Table of Contents
ToggleDetermination of the configuration of geometrical isomers is basically of two types. They are as follows
- Physical methods
- Chemical methods
Determination of configuration of geometrical isomers by physical methods has been already discussed in our previous article. Now let us discuss the chemical method to determine the configuration of geometrical isomers.
Determination of configuration of geometrical isomers by chemical methods:
The different three methods under chemical methods are discussed below. With the help of this method, we can easily determine the configuration of geometrical isomers.
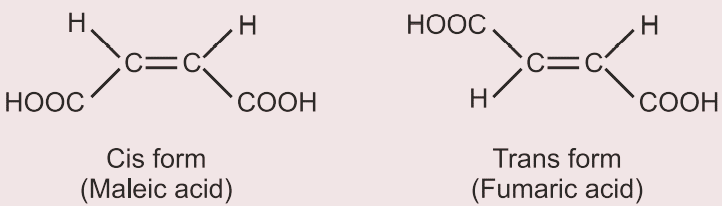
- Absolute method
- Correlative method
- Mechanistic method
Now let’s know these methods briefly:
Absolute method of determining the configuration of geometrical isomers:
In this method, trans isomers cannot be converted into cyclic lactones, anhydrides, or amides from functional groups in cis isomers that are situated cis to one another. Along with trans isomers cannot be produced in the same ways as cis isomers from small ring compounds.
For example, in the case of maleic acid, the maleic acid is converted into cyclic acid anhydride, but trans is difficult to convert into acid anhydride. Hence, it can be identified easily between cis and trans isomers by chemical method.
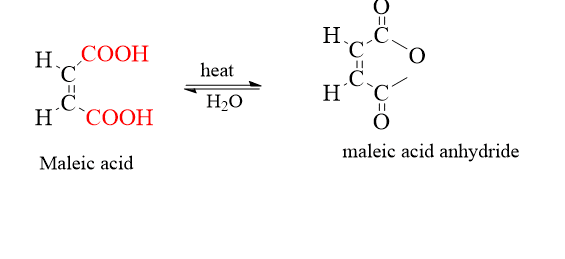
Whereas trans isomers don’t convert into acid anhydrides. Another example is salicylaldehyde which undergoes a perkin reaction and forms ortho-hydroxy cinnamic acid which is a stable acid. There are two ortho hydroxycinnamic acids. The cis isomer is coumarinic acid and the trans isomer is coumaric acid. If it is cis, it will give the lactone (coumarin).
however, in drastic conditions, trans isomers get changed into maleic acid and converted into acid anhydride.
Another example is cis (citraconic acid) and trans (mesaconic acid)
Correlation method of determining the configuration of geometrical isomers:
By converting into the compound with known configuration: Geometric isomers of the pair in some situations can be converted into compounds with known configurations. The configuration of the end product will match the configuration of the starting component. if we assume that there is no isomerization throughout the reaction, the conversion of one form of trichlorocrotonic acid into fumaric acid on hydrolysis is a well-known example, proving that the trichlorocrotonic acid mentioned above must be trans isomers.
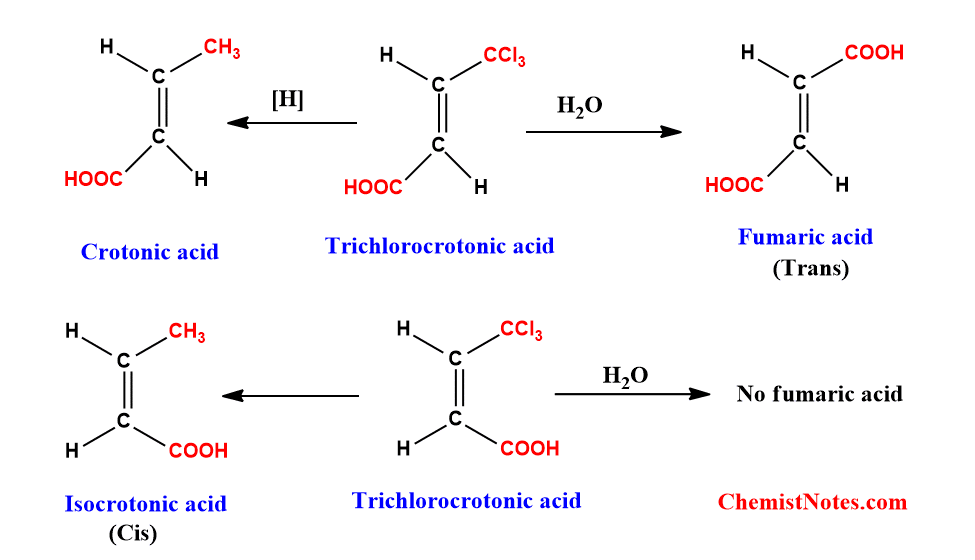
Mechanistic method of determining the configuration of geometrical isomers:
We can ascertain the configuration of cis and trans isomers with the aid of a different technique known as the mechanistic method. It generally includes the stereoselective addition and elimination reactions as its two methods.
Stereoselective reaction:
Generally, the stereotype reaction is of two types, they are stereoselective and stereospecific reaction in the stereoselective type of reaction, one product is predominantly formed than the other. For example, in the conversion of alkynes to alkenes, in which whenever we use Lindlar catalyst that is pd / BaSO4 in presence of H2 then the product will be cis predominantly but whenever we used Na/ liq NH3, the product is obviously trans so by using a selective type of reagent we can covert into cis or trans predominantly.
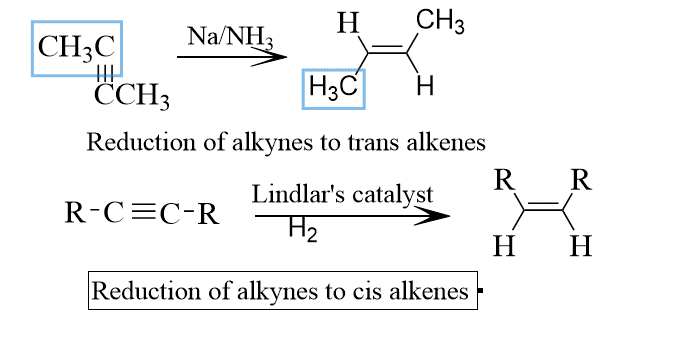
Such reactions which yield predominantly one stereoisomer of several possible stereoisomers are called stereoselective reactions and are encountered in addition to the reaction of alkynes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes.
Stereospecific reaction:
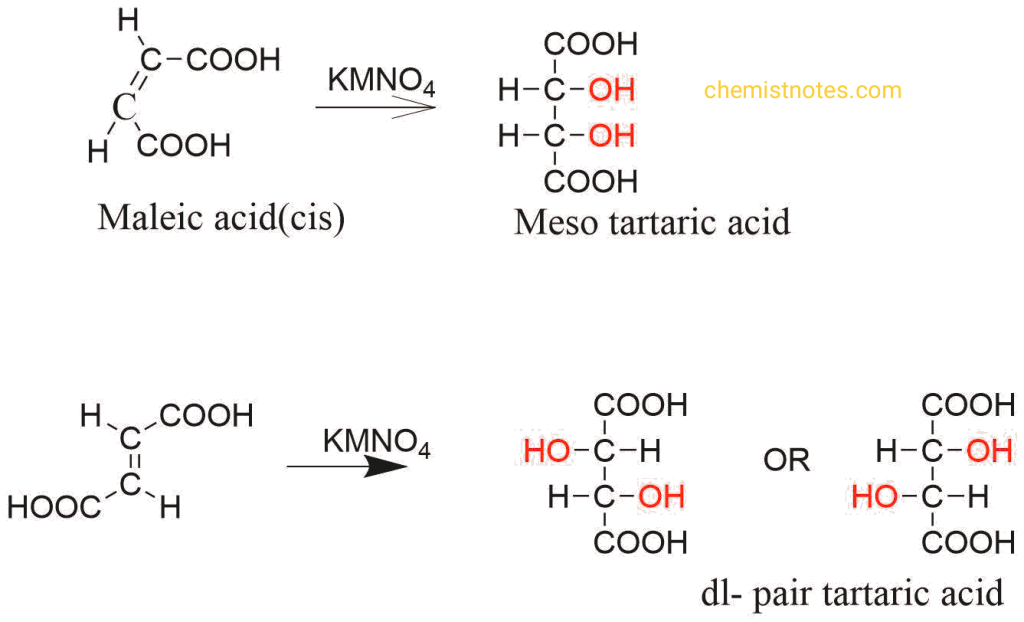
Those are the type of reactions in which the formation of a product is specific with respect to a stereoisomer. For example, the hydroxylation of maleic acid with potassium permanganate gives meso tartaric acid while the hydroxylation of fumaric acid gives dl tartaric acid. From this, we can easily differentiate between cis and trans isomers.
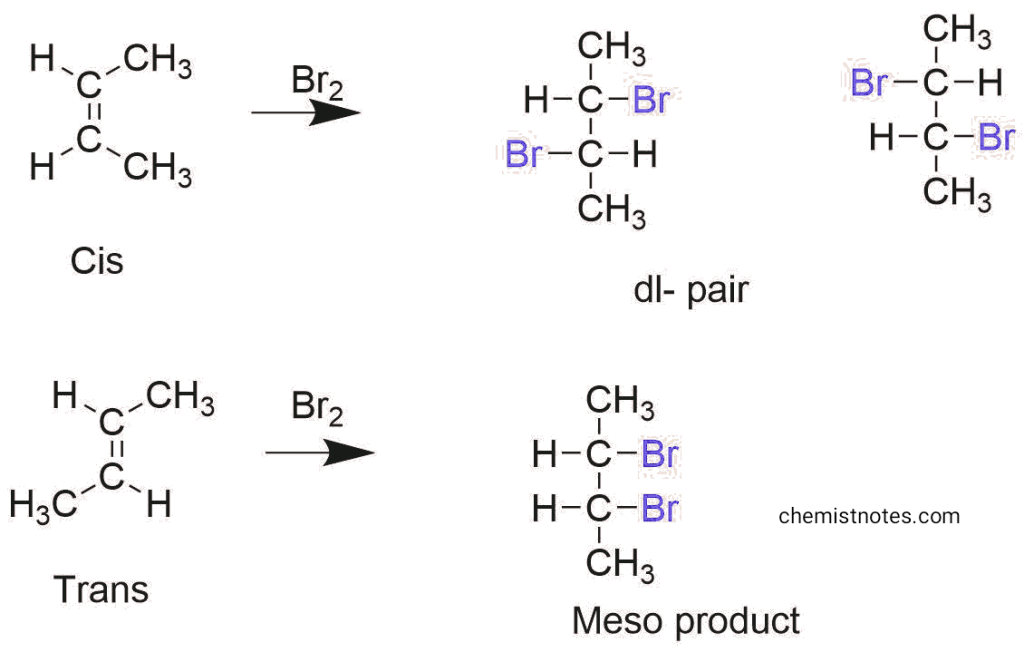
On the other hand, bromination of cis and trans 2- butene dl pair and meso product respectively.
From the stereoselective and stereospecific reactions, we can easily determine the configuration of cis and trans isomers.
Elimination reaction
Some elimination reactions are stereospecific, just like addition reactions. The production of acetylene or olefins is an important stereospecific elimination process.

By following three methods of chemical process, we can easily determine the configuration of the cis and trans isomers.
You can also study the determination of the configuration of cis and trans isomers by physical methods.
FAQs/MCQs
What are three chemical methods for determining the configuration of geometrical isomers?
The three methods for determining the configuration of geometrical isomers are
1. Absolute methods
2. Correlation methods
3. Mechanistic methods
How to determine the configuration of cis and trans isomers?
The alkene is the cis isomer if the two groups are on the same side of the double bond. The alkene is the trans isomer if the two groups are on different sides of the double bond.
What product will be expected from the hydroxylation of maleic acid and fumaric acid?
Hydroxylation of maleic acid gives meso tartaric acid while trans give dl pair tartaric acid.






