Table of Contents
ToggleTotal phenolic content can be determined by the Folin Ciocalteu method, also known as the FC reagent method. This method uses a microplate reader to determine the absorbance of phenolic compounds present in natural products like plant extracts. Since high phenolic content has been linked with high antioxidant capacity, this assay is significant in determining total antioxidant capacity.
Total Phenolic content
Different phytochemicals, such as phenols, flavonoids, alkaloids, glycosides, lignins, and tannins, are naturally found in plants and plant-based products. The most prevalent phytoconstituents in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and aromatic and medicinal plants that have antioxidant properties are phenols and flavonoids. It is generally based on the principle of absorbance.
Phenolic compound
Phenolic compounds are secondary metabolites produced from the metabolism of phenylpropanoid in pentose phosphate and plant shikimic acid. They can be anything from simple phenolic molecules to complex polymerized substances, but they always contain benzene rings with one or more hydroxyl substituents. Examples caffeic, chlorogenic, and gallic acid.
Principle of Total phenolic content
In alkaline mediums, the F-C reagent is reduced with phenolic compounds to perform the F-C assay. The formation of a blue complex with a peak absorbance at 765 nm occurs concurrently with the process. The TPC, described as the Gallic acid equivalent, is directly proportional to the absorbance. Several factors need to be studied to provide accurate results, including the maximum absorption wavelength (max), the reaction time for color development, and the volume ratio of alkali and F-C reagent.


Chemical required for TPC determination
For the determination of TPC, we generally use gallic acid, ethanol, gallic acid of various concentrations, sodium carbonate, and FCR.
Protocol for determining TPC
Using the Folin Ciocalteau reagent, the total phenolic contents of the aqueous and ethanolic extracts of were determined. By combining 1 ml aliquots of 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, and 450 g/ml Gallic acid solutions with 5.0 ml of tenfold-diluted Folin Ciocalteu reagent and 4.0 ml of sodium carbonate solution (75 g/l), the calibration curve was formed. At 765 nm, the absorbance was measured after 30 minutes. In order to make the calibration curve, 1 ml of each of the aqueous and ethanolic extracts (1 gm/100 ml) was combined separately with the same reagents. The absorbance was measured after one hour to ascertain the total phenolic content.
By using the formula, we can calculate the total phenolic contents of the extracts,
C=cV/m
where C is the total content of phenolic compound in mg/g in gallic acid equivalent(GAE)
c= concentration of gallic acid established from calibration curve in mg/mL
V= volume of extract in mL
m= weight of extract
The regression equation is given as
y = 0.0012x + 0.0659, where R2 must be less than 1
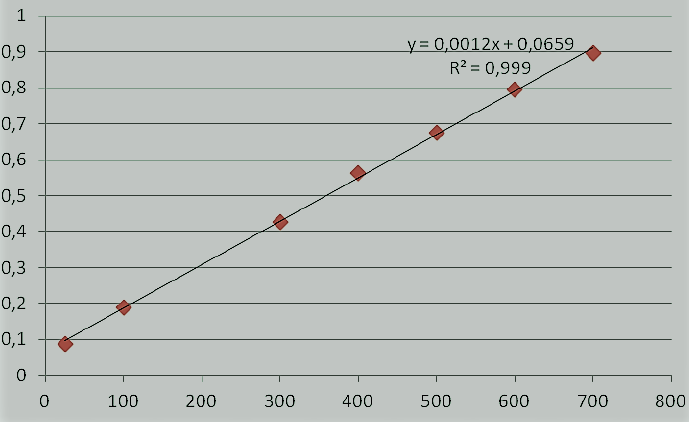
y= absorbance of the extract
m= slope from the calibration curve
x= concentration of extract
c= intercept
Role of Gallic acid
Gallic acid is used as a standard during the estimation of total phenolic content. Because it is one of the naturally occurring, stable phenols and is relatively inexpensive compared to other phenols, gallic acid was used as a standard solution.
Trihydroxybenzoic acid, or gallic acid, is a widely distributed plant metabolite in the plant kingdom. It can shield biological cells, tissues, and organs from oxidative stress-related damage because of its potent antioxidant and free radical scavenging properties.
Role of sodium carbonate in FC reagent
Sodium carbonate is essential to the Folin ciocalteu method because its presence there makes the environment more alkaline and allows for the production of a high yield of phenolate ions.
Use of estimating TPC
The percentage inhibitions of DPPH radicals against the samples are computed using these values. The percentage inhibitions at various concentrations were used to calculate the IC50 values for various extracts. The extract with a high phenolic content displayed strong anti-radical action. The amount of phenolic content can be easily determined.
MCQs/FAQs
Which assay is used for the determination of total phenolic content?
FC reagent method is used for this assay.
What are phytochemicals?
Phytochemicals are chemical substances that plants make, usually to aid in their resistance to diseases by fungi, bacteria, and plant viruses. They are also consumed by insects and other animals.