Table of Contents
ToggleAntioxidants are substances that stop oxidation, a chemical process that can result in the production of free radicals. Polymerization and other chain reactions may result from this.
However, it is inaccurate to refer to chemicals as “antioxidants.” Actually, it is a chemical attribute, specifically the capacity to serve as an electron donor. Some compounds that function as antioxidants in one circumstance might function as pro-oxidants—electron grabbers—in another. Antioxidants being interchangeable is another common misunderstanding. They’re not.
Each one has distinct biological and chemical characteristics. With each molecule (or family of compounds) having slightly distinct roles, they probably certainly arose as a component of complex networks. This implies that no one substance can carry out the tasks of the entire group.

What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants are a chemical that shields cells against free radical damage (unstable molecules made by the process of oxidation during normal metabolism). In cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other aging-related disorders, free radicals may be involved.
History of Antioxidants:
Since the beginning of time, fats and oils have played a crucial role in human nutrition because of their nutritive value, calorie content, and numerous other advantageous aspects. They are now even thought of as genuine luxuries that only a select few can afford.
People have always had to find ways to keep fats and oils from decomposition and degradation ever since mankind started to gather and store their food, and later market it. People have come up with various methods like refrigeration or the use of chemicals to lengthen shelf life. Some of them have really served as food antioxidants.
Health benefits of Antioxidants
Free radicals are unstable molecules that the body produces as a response to environmental and other pressures. Antioxidants are substances that can stop or slow cell damage caused by these unstable molecules.
Some people refer to them as “free-radical scavengers.” Some antioxidants, referred to as endogenous antioxidants, are also produced by the body. Exogenous antioxidants are those that originate from outside the body.
Free radicals are waste products that cells make as they digest food and respond to their surroundings. Oxidative stress can occur if the body is unable to effectively eliminate and process free radicals. Cells and physiological functions may be harmed by this. The term “reactive oxygen species” also refers to free radicals (ROS).
1. Fight Free radical
Antioxidants aid in preventing free radical damage to our cells. What exactly are free radicals then? They are very reactive, insecure molecules that are attempting to stabilize. To keep themselves steady, they essentially steal an electron that they do not have. They attack a nearby molecule, such as a lipid or protein, and take an electron from it.
Now that it has been “robbed,” the molecule transforms into a free radical and assaults a nearby molecule, setting off a chain reaction. Our DNA and cells are harmed by all of this stealing. With enough harm, we develop early aging and illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
2. Reduce oxidative stress
When we are out of equilibrium, we experience oxidative stress, which harms both our body and brain. Atherosclerosis, cancer, diabetes, age-related macular degeneration, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, autoimmune illnesses (including systemic lupus), mental stress, depression, and memory loss are all linked to it.
Additionally, oxidative stress is exacerbated by chronic illness, mood problems, and excessive stress.
Inflammation can be decreased by antioxidants. For instance, vitamin C has been demonstrated to lower c-reactive protein (CRP). Increased cardiovascular disease is linked to elevated CRP. In one study, vitamin C was observed to lower CRP by 25% in people with increased CRP. This is incredible and equivalent to CRP decreases brought on by statin use.
3. Healthy eyes
Antioxidants have been found in studies to protect against age-related eye disease (AMD). The macula of the eye is harmed by AMD, which develops as we age. For persons 50 years of age and older, AMD is the main cause of vision loss.
Although it doesn’t result in total blindness, it impairs our central vision. For activities like reading, driving, face recognition, and close-up tasks like cooking, we require our central vision.
Which food is rich in antioxidants?
In addition to artichokes, cabbage, asparagus, avocados, beets, radish, lettuce, sweet potatoes, squash, pumpkin, collard greens, and kale, foods strong in antioxidants include broccoli, spinach, carrots, potatoes, and spinach.

How does tea act as an antioxidant?
The polyphenols in tea, such as catechins, theaflavins, and thearubigins, are particularly abundant and are thought to contribute to the health advantages of tea. By removing reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and chelating redox-active transition metal ions, tea polyphenols function as antioxidants in vitro.
Does milk destroy the antioxidants present in tea?
Although in various amounts, adding milk does reduce the antioxidant content of tea. Tea polyphenols may bind to milk proteins, reducing the antioxidant power of tea polyphenols. According to the type and quantity of milk used, one review of the research that examined the phenomena indicated an antioxidant loss of up to 18%.
How does an antioxidant work?
Free radicals are countered by antioxidants by sacrificing some of their own electrons. They serve as a natural “off” switch for the free radicals by making this sacrifice. This aids in stopping a chain reaction that may have an impact on other cellular molecules and other cells across the body.
Determination of antioxidant activity by DPPH assay
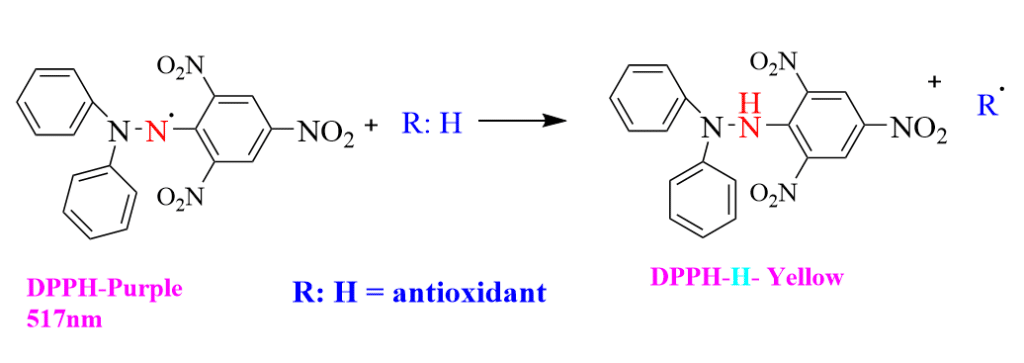
Blois (1958) devised this method with the goal of determining the antioxidant activity similarly by utilizing a stable free radical called DPPH (C18H12N5O6, M = 394.33). The assay is based on the evaluation of the antioxidants’ ability to scavenge it.
A recognized method for evaluating the antioxidant activity of plant extracts is DPPH free radical scavenging. In the DPPH assay, the addition of the extract reduces the violet-colored DPPH solution to diphenylpicryl hydrazine, a yellow-colored result, in a concentration-dependent way.
The 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl molecule, also known as DPPH:1, is thought to be a very stable free radical. Most other free radicals lack this special property, but the delocalization of spare electrons over the molecule prevents dimerization. A deep violet hue is also produced by delocalization, which is indicated by an ethanol solution absorption band with a center wavelength of 517 nm.
When antioxidants react with DPPH, a stable free radical, it pairs off in the presence of a hydrogen donor (such as an antioxidant that scavenges free radicals) and is reduced to the DPPHH. As a result, the absorbance from the DPPH radical to the DPPH-H form decreases, which leads to decolorization (yellow color) depending on how many electrons are captured. The ability to reduce is more effective the more coloration there is. The antioxidant activity can be expressed in the form of an IC50 value. The greater the value of IC50 value, the lower will be the antioxidant activity.
FAQs/MCQs
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants are a chemical that shields cells against free radical damage (unstable molecules made by the process of oxidation during normal metabolism).
Does milk decrease the antioxidant activity of tea?
Although in variable degrees, adding milk does reduce the antioxidant content of tea. Tea polyphenols may bind to milk proteins, reducing the antioxidant power of tea polyphenols. According to the type and quantity of milk used, one review of the research that examined the phenomena indicated an antioxidant loss of up to 18%.
What are free radicals?
A specific class of unstable molecules is produced throughout typical cell metabolism (chemical changes that take place in a cell).
What foods are highest in antioxidants?
Blueberry – the king of antioxidant foods.
What are the three benefits of antioxidants?
Numerous specialists claim they shield us from early aging, heart disease, and cancer, as well as perhaps despair and anxiety.
Which method is used for determining antioxidant activity?
DPPH assay is used to determine antioxidant activity.
In which color did DPPH is changed after being treated with antioxidants?
The purple color of DPPH is converted into yellow or colorless.






