Table of Contents
TogglePaper chromatography is a form of partition chromatography in which chemicals are dispersed between two liquids, one stationary and the other is moving. The compounds in the mixture to be separated migrate at various rates and migrate as spots on the paper at different places.
Principles of paper chromatography
The adsorption column is replaced by a high-quality filter paper in paper chromatography. When a filter paper is immersed in a solvent and its bottom is dipped into the solvent, the solvent rises slowly on the filter paper owing to capillary action. If a solution of the substances to be separated is used instead of the solvent, the dissolved substances will rise with the solvent on the filter paper and separate due to different rates of movement for different substances, and if they are colored, different distinct spots will be observed for each compound. In the case of colorless substances, some locating reagent is used depending on the types of the compound.
Stationary and Mobile phase of paper chromatography
In paper chromatography, the stationary phase is the strip or sheet of paper that is immersed in the solvent. The solvent that travels through the paper, bringing various compounds with it, is known as the mobile phase. The stationary phase remains stationary on the paper and does not move.
Paper Chromatography experiment/method in lab
In paper chromatography, a drop of test solution is applied as a small spot on a filter paper. This spot should be near the edge of the filter paper and dried. The paper is placed in a chromatographic chamber and the edge of the filter paper is then dipped into a solvent called developing solvent. Close the lid of the chromatographic chamber and allow the chromatogram to develop till the solvent front has travelled about three-fourths length of the filter paper strip. Take out the paper, mark solvent front and dry it. The paper is dried and various spots are visualized by a suitable reagent called visualizing reagents. Calculate the Rf value of different spots.
Paper Chromatography Rf Value
The Rf value for a specific solvent describes the properties of that substance and defines the movement of the substance relative to the solvent front in a given chromatographic system.
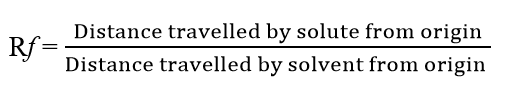
FAQs
What is Paper Chromatography?
Paper chromatography is a form of partition chromatography in which chemicals are dispersed between two liquids, one stationary and the other is moving.
How does paper chromatography work?
In paper chromatography a drop of the mixture, the solution is spotted near one end of the paper and then dried. The solvent flows along with the paper through the spots and on, carrying the substances from the spot.
what is mobile phase in paper chromatography?
The solvent that travels through the paper, bringing various compounds with it, is known as the mobile phase.






