Table of Contents
ToggleCannabinoids are the generally found in Cannabis sativa. The structural groups of substances known as cannabinoids are mostly present in the cannabis plant, as well as in most mammalian beings (though insects do not have these receptors) and synthetic drugs. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the main psychoactive ingredient of cannabis, is the most well-known phytocannabinoid.

What is cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are highly present in cannabis plants and are generally found in leaf, flower, and bud of cannabis plants. Endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives, whereas phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds chemically linked to THC. In addition to eicosanoids connected to endocannabinoids, nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include aminoalkylindoles, 1,5-diarylpyrazoles, quinolines, and arylsulfonamides.
Examples of Cannabinoids
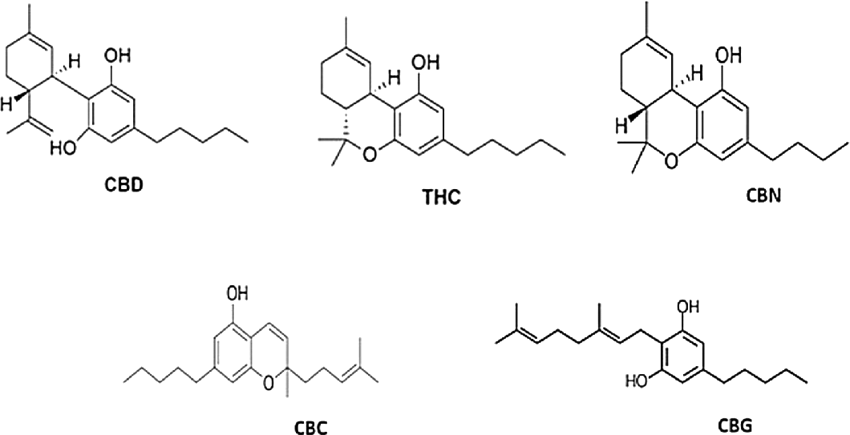
The various examples of cannabinoids are:
- Cannabinol
- Cannabichromene
- Tetrahydro cannabinol
- Cannabidivarin
- Cannabicyclol
- Cannabitriol
Types of cannabinoids
They are generally classified into three categories:
- Phytocannabinoids
- Endocannabinoids
- Synthetic cannabinoids
- Phytocannabinoids
On the planet, Phyto cannabinoids are also known as plant cannabinoids are most abundant and diversified form in cannabis. The cannabis plant contains about 150 distinct cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are not, however directly produced by cannabis plants. Instead it, yield cannabinoids acids such as THCA, and CBDA, which need to be activated in order to transform into well known and love cannabinoids., THC, and CBD for consumer use. Heating these acids over time activates it, by the process of decarboxylation. Then it convert these acids to THC, and CBD etc.
2. Endocannabinoid
The body’s endocannabinoid system includes endocannabinoids. These substances sometimes referred to as endogenous cannabinoids are synthesized by various bodily tissues and organs and share structural similarities with the cannabinoids present in cannabis.
3. Synthetic cannabinoids
These substances are created chemically neither plants nor human naturally contain them. Almost all of the more than 200 synthetic cannabinoids on the markets are made to have strong effects on the body cannabis receptor.

Role of cannabinoids
Additionally, cannabinoids have very important role in protecting the health of the cannabis plants. The sticky resinous trichomes of cannabis, which are primarly seen on female buds, are where cannabinoids gather. Recent studies suggest that can function as a sunscreen by absorbing UV-B rays that could hinder plant ability to thrive. Futhermore, research has demonstrated that subjecting cannabis flower to elevated UV-B radiation increases their production of cannabinoids.
According to research, the cannabis plant generally over 300 non-cannabinoid compound in addition to 80-100 cannabinoids. CBD and THC are the main types of cannabinoids.
Benefits of using cannabinoids
It is used medicinally to alleviate spasticity, nausea after chemotherapy, and perhaps neuropathic pain.

Harmful effects of cannabinoids
The effects of cannabinoids are:
- Freely of well being
- increased appetite
- dry mouth
- excitement
- euphoria
Cannabinoids Receptors
Prior to the 1980s, there was hypothesis that cannabinoids, rather than engaging with particular membrane-bound receptors, produced their physiological and behavioral effects through nonspecific contact with cell membranes. This controversy was settled in part by the 1980s discovery of the first cannabinoid receptors. In mammals, these receptors are widespread. There is growing evidence that there are additional cannabinoid receptors beyond the two recognized ones, CB1 and CB2. More cannabinoid receptors than any other kind of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) are found in the human brain.
- CB1
The brain’s basal ganglia and limbic system, which includes the striatum and hippocampal regions, are the main locations of CB1 receptors. Additionally, they are present in the female and male reproductive systems as well as the cerebellum. The medulla oblongata, the area of the brain stem in charge of respiratory and circulatory processes, lacks CB1 receptors. The anterior eye and retina of humans also contain CB1.
2. CB2
The immune system and immune-derived cells exhibit different expression patterns of CB2 receptors. Despite being restricted to the peripheral nervous system, a research suggests that a subset of microglia in the human cerebellum expresses CB2. Based on findings in vitro and in animal models, CB2 receptors seem to be involved in the immunomodulatory and maybe other therapeutic actions of cannabis.
FAQs/MCQs
What are the components of cannabis plants?
The components of cannabis plants are cannabinoids, CBD, THC, etc.
What is cannabinoids?
cannabinoids are the main components which are generally found in cannabis sativa.
What is the full form of CBD and THC?
CBD stands for cannabinol, and THC stands for tetrahydrocannabinol.
What is entourage effect?
The enhanced potency of whole plant cannabis medicine above CBD or THC alone is known as entourage effect. The plants different chemicals work together to produces effect that are stronger than they would be apart.
Phytochemical found in cannabis?
Terpenes, Flavanoids and cannabinoids are just a few more than 500 naturally occurring substances found in cannabis plants.
What is vaping?
Vaping is the practice of progressively heating cannabis flower flower or oil extracts to temperature that is low enough to prevent quick combustion.
What is CBD?
One kind of cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant is CBD. Unlike THC, CBD didnot produce the same potent (high).
How many people use cannabis?
In 2021, 18.7% of those who were 12 years of age or older—or around 52.5 million people—reported having used cannabis in the previous year.