Table of Contents
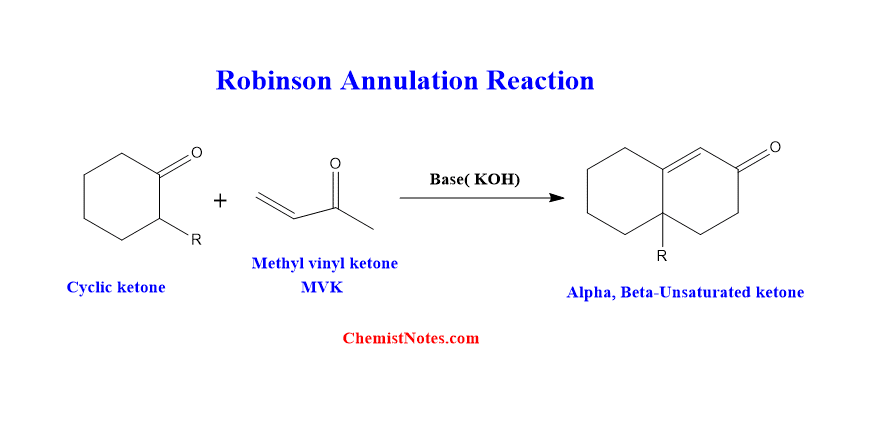
ToggleRobinson Annulation reaction is the reaction of an acyclic ketone, cyclohexanone, with methyl vinyl ketone, resulting in a ring closure and the formation of a bicyclic alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone. This reaction was first of all given by Rapson and Robinson in 1935
Robinson annulation
Six-membered alpha,beta-unsaturated ketones are obtained through Michael’s addition of cyclohexanone to methyl vinyl ketone followed by intramolecular aldol condensation. This reaction is known as Robinson annulation. Robinson annelation is another name for this reaction, which is also known as Robinson cyclization. Therefore, the Robinson annulation involves two sequential reactions viz Michael addition and aldol condensation.
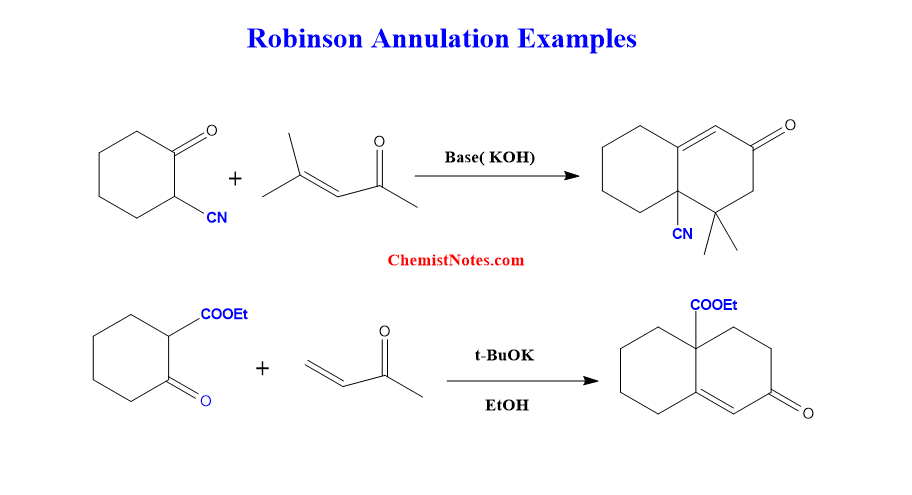
Robinson annulation reaction examples
Some of the examples of this reaction are shown below:
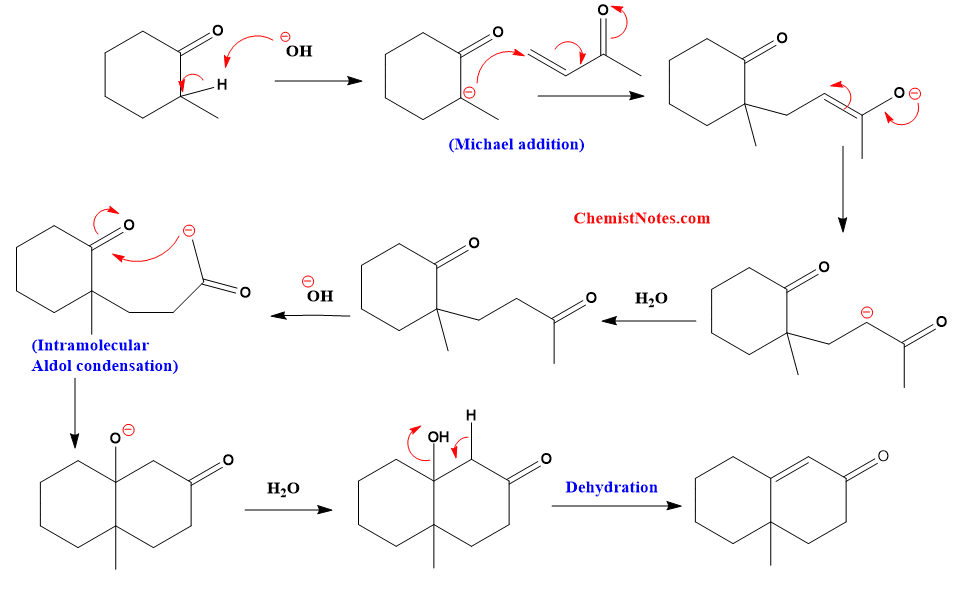
Robinson annulation reaction mechanism
The Robinson annulation is a two-step reaction that starts with a Michael addition and ends with an aldol reaction. The cyclic ketone is first deprotonated with a base to yield an enolate, which then undergoes conjugate addition to the methyl vinyl ketone, i.e. a Michael addition, to yield 1,5-diketones.
This reaction involves the following steps.
- Generation of an enolate from the ketone.
- Michael addition of the enolate to the alpha, beta-unsaturated ketone
- Aldol condensation
- Dehydration
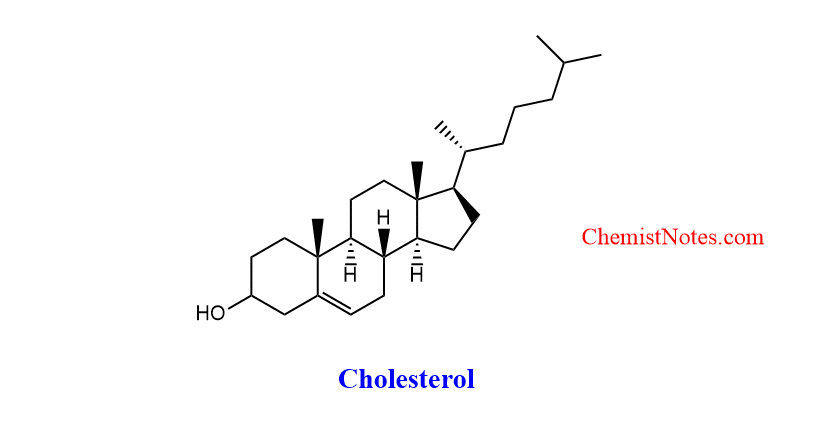
Robinson annulation reaction applications
Robert Robinson employed the Robinson annulation for the synthesis of cholesterol. This reaction has found widespread use in the synthesis of terpenes, particularly steroids. The Robinson annulation is an essential reaction in organic synthesis because an annulated six-membered carbocyclic is a prevalent structural feature of natural products.
References:
- Bradford P. Mundy, Michael G. Ellerd, Frank G. Favaloro, Jr., Name Reaction and Reagents in Organic Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons, 2005
- Laue T., Plagens A., Named Organic Reactions, Second edition, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005
- Wang, Z., Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.,2010
- J.J. Li, Name Reactions, 4th ed.,© Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2009






