Table of Contents
ToggleDetermination of Total flavonoid content is done by the Aluminum Chloride colorimetric method. 4 milligrams of quercetin is dissolve in 1 mL of methanol to create a stock solution (4 mg/mL). To create different concentrations of 0.25 mg/mL, 0.5 mg/mL, 0.75 mg/mL, and 1 mg/mL solutions, this standard solution is serially diluted. Each dosage of quercetin is apply in 1 mL increments to the test tube containing 4 mL of distilled water.
Determination of Total Flavonoid Content
Determination of total flavonoid content is determined from the calibration curve’s regression equation. The relationship between antioxidant activity and total phenolic and flavonoid content. Due to their capacity to donate hydrogen atoms to free radicals, phenolic and flavonoid molecules are crucial antioxidant components that deactivate free radicals.
Flavonoid
Flavonoids are the class of compounds containing variable phenolic structure. Flavonoids are widely distributed in fruits, vegetables, grains, roots, stems, flowers, tea, wine, etc. They are well known for different types of therapeutic properties. Flavonoids are responsible for the production of yellow and other pigments in plants and vegetables. Flavones, flavonols, flavanones, flavan-3-ols/catechins, anthocyanidins, and chalcones are some of these subclasses.
Sources of Flavonoids
The main dietary sources of flavonoids in eastern and western civilizations, respectively, are tea and wine. Other foods that are regarded as major sources of dietary flavonoids include citrus fruits, onions, apples, berries, cherries, soybeans, and leafy greens. The main sources of flavones are celery, parsley, red peppers, chamomile, mint, and ginkgo biloba. This group of flavonoids includes luteolin, apigenin, and tangeritin.
Uses of Flavonoid
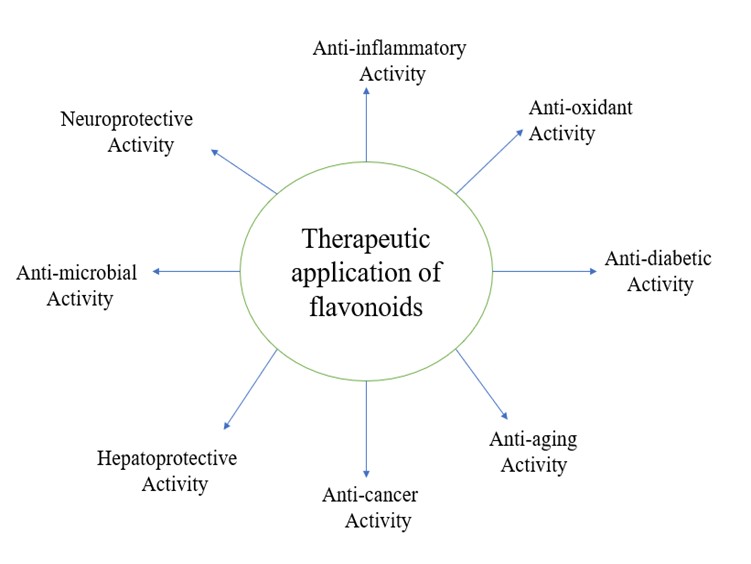
Flavonoids have a variety of health advantages, such as antiviral, anticancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, they have cardio-protective and neuroprotective properties. The kind of flavonoid, its (potential) method of action, and its bioavailability all affect these biological functions.
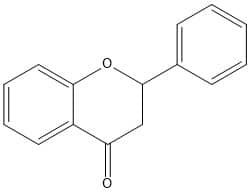
Principle of Total Flavonoid Content
The total flavonoid content is determined by the Aluminum Chloride colorimetric method. The aluminum chloride colorimetric method’s main principle is that aluminum chloride forms a stable complex with C-4 keto group and either with the C-3 or C-5 hydroxyl group of flavonoids. The AlCl3 also forms labile complex with ortho-dihydroxyl groups present in A or B ring of flavonoids. The complex imparts yellow color and is detected by the absorbance at about 510 nm.
Chemical and Reagent required for TFC
For the determination of TFC, the following reagents are required:
- Quercetin (standard),
- Anhydrous AlCl3,
- Potassium acetate,
- Methanol/ethanol, and
- distilled water
Procedure to determine TFC
- The total flavonoid content of plant extract is determined aluminum chloride colorimetry method. To determine TFC, 20 µL plant extract was loaded in the 96 well plates along with 110 µL distilled water and 60 µL ethanol.
- The initial reading is taken at 415 nm. After that, 5 µL 10 % AlCl3 solution and 5 µL (1 M) CH3COOK/CH3COONa solution was added and incubated at room temperature.
- After 30 minutes the absorbance was taken at 415 nm.
- In order to make the calibration curve different concentration of quercetin was used instead of plant extract.
The total flavonoid content of the plant extract can be evaluated by using the formula:
C = cV/m
Where, C = Total flavonoid content of plant extract in mg QE/g (milligrams of Quercetin equivalent per gram of dry weight)
c = Concentration of quercetin in mg/mL obtained from calibration curve.
V = Volume of extract in mL.
m = Mass of plant extract in gm.
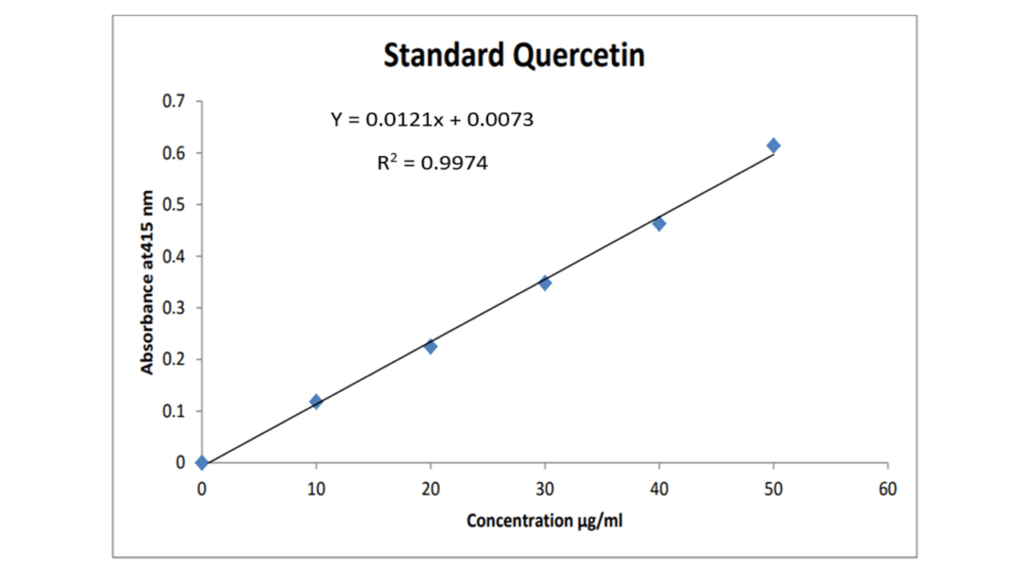
The regression equation is given as:
Y = 0.0121x + 0.0073
Y = Absorbance of the extract
m = Slope from the calibration curve
x = Concentration of the extract
c = intercept
Therapeutic application of flavonoid
The main therapeutic applications of flavonoids are as follows: