Table of Contents
ToggleStork enamine reaction, examples, mechanism, and its application have been discussed here. Stork enamine reaction was first of all reported by Stork in 1954.
stork enamine reaction
Stork enamine reaction is the alkylation of cyclic ketone in presence of pyrrolidine via the formation of enamine as an intermediate. When cyclic ketone reacts with pyrrolidine gives enamine which reacts with alkyl halide followed by hydrolysis generates alkylated cyclic ketone.
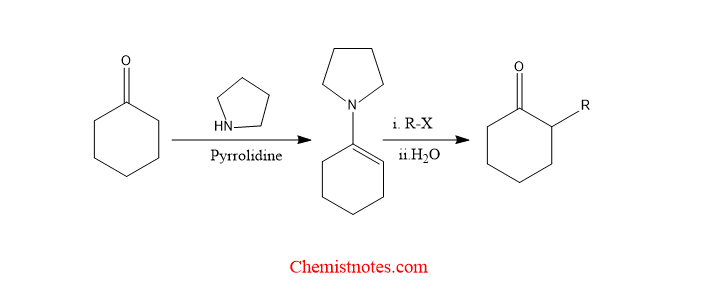
stork enamine reaction examples
Let’s see some examples of stork enamine reaction.
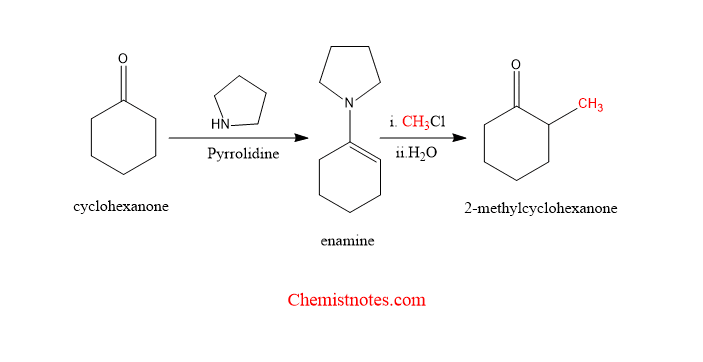
stork enamine reaction mechanism
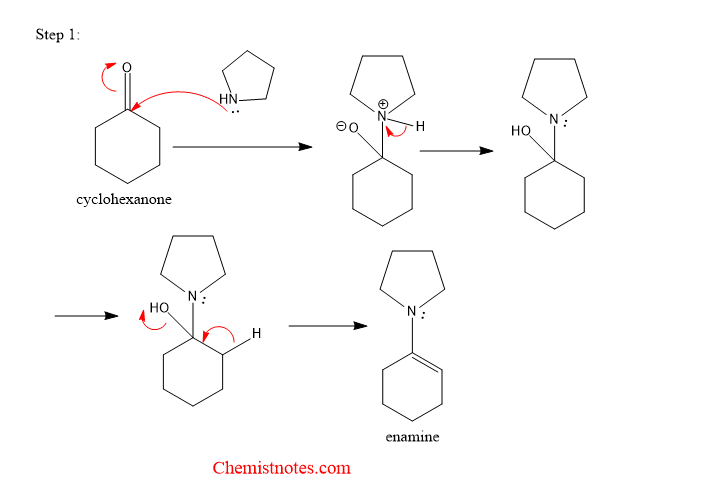
The mechanism of stork enamine reaction can be explained in the following steps.
Step 1: The lone pair of electrons of present on the N-atom of pyrrolidine attacks the carbonyl carbon of cyclic ketone, and forms enamine.
Step 2: The enamine attack the alkyl group of alkyl halide.
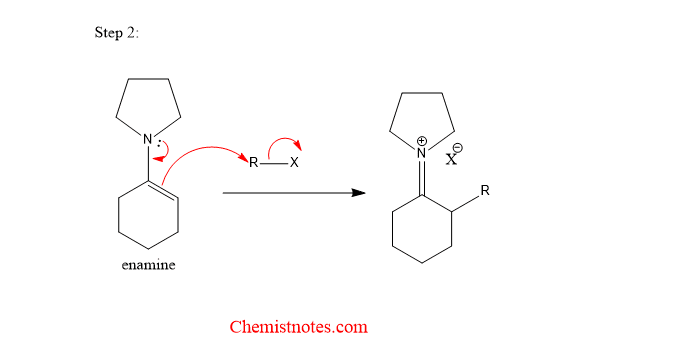
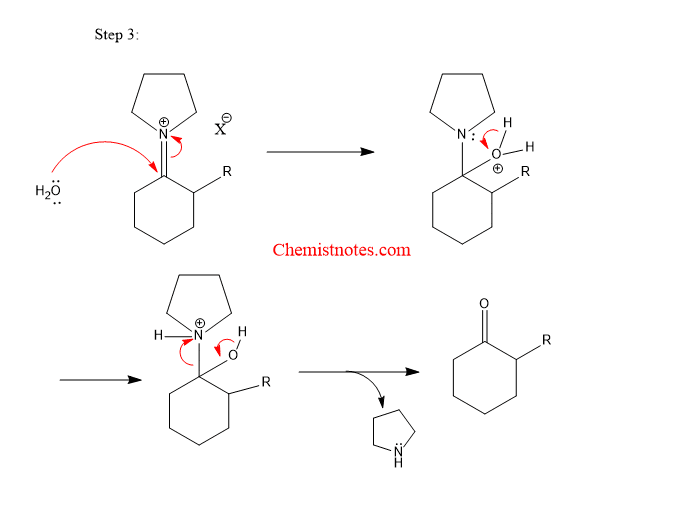
Step 3: Hydrolysis of alkylated product
applications of stork enamine reaction
This reaction can be used in the alkylation of cyclic ketones. Moreover, acylation of cyclic ketones can be done to form diketones using this reaction..
stork enamine reaction youtube
References
- Wang, Z., Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.,2010
- J.J. Li, Name Reactions, 4th ed.,© Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2009
- Morrison, R. T., & Boyd, R. N., Organic chemistry, Allyn and Bacon, Inc. 1987
Please mention any mistakes in the comment section below. If you want to learn more about Riemer Tiemann reaction, then click here.
FAQs/MCQs
what is a stork enamine reaction?
Stork enamine reaction is the alkylation of cyclic ketone in presence of pyrrolidine via the formation of enamine as an intermediate.
which side does R group attach in stork enamine reaction?
The alkyl group R gets attached to the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group.






