Table of Contents
ToggleWolf Kishner reduction, examples, mechanisms, and applications in organic chemistry have been discussed here:
Wolf Kishner reduction definition
The reaction that involves the reduction of hydrazone, semicarbazone or azines of aldehydes and ketones to hydrocarbons under basic conditions is known as wolf-kishner reduction. In such a reaction, Nitrogen (N2) is evolved out.
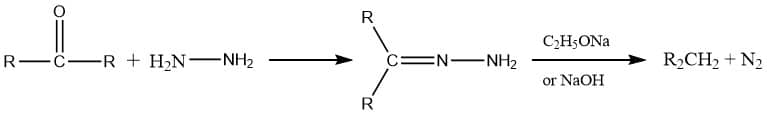
Some Wolf-Kishner reduction examples are shown below:
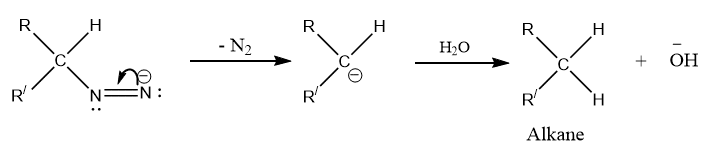
Wolf Kishner reduction Mechanism
The mechanism can be carried out into 3 prominent steps:
Step 1: Nucleophilic addition to C=O groups followed by removal of water forming hydrazone
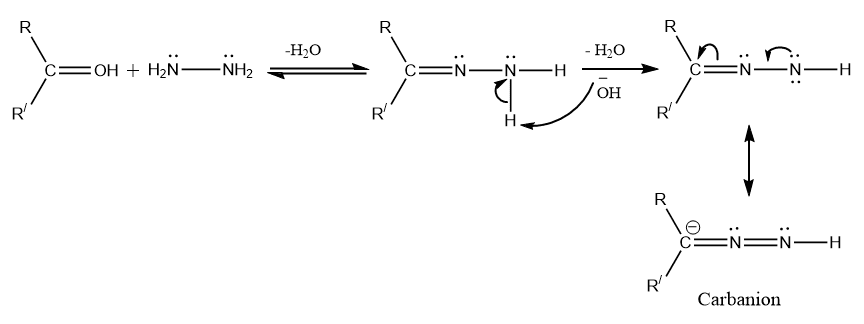
Step 2: Utilization of base to form carbanion that undergoes a sequence of reactions to elimination water and nitrogen
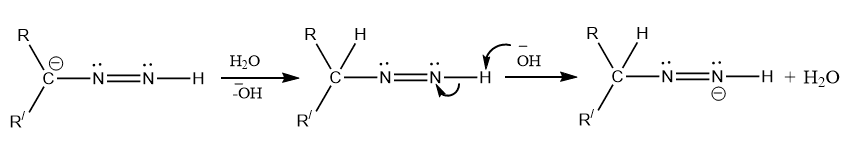
Step 3: Addition of hydrogen to carbanion to give alkene
Application of Wolf kishner reduction
Some of the applications of wolf kishner reduction are given below:
The Wolf-Kishner reduction has been widely utilized to convert carbonyl groups to methylene (CH2) groups.
- Synthesis of pyrroles
- Reduction of camphor to comphane
FAQs/MCQs
What is wolf-kishner reduction?
Reduction of hydrazone, semicarbazone or azine of aldehyde or ketone under basic conditions is called wolf-kishner reduction
Wolf kishner reduction reaction is used to
Wolf Kishner reduction reaction is used for the reduction of carbonyl group to a methylene group.
Can aldehyde and ketone be reduced by wolf kishner reaction?
Yes, aldehyde and ketone can be reduced by wolf kishner reduction by forming its hydrazone or semicarbazone, or azine under basic conditions.
References
- Morrison, R. T., & Boyd, R. N., Organic chemistry, Allyn and Bacon, Inc. 1987.
- March, J., Advanced Organic Chemistry, Wiley Eastern Limited, 1986.
- Skyes, P., A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Second edition, Orient Longman Ltd., 1988