Table of Contents
ToggleLinear and Convergent Synthesis are the two major categories of organic synthesis. A linear synthesis is one in which the targeted molecule ( TM) is assembled in a stepwise manner from the available starting materials, and a new fragments molecule is synthesized through a series of linear transformations whereas convergent synthesis is the key pieces of the target molecule are synthesized separately or independently in convergent synthesis and then brought together at a later point in the synthesis to form the target molecule.
Linear Synthesis and Convergent Synthesis
Linear and convergent synthesis is that the former is longer and less effective while the latter is quicker and more effective which is the main distinction between them. A convergent synthesis is a method used in chemistry to increase the effectiveness of multistep synthesis, most frequently in organic synthesis. Several separate components of a complex molecule are synthesized in stage one of this sort of synthesis, and in stage two, these components are joined to form the finished product.
Synthesis in Organic Chemistry
Before going to linear and convergent synthesis, we have to understand the basis of synthesis in chemistry. Let us talk about a little bit of organic synthesis. Organic synthesis is a type of organic chemical synthesis that deals with the intentional building of organic molecules from available starting materials in one or more steps. The synthesis and formation of the inorganic compound are easier than organic compound synthesis. The synthesis of organic compounds is very important for the various field of chemistry.
Chemical reactions differ from synthesis in a different way, a chemical reaction is the backbone of organic chemistry. Organic synthesis is applied for critical in chemistry, biochemistry, medicine, agriculture, molecular biology, physics, materials science, electronics, and engineering because it allows for the manufacture of specific molecules for scientific and technical studies. Before the carried out the method of synthesis, choosing the starting material is very interesting and important for the obtained desired product. The following criteria are used for the selection of excellent starting materials.
- Target selection.
- Structure verifications
- Biological activity
- Analog studies
- Structural or biological challenges
- Development of new reactions and new reagents
Synthetic Planning
Synthesis is a construction process that involves converting simple or commercially available molecules into complex molecules using specific reagents associated with known reactions in the retro-synthetic scheme.
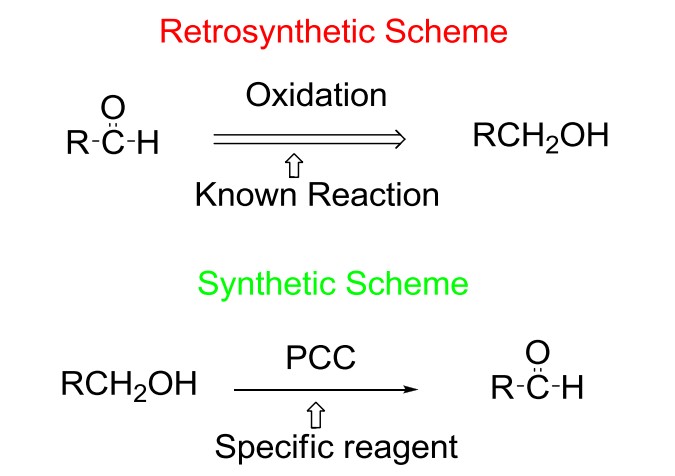
After completing the above criteria we have to process the organic synthesis, mainly organic synthesis is into two types:
1. Linear synthesis
A linear synthesis is one in which the targeted molecule (TM) is assembled in a stepwise manner from the available starting materials, and a new fragments molecule is synthesized through a series of linear transformations. The formed transitions state is act as a reactant for the other product during synthesis. let us do a five-step linear synthesis each step has a 90% yield. The overall yield can be calculated as follows ways:
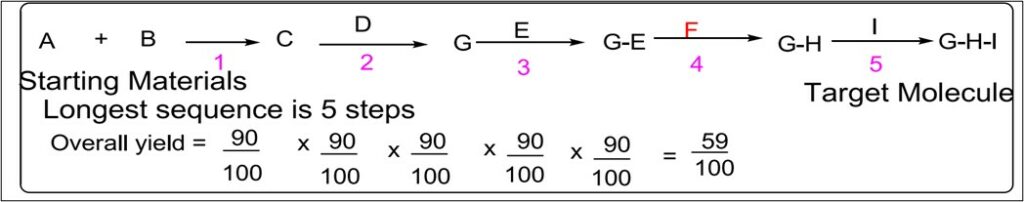
Since the overall yield of the synthesis is based on the single longest route to the target molecule, by being long, a linear synthesis suffers a lower overall yield.
Limitation of Linear synthesis
Linear synthesis has the following demerits which make linear synthesis less useful in organic synthesis.
- Lower efficiency
- Longer steps
- Lower overall yield
- Time-consuming
- Tedious and rigorous methods
2. Convergent Synthesis
The Key pieces of the target molecule are synthesized separately or independently in convergent synthesis and then brought together at a later point in the synthesis to form the target molecule. The overall yield can be calculated in the following ways:
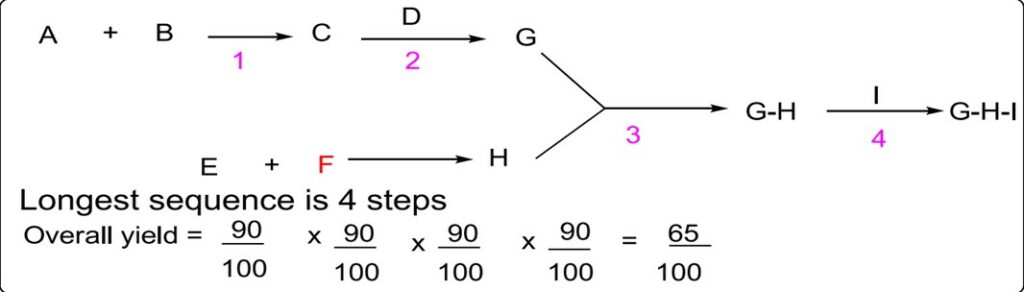
Why is convergent synthesis preferred to linear synthesis?
Convergent synthesis is a more preferred and widely used technique in the field of organic synthesis in chemistry. It is a very common and modern concept for the synthesis of new novel compound which is applicable in various field. Convergent synthesis is preferred to linear synthesis due to the following reason:
- More efficiency
- Lower steps
- More yield
- Less time consuming
- Modern concept for the synthesis
Differences between Linear and Convergent synthesis
The major difference between linear and convergent synthesis i.e linear synthesis vs convergent synthesis are given below.
| Linear synthesis | Convergent synthesis |
| It gives the target molecules when two more reactants are added sequentially. | It gives the target molecule when two or more fragments are added in a convergent manner. |
| The Linear synthesis contains a number of steps. | Convergent synthesis contains fewer steps than linear synthesis. |
| The yield % is less than expected. | Gives higher yield during synthetic target molecule. |
| less effecient | More efficient |
| tedious, time-consuming | modern, less time-consuming, highly used technique |






