Table of Contents
ToggleSteam distillation is a technique used to separate volatile and non-volatile substances by distilling them together with water. The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure becomes equal to applied pressure or atmospheric pressure (P). In steam distillation, at every stage, the vapors of the organic compound are miscible with steam. For the liquid mixture to boil, the vapor pressure of organic compound P1, and the water vapor pressure of P2 must equal P.
P = P1+P2
and P1 = P – P2
Hence, when the organic compound is boiling its vapor pressure P1, is less than that of atmospheric pressure and the compound is boiling at a much lower temperature than its usual boiling point. For example, the normal boiling point of aniline is 184oC but in steam distillation, it boils at 98.4oC.
The relative amounts of an organic compound and water in the distillate in steam distillation are given by the following relation.
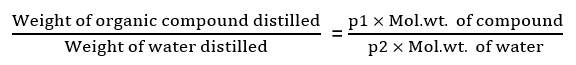
Not only liquids but certain stem-volatile water-insoluble organic solids can be easily purified by distillation in a current of steam. The method is applicable to substances insoluble in water having;
- Non-volatile impurities and,
- fairly high vapor pressure near the boiling point of water
Apparatus for steam distillation
The apparatus used for steam distillation is shown in the given figure:
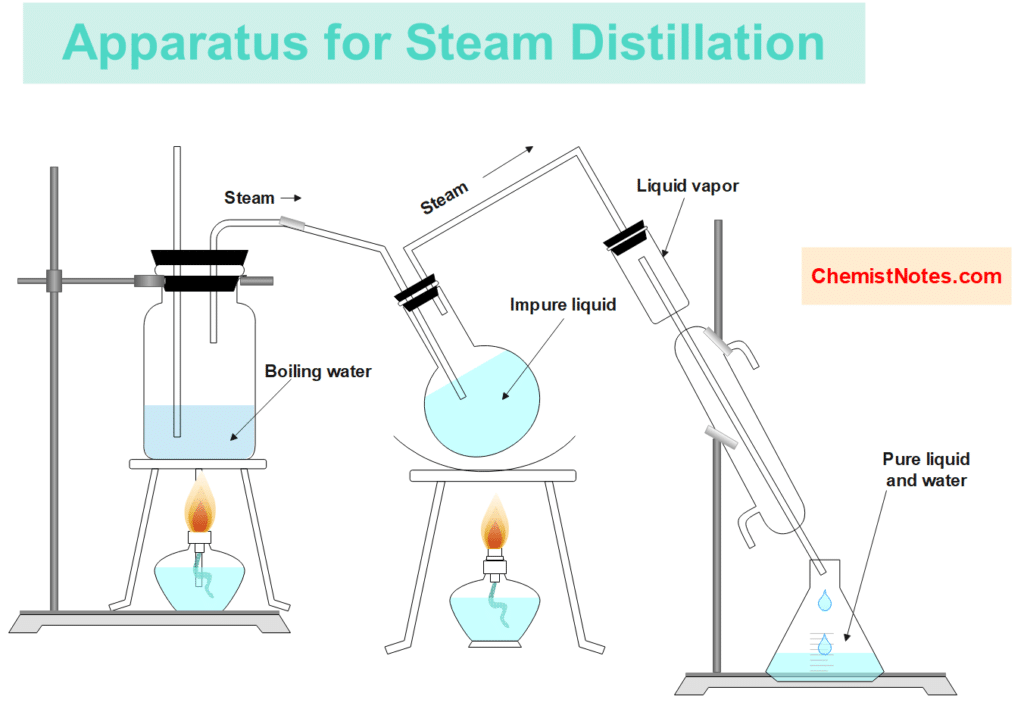
It consists of a steam generator (boiler), a distilling flask, a condenser, and a receiver. The distillation flask, containing the organic compound to be distilled, is clamped in a slanting position and fitted with a double-bored cork. From one of the bores a delivery tube, reaching the bottom of the flask, is connected to the steam generator. From another bore, a tube connects it to the condenser. The slanting position of the flask prevents the liquids from splashing into the condenser.
The stem passes from the generator to the distillation flask which is gently heated to avoid too much condensation of the water in it. Boiling of the liquids in the flask starts soon and the organic compound along with water collects in the receiver.
Examples of the steam distillation process
Extraction of clove oil from crushed cloves
In the round bottom flask take crushed cloves and add just sufficient water to immerse them. Start heating the steam generator. The steam from the generator heats up the clove-water mixture in the round bottom flask which is also heated gently and vapors of the clove oil along with water vapors start distilling over which are collected in the receiver.
Since clove oil is liquid and insoluble in water it forms a separation from water using a separating funnel, It is then dried over anhydrous calcium chloride in a vacuum desiccator.
Separation of o-nitrophenol from p-nitrophenol using steam distillation
Place the mixture of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol in the distillation flask. Start heating the steam generator to pass steam into the flask and heat the flask gently. Steam distillation separation of o-nitrophenol from p-nitrophenol is based on the fact that o- nitrophenol has intramolecular hydrogen bonding which prevents association while p-nitrophenol has intermolecular hydrogen bonding which leads to the association. As a result, o-nitrophenol is steam volatile while p-nitrophenol is not volatile.
As the steam heats the aqueous mixture of nitrophenols only the o-nitrophenol being steam volatile, distills over along with water vapors and is collected in the receiver.
o-nitrophenol being solid and insoluble in water can be easily separated from water by filtration. The p-nitrophenol left behind in the distillation flask is also separated from water by filtration. `
FAQs
What is steam distillation?
Steam distillation is a technique used to separate volatile and non-volatile substances by distilling them together with water.
How does steam distillation work?
In steam distillation, at every stage, the vapors of the organic compound are miscible with steam. For the liquid mixture to boil, the vapor pressure of organic compound P1, and the water vapor pressure of P2 must equal P. Boiling of the liquids in the flask starts soon and the organic compound along with water collects in the receiver.






