Table of Contents
ToggleStripping voltammetry is a very sensitive electrochemical method for determining trace elements. It applies two values of potential, oxidation occurs at one value of potential and reduction occurs at another value of potential. The details of this technique have been discussed below:
Principle of Stripping Voltammetry
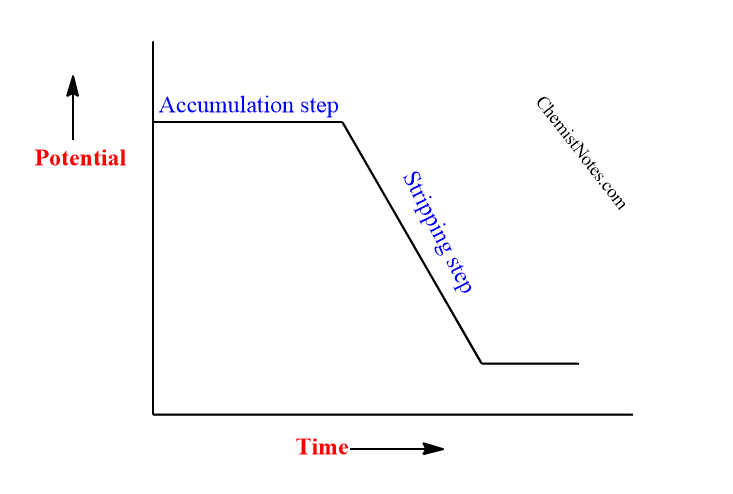
In stripping voltammetry, there are mainly two principle steps i.e it is a two-step technique viz: Pre-concentration step and Stripping step.
In the Pre-concentration step, the potential is set so that the electrodeposition of analytes occurs at suitable electrodes(cathode) such as H-DME(Hanging Dropping Mercury Electrode) or graphite. This process includes an electrolytic accumulation of a small portion of the metal ions in solution into the mercury electrode to preconcentrate the metals.
In the stripping step, the deposited analyte in the pre-concentrated step is now dissolved by applying the opposite potential to that of the pre-concentrated step. Therefore, this step is also known as the measurement step. Different types of stripping analysis can be applied depending upon the nature of the deposition and measurement step.
Types of Stripping Voltammetry
There are two types of stripping voltammetry.
- Anodic stripping voltammetry
- Cathodic stripping voltammetry
Anodic stripping voltammetry
The most commonly used stripping technique is the anodic stripping voltammetry technique. In this technique, the metals are preconcentrated by electrodeposition into a small-volume mercury electrode.The preconcentration is done by cathodic deposition at a controlled time and potential. The metal ions reach the mercury electrode by diffusion and convection, where they are reduced and concentrated as amalgams.
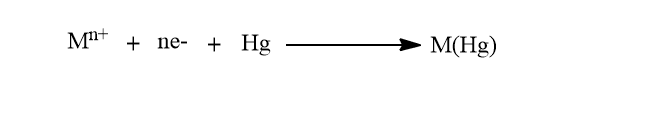
The convective transport is due to the stirring of the solution.The duration of the deposition step is choosed according to the concentration level of the metal ions in sample.
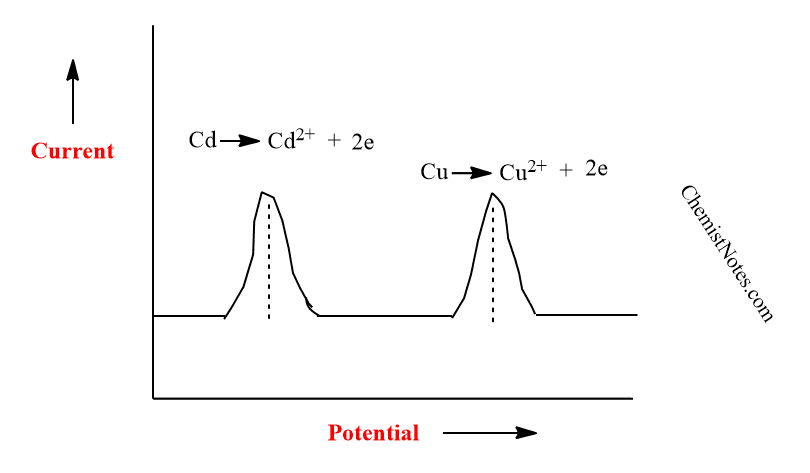
After the completion of deposition, the convection is eliminated and the potential is scanned anodically. Since the electrodepostion was done by cathodically, the dissolution of metal ion from the electrode is done by applying anodic potential. Thus, during the anodic scan, the amalgamated metals are reoxidised stripping out of the electrode and a current flows.
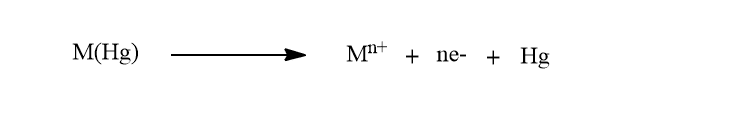
During the metal scan, the voltammetric peak represents the time-dependent concentration gradient of the metal in the mercury electrode. Peak potentials are used to determine the metals present in a sample.
Cathodic stripping voltammetry
Cathodic stripping voltammetry is just opposite of the anodic stripping voltammetry(ASV) therefore it can be regarded as the mirror image of ASV.
In this technique, electrodeposition is done by applying anodic potential. Then, the deposited analytes are stripped out of the electrode by applying cathodic scan of potential.
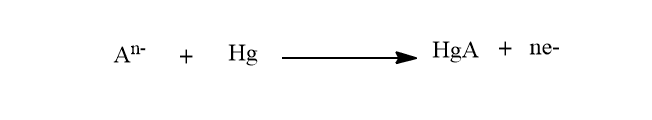
The resulting reduction peak current provides the desired quantitative information.. Cathodic stripping voltammetry is used to analyze a variety of chemical and inorganic compounds that can form insoluble salts with mercury.
Application of Stripping voltammetry
- This technique is widely used method for the detection of trace, heavy metal ions in very low concentration in various sources like drinking water, soils, food stuffs etc.
- It is mainly used in food industry for the determination of food contaminants such as toxic metal, pesticides, fertilizer etc.




2 Responses
can you please send me the pdf version of this to my mail
Please download our app from Playstore,in which you can download any notes for offline use.