Table of Contents
ToggleAldol condensation mechanisms, examples, reactions, and applications in organic chemistry have been discussed here:
Aldol condensation reaction
Aldol condensation reactions are base or acid-catalyzed condensation reactions involving two molecules of carbonyl compounds, similar or different, with at least one of them having α-H atom, which gives rise to β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds or α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. In this case, the reaction is caused by one α-H atom of a carbonyl molecule. A simple aldol condensation reaction does not take place when the α-H atom is missing from both carbonyl molecules.
As base and acid catalysts, dilute aqueous solutions of NaOH, KOH, Ba(OH)2, HCl, etc. are typically used. Some of the examples of aldol condensation reactions are

Aldol Condensation Mechanism
The mechanism of the aldol condensation reaction takes place in two ways:
Acid catalyzed aldol condensation mechanism
Step 1: Protonation of one of the carbonyl compounds to form the conjugate acid.
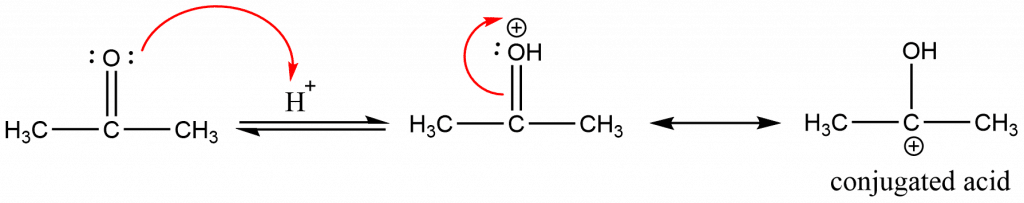
Step 2: Electrophilic addition of the activated carbonyl compound to the conjugated acid

Step 3: Protonation of the aldol’s alcoholic OH and elimination of H2O to form the carbonium ion.
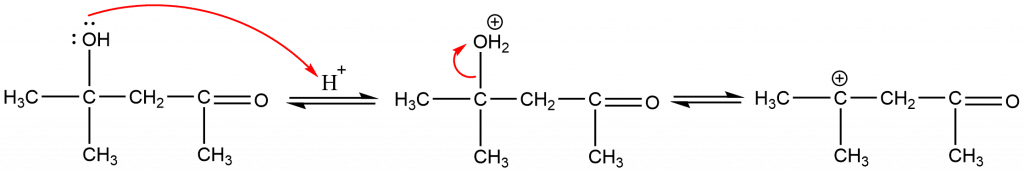
Step 4: Formation of α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound by the loss of H+ from the alpha-carbon atom

Base catalyzed aldol condensation mechanism
Step 1: H+ is abstracted from α-C atom of one of the carbonyl molecules in order to form a resonance stabilized carbanion.
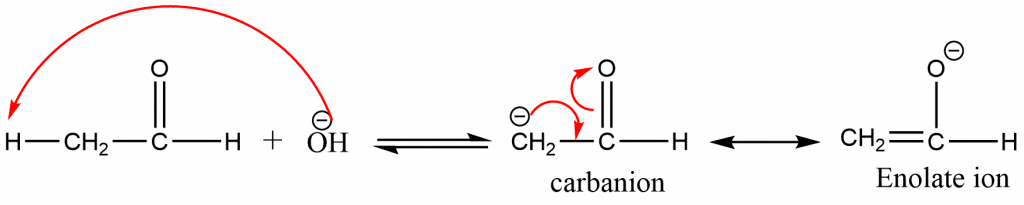
Step 2: The addition reaction takes place between carbanion and the carbonyl carbon atom of other molecules via nucleophilic addition.
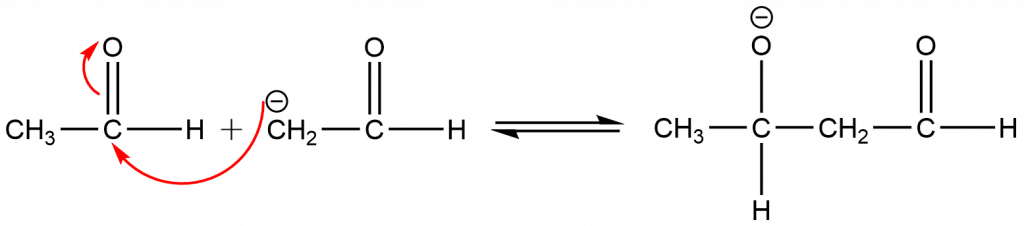
Step 3: The oxide ions take up a proton from the H2O and leads to the formation of β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds.
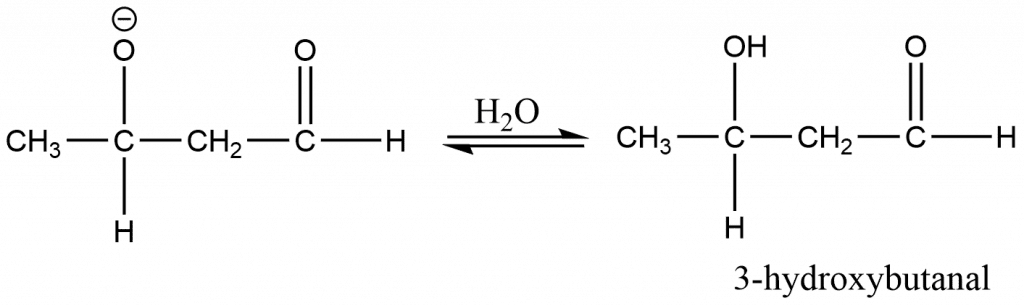
Cross aldol Condensation
Crossed aldol condensation occurs when two separate carbonyl compounds undergo aldol condensation, resulting in four different aldols and four different, α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Such reactions occur between two distinct aldehydes or ketones, as well as between an aldehyde and a ketone containing alpha-hydrogen atoms.
Cross aldol condensation mechanism takes place as:

Applications of Aldol condensation
Some of the major applications of aldol condensation reactions are:
1. Formation of β-hydroxy compounds and α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.

2. Formation of cyclic compounds by intramolecular aldol condensation
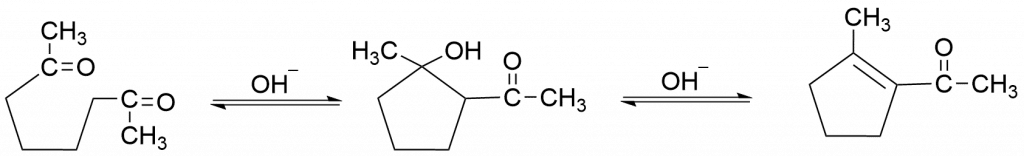
3. Synthesis of sorbic acid that acts as a food preservative
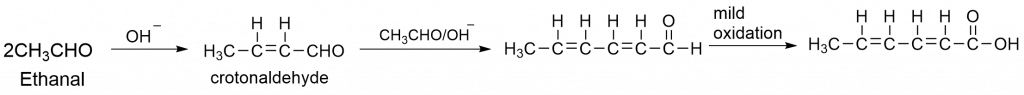
Limitations
Some of the compounds like formaldehyde, aromatic aldehyde, trimethyl acetaldehyde, and diaryl ketones do not undergo aldol condensation reaction due to the lack of α-H atom.
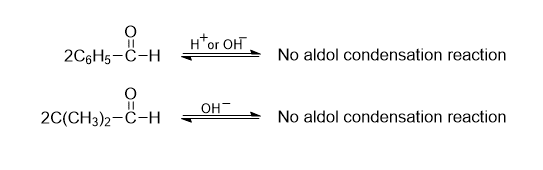
Aldol Condensation Video
FAQs/MCQs
Aldol condensation
Such reactions that involve two molecules of carbonyl compounds, similar or different, with at least one of them having α-H atom catalyzed by acid or base reagents to form β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds or α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are called aldol condensation reactions.
Intramolecular aldol condensation
The condensation reaction of two aldehyde or ketone groups in the same molecule to yield five or six-membered α, β-unsaturated ketone or aldehydes known as an intramolecular aldol condensation reaction.
Aldol condensation of acetone

The aldol condensation of acetone forms α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Retro aldol condensation
When β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds or α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound is treated with an acid or base catalyst in an aqueous media, the reverse reaction takes place. Such a reaction is known as retro-aldol condensation reaction or reverse aldol condensation.
Aldol condensation aldehyde

Aldol condensation of aldehyde gives rise to β-hydroxy carbonyl compound.
Aldol condensation of cyclohexanone

Aldol condensation of cyclohexanone yields β−hydroxy ketone.
What is the limiting reagent in aldol condensation?
Acetone is one of the limiting reagent in aldol condensation reaction.
Aldol condensation and cannizzaro reaction
The reaction in which aldehydic compounds having no α-hydrogen atoms is treated in presence of strong base to form an equal amount of corresponding alcohol and carboxylic acids called as Cannizzaro reaction, while aldol condensation is the condensation reaction of two molecules of carbonyl compound having at least one α-hydrogen atoms to form β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds or α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
Aldol condensation problems
The compounds that lacks α-H atom do not undergo aldol condensation reactions.
References
- Morrison, R. T., & Boyd, R. N., Organic chemistry, Allyn and Bacon, Inc. 1987.
- March, J., Advanced Organic Chemistry, Wiley Eastern Limited, 1986.
- Skyes, P., A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Second edition, Orient Longman Ltd., 1988.






