Table of Contents
Toggle
Food preservatives are food additives that are essential for extending the shelf life or improving the flavor of food. Food preservatives specifically aid in regulating and preventing food deterioration and provide defense against spoiling from microorganisms (such as bacteria, yeast, and molds), lethal botulism, and other organisms that can cause food poisoning (antimicrobial function).
Food preservation definition
The method of food preservation protects against microbiological contamination, food poisoning, and food spoiling.
It is the process that includes modern as well as old ancient techniques to preserve the food against rancidity, bacteria, etc.
What is food preservation?
One way to protect food against unwelcome microbial growth is through food preservation. We cover the rice and curries with lids after the food is cooked to store and protect it and keep flies and other insects out. By doing this, we are protecting it against any infection brought on by them.
This is a temporary state of things. Contrarily, food preservation aims to extend the shelf life of food.
Principle of Food preservation
- Delay in microbial breakdown or preservation is recorded by:
- Keeping bacteria away (asepsis)
- Microorganism removal, i.e., filtration low temperature, dryness, anaerobic conditions, and other factors that inhibit the growth and activity of microorganisms using heat or radiation to kill the germs.
- Food can be preserved or delayed via self-decomposition.
- This is the result of food enzymes being destroyed or rendered inactive, such as via blanching.
- Chemical reactions can be stopped or delayed, such as oxidation, by using an antioxidant.
Food preservation methods
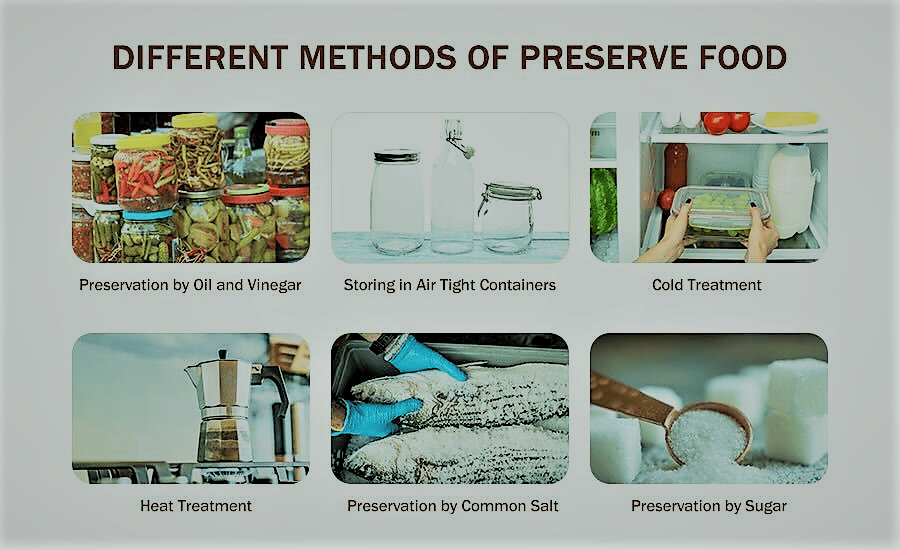
There are various modern and ancient homey food preservation methods, some are discussed below:
- Drying
- Freezing
- Smoking
- Vacuum packing
- Salting and pickling
- Sugar
- Lye
- Canning and bottling
- jellying
- potting
- jugging
- modified atmosphere
- controlled uses of an organism
- pasteurization
The first one is drying,
1. Drying
The first method of food preservation is drying. By using this technique, water activity is reduced, preventing bacterial growth. Drying makes food lighter so it can be carried more readily.
Modern drying methods include bed dryers, fluidized bed dryers, freeze drying, shelf dryers, spray drying, commercial food dehydrators, and household ovens in addition to the traditional methods of using the sun and wind.
Examples of items dried using this technique include meat and fruits including apples, apricots, and grapes.
2. Freezing
Food that has been prepared and frozen is kept in cold storage. Although potatoes can be kept in dark areas, potato preparations must be frozen.
3. Smoking
Food is cooked, flavored, and preserved through the process of smoking, which exposes it to wood smoke.
Meats and fish are typically smoked because the smoke has antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Assorted smoking techniques, including hot smoking, cold smoking, smoke roasting, and smoke baking, are used. Smoking increases the risk of cancer when used as a preservative.
4. Vacuum packing
By making bottles and bags impermeable, vacuum packing creates a vacuum. Bacteria die because there is no oxygen in the newly generated vacuum. typically applied to dry fruit.
5. Salting and pickling
Curing, commonly referred to as salting, is the process of removing moisture from goods like meat. Pickling is the process of preserving food in a salt solution (brine) or vinegar (acetic acid); in Asia, food is sometimes preserved in oil.
At a 20% concentration, salt stops the growth of germs and kills them. Pickling can be done in a number of ways, including chemical pickling and fermentation pickling.
To extend the shelf life of commercial pickles, sodium benzoate or EDTA is added.
6. Sugar
Fruits can be preserved with sugar in syrup form or crystallized form, depending on whether the material to be preserved is boiled in the sugar until it crystallizes, like candied peel and ginger.
Another use is for fruit that has been superficially coated in sugar syrup and then glazed. Alcohol and sugar are also combined to preserve upscale foods like fruit in brandy.
7. Lye
Lye, also referred to as sodium hydroxide, makes food alkaline and inhibits the growth of microorganisms.
8. Canning and bottling
Sealing cooked food in sterile bottles and cans is the definition of canning and bottling. Boiling the container destroys or weakens bacteria. Various amounts of time or space are used to cook food. The food is once more at risk of rotting after the can or bottle has been opened.
9. Pasteurization
Microbial growth in food is slowed down by pasteurization. The goal of pasteurization is not to completely eradicate all pathogenic microbes from food (typically milk and milk products), but rather to reduce the number of pathogens that are still alive and able to cause disease if the pasteurized product is stored as instructed and consumed before its expiration date.
Chemical preservatives
Chemical food preservatives are compounds that, depending on the situation, either stop microbe growth without necessarily eradicating it or stop product quality from degrading during production and distribution. The former category contains several naturally occurring food components that, when added to foods, slow or stop microbial growth. Making jams, jellies, and marmalades as well as candying fruit both require sugar in part for this purpose.
This includes the pickling processes that use vinegar and salt as well as the brandying processes that utilize alcohol. To stop the growth of microbes, some chemicals that are not naturally present in food are added.
Organic chemical preservatives
One of the main chemical preservatives is sodium benzoate, along with other benzoates. Most countries allow the use of benzoates in specific products in a regulated amount (often not exceeding 0.1 percent), while some of them need a statement of its usage on the label of the food container. Benzoates must be employed in an acidic media in order to be effective since free benzoic acid is the true active ingredient.
Because they contain a lot of benzoic acids, cranberries are able to resist deteriorating quickly. Benzoic acid works better against yeast than it does against bacteria and mold.
Salt is a type of food preservative?
Due to the fact that salt lowers the water activity of foods, it is useful as a preservative. The amount of unbound water that is available for microbial growth and chemical reactions is known as a food’s water activity.
Effect of potassium bisulfite as a food preservative?
Sulfurous acid is created when potassium bisulfite dissolves in water. The acid reduces the food’s pH, which aids in preventing the growth of dangerous germs like E. coli as well as yeast and mold.
Are preservatives bad for us?
Although careful analyses reveal that it is primarily based on misunderstanding rather than on clearly defined adverse reactions, there has been considerable public concern that some food additives induce bad reactions. True allergic (immunological) reactions to preservatives have only been little demonstrated. Several inorganic sulfite additives (E220-228), benzoic acid and its derivatives (E210-213), and some preservatives from the group of sulfating agents have been reported to cause adverse reactions in sensitive (e.g., asthmatic) people.
Asthma is characterized by breathing difficulties, shortness of breath, wheezing and coughing. 5,7 Preservatives can, however, generally be regarded as safe for the majority of customers due to strict EU legislation governing the safety assessment of additives.
MCQs/FAQs
What are food preservatives?
It is the process that includes modern as well as old ancient techniques to preserve the food against rancidity, bacteria, etc.
What are examples of food preservation?
Sugar, salt, nitrites, butylated hydroxy anisol (BHA), butylated hydroxyl toluene (BHT), tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ), vinegar, citric acid, and calcium propionate are all chemicals that preserve foods.
What is the best preservative for food?
Calcium Propionate. The finest food preservative and food enhancer, calcium propionate, is often made from calcium hydroxide and propionic acid. It prolongs the shelf life of bakery products while preventing the formation of mold and other microorganisms.
What are natural preservatives?
Natural preservatives are ingredients that inhibit the growth of bacteria or mold, which can ruin baked goods. They also serve to prevent changes in flavor, texture, and color. The consumer anticipates that they will be effective and come from natural sources, like vinegar. C vitamin
What are some toxic preservatives?
Commonly used by clean brands are low-hazard preservatives: Plant-based glycerin. Phenoxyethanol. Ethylhexylglycerin.






