Table of Contents
ToggleClathrate compounds are those compounds that are formed by the physical trapping of inert gases such as Argon, Krypton, Xenon, etc. within the crystal lattice of different compounds.
What are clathrates?
Noble gases are trapped in the cavities of crystal lattices of certain organic and inorganic compounds and form solid compounds. These are called clathrate compounds. These are also known as inclusion compounds or cage compounds.
Certain organic molecules such as phenol, hydroquinone, and C6H4(OH)2 under pressure, enclose inert gases into the crystal lattices of organic molecules. These organic or inorganic compounds have a cavity of crystal lattices are called the “host’ and the atoms of noble gases which are trapped in the lattice are called “guest” molecules. Therefore, clathrates are also known as host-guest compounds.
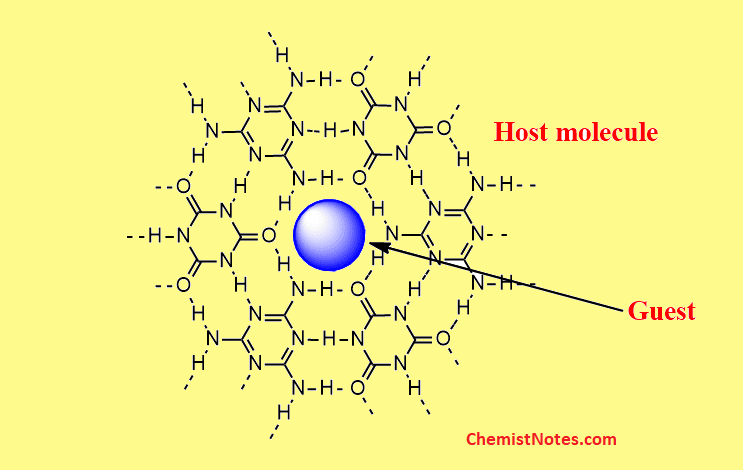
The guest molecules i.e atoms of inert gases are held by Van der Waal’s forces in the crystalline cage of the host molecules. Therefore, there is no involvement of chemical bonding between the host and guest. Due to very weak Van der Waal interaction, on heating the crystal or dissolving in suitable solvents, the guest molecules can escape from the cavity of the host.
Clathrates can be regarded as non-stoichiometric compounds because the host molecule’s all cavities are not filled by guest molecules.
Conditions for the Clathrates formation
The main criteria for the formation of inclusion compounds are given below:
- The host molecules must have cavities of appropriate size.
- The size of the guest molecules should be such that they must fit the cavities of the host.
Reasons for the stability of Clathrate compounds
The stability of Clathrates is mainly due to the following reasons:
- Guest molecules are held tightly within the cavities of host molecules.
- The guest molecules are at minimum potential energy within the cages.
The guest molecules only leave the cavities of host molecules only when the guest molecules get energy enough to overcome the force holding host and guest. The force can be overcome by either applying heat or by dissolving in suitable solvents.
Types of clathrates
- Gas hydrates
- Quinol clathrates
- Phenol and β-hydroquinone clathrates
Gas hydrates or Clathrate hydrate
- In gas hydrates, water molecules act as host components. These can be prepared by solidifying the water in presence of Ar, Kr, and Xe.
- In gas hydrates, water molecules are linked together by hydrogens bonds, creating spherical voids which are filled by the gas atoms.
- Due to its small size and volatile nature, gas hydrates of He and Ne have not been prepared yet.
- The stability of such compounds depends on the atomic no. of the guest molecules. Generally, the higher the atomic number of guest molecules forms stable compounds.
Quinol clathrates
- These are prepared by dissolving noble gases in an aqueous saturated solution of quinol under a pressure followed by slow cooling.
- Quinol molecules forms cavities and these cavities are held together by H-bonds.
- When heated or dissolved in water, the noble gas atoms easily escape.
Phenol and β-hydroquinone clathrates
- These are prepared by dissolving inert gases in phenol or β-hydroquinone followed by slow crystallization.
- These are the most stable clathrates.
Uses of clathrates
- These can be used to separate Nobel gases. For example, Ne can be separated from Ar, Kr, and Xe. This is because Ne can not form clathrate with Quinol.
- Kr-85 clathrate is used as a safe and useful source of β-radiation.
- Xe-133 clathrate is the source of gamma radiation.
- Clathrate play important role in some physiological actions.
FAQs/MCQs:
What are clathrate compounds of noble gases?
Clathrate compounds are those compounds that are formed by the physical trapping of inert gases such as Argon, Krypton, Xenon, etc. within the crystal lattice of organic or inorganic compounds.
Why are clathrates compounds regarded as non-stoichiometric compounds?
Clathrates can be regarded as non-stoichiometric compounds because the host molecule’s all cavities are not filled by guest molecules.
What is a host-guest compound?
Host guest compounds are those compounds in which small guest molecules are trapped within the cavities of the host molecules.
Which noble gas does not form clathrate compound?
Helium does not form clathrate compounds.
Why do helium and neon do not form clathrate compound?
Helium and Neon are very small in size and they are highly volatile in nature, thus they do not form clathrate compounds.