Table of Contents
ToggleThe lattice energy (U) of a crystal is the energy that evolved when one gram of the crystal is formed from gaseous ions. For sodium chloride, the lattice energy, U, is equal to the enthalpy change for the reaction.
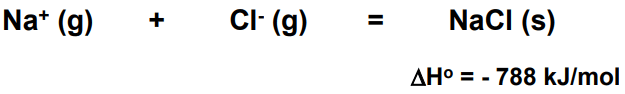
Schematic representation of lattice energy at inter-ionic distance ro
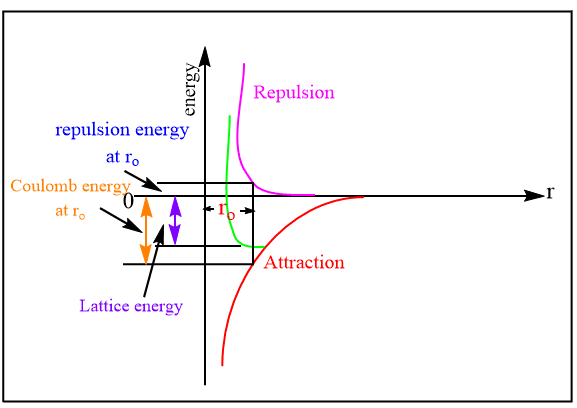
Lattice energy is defined as the energy released in the process when the constituent ions are placed in their respective positions in the crystal lattice or, the amount of energy required to separate the solid ionic crystal into its constituent ions.
Calculation of Lattice Energy
Lattice energies cannot be measured directly, but experimental values are obtained from thermodynamics data using the Born Haber cycle.

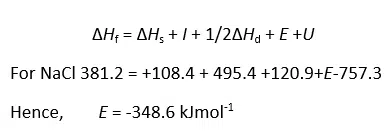
Theoretical evaluation of lattice energy
Theoretical values for lattice energy may be calculated. The ions are treated as point charges, and the electrostatic energy E between two ions of opposite charge is calculated.
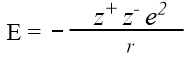
e is the charge on an electron
r is the interionic distance.
Attractive energy for a simple lattice of the crystal
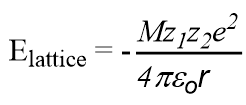
Repulsive force
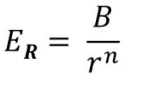
n = Born-exponent
Total energy = Attractive energy + Repulsive energy
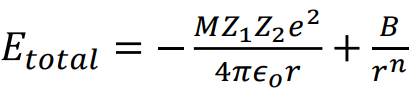
For one mole of the ionic crystal U = Etotal NA
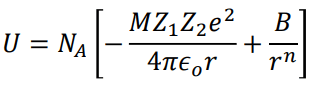
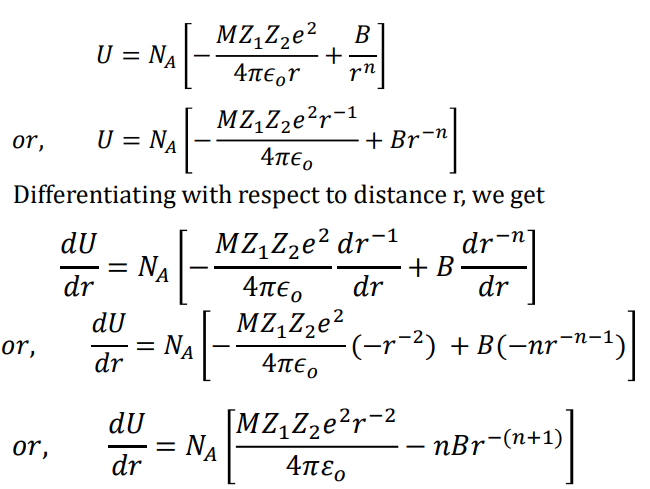
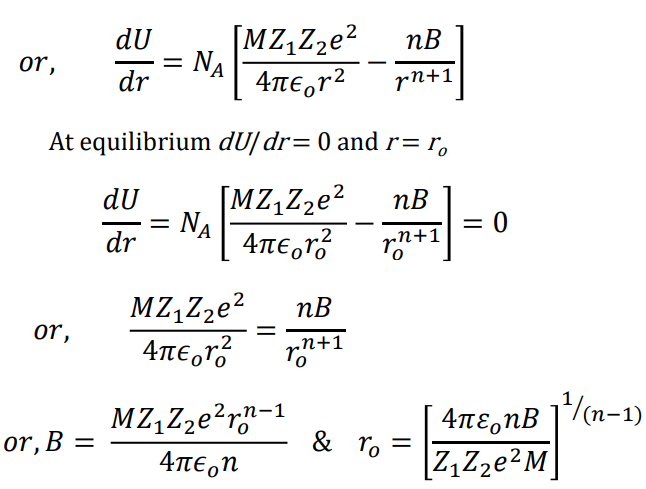
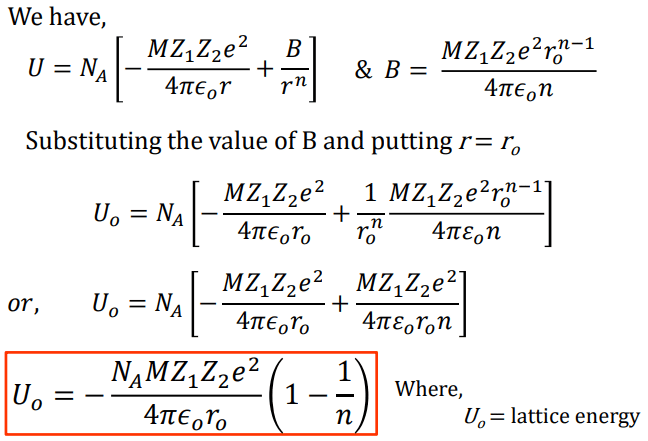
Where NA is the Avogadro constant, the number of molecules in a mole has the value 6.023×1023 mol-1; A is the Madelung constant, which depends on the geometry of the crystal.
The lattice energy of the ionic crystal is inversely proportional to the Inter-ionic distance and directly proportional to the product of charges of the ions, Madelung constant, and Born exponent.
Madelung Constant (A)
The value of the Madelung constant has been calculated for all common crystal structures by summing the contributions of all the ions in the crystal lattice.
Madelung constant value of some structure
| Types of structure | Madelung constant (A) |
| zinc blende | 1.63806 |
| wurtzite ZnS | 1.64132 |
| sodium chloride NaCl | 1.74756 |
| Caesium chloride CsCl | 1.76267 |
| rutile TiO2 | 2.408 |
| fluorite CaF2 | 2.51939 |
| Corundum Al2O3 | 4.17186 |
FAQs
What is lattice energy?
The lattice energy (U) of a crystal is the energy that evolved when one gram of the crystal is formed from gaseous ions.
How lattice energy can be calculated?
Lattice energy can be calculated by using the Born Haber cycle.
What is the lattice energy of CaCl2?
The lattice energy of CaCl2 is -2195.5 KJ mol-1.
What is the lattice energy of MgO?
The lattice energy of MgO is -3791 KJ mol-1.
What is the lattice energy of KCl?
The lattice energy of KCl is -715 kJ/mol