently used to treat both acute and chronic illnesses.
6. gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
Depending on the staining techniques, bacteria might be either gram-positive or gram-negative. In contrast to gram-negative bacteria, which lose their crystal violet color and stain red, gram-positive bacteria keep their crystal violet color and stain purple.