Table of Contents
ToggleThe half-wave potential is a potential at the point of inflection of the current-voltage curve at which the current is one-half of the limiting current(diffusion current). The equation for the half wave potential is generally known as the polarographic equation or “The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation”.
Half-wave potential
The potential at which the faradaic current is one-half of the diffusion current is called half-wave potential. It is usually denoted by E(1/2). The E(1/2) value is the characteristic constant of an analyte therefore, it helps in both the identification and quantification of the analyte.
Half-wave potential derivation
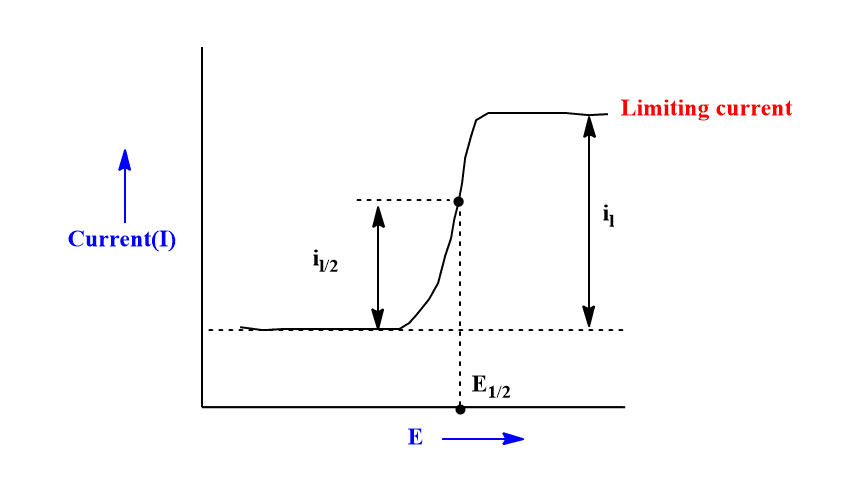
To derive the equation for half-wave potential, let us consider an oxidation-reduction system at a Dropping Mercury Electrode(DME).
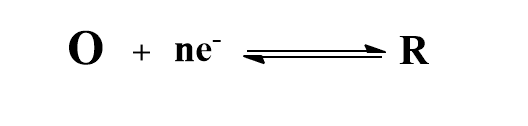
The Nernst equation for this reversible reaction can be written as:
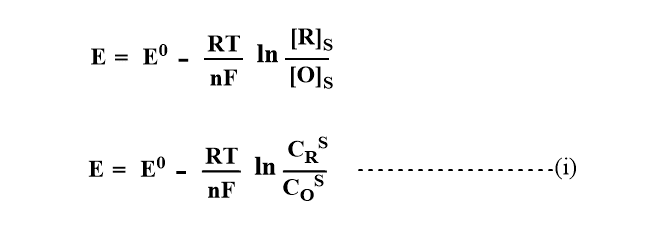
Where E0= Standard reduction potential
CRs=Concentration of reduction at the surface of the electrode.
Cos= Concentration of reductant at the surface of the electrode
E=Emf, R=constant, F= Faraday’s constant, and
n= number of electrons involved in the redox process.
When potential exceeds the decomposition potential, the current flows and it depends on the concentration gradient. According to the Ilkovic equation, the diffusion current is given by the following equation.
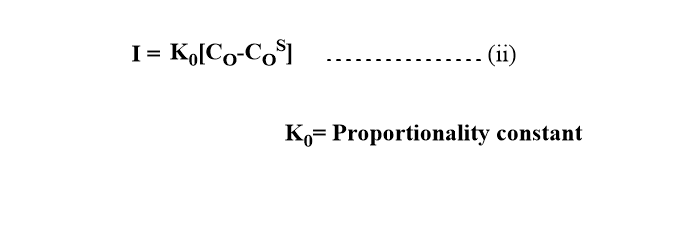
When the current attains the limiting value, the concentration of oxidant at the electrode-solution interface will be essentially zero. So, Cos =0
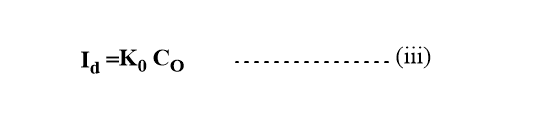
From equations (i) and (ii)
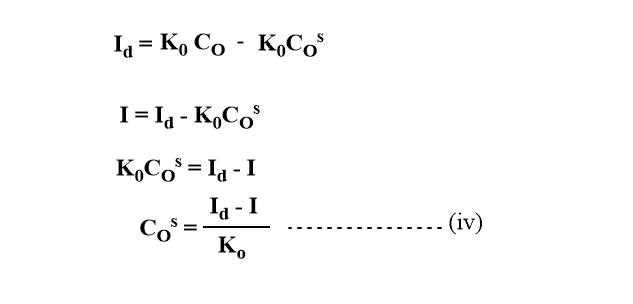
For reductant, if all the oxidant(O) is reduced to R and R forms amalgam with Hg, the current is proportional to the concentration of the reduced form of R.
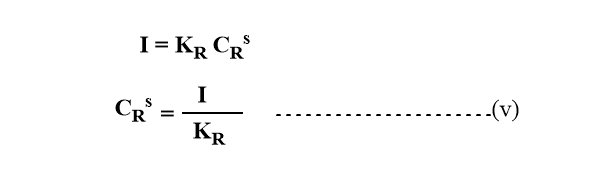
Substituting the value of COs and CRs in equation (i)
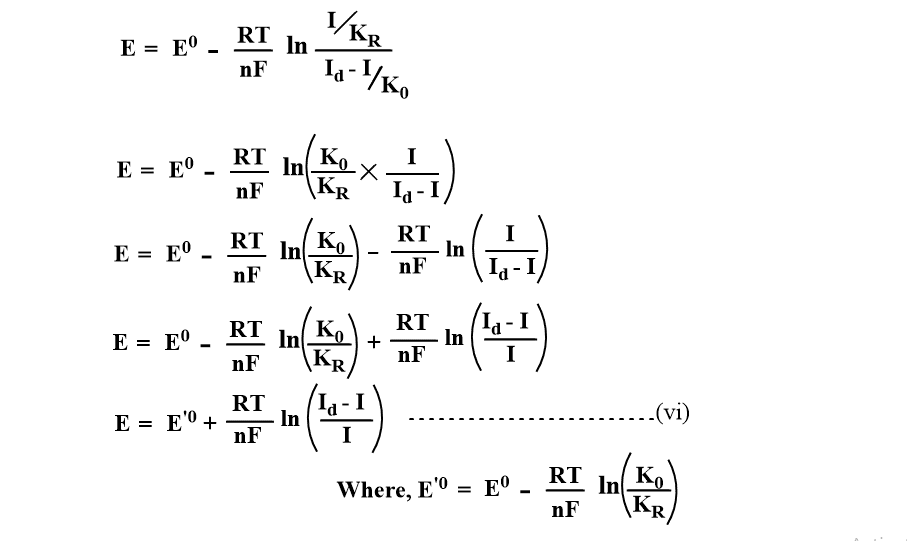
When I=Id/2 at half-wave potential, the above equation becomes,
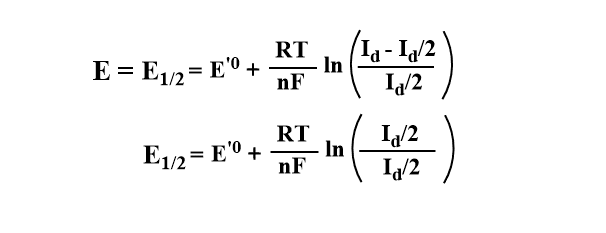
It shows that half-wave potential is concentration independent.
Since the 2nd term is close to zero,
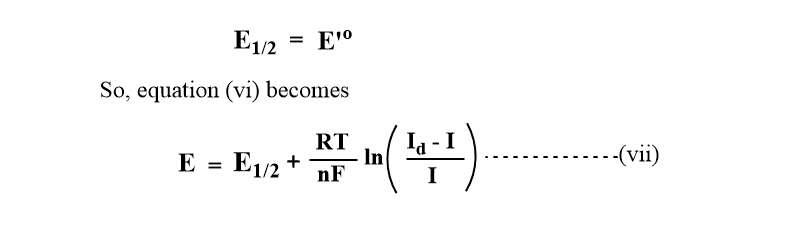
This is the equation of polarographic wave that relates Emf(E) as a function of limiting current(I) at any point of the polarographic wave.
Significance of half-wave potential
The half-wave potential value(E1/2) is not characteristic of the concentration of electroactive species. It is a constant value for every electroactive species. It means, every electroactive species has its own constant E1/2 value. It forms the basis for the qualitative identification of metal ions by using polarography. Therefore, one of the most useful applications of half-wave potential is the qualitative identification of certain electroactive species.
For examples:
- E1/2 value for Pb = -0.40 V
- E1/2 value for Cu= -0.02 V
- E1/2 value for Cd= -0.059 V