Table of Contents
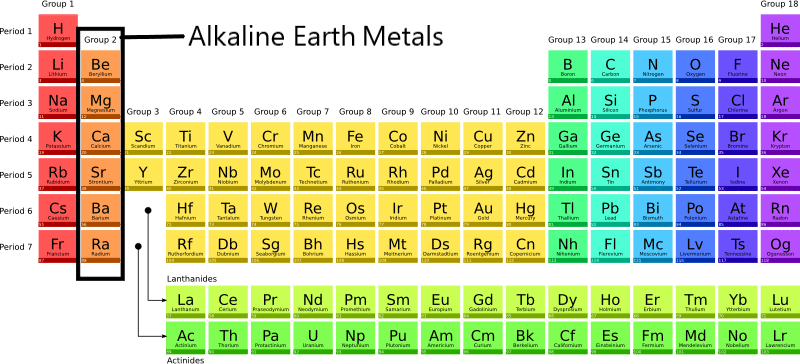
ToggleAlkaline earth metals are composed primarily of six elements: beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). These are the Group 2 elements in the periodic table.
The physical and chemical properties of the elements in this group are very similar as the main objective of the periodic table is to study the elements and their compounds in a structured way and organized manner.
What are Alkaline earth metals?
Alkaline earth metals are the elements that belong to group 2 of the periodic table i.e., the second vertical column. This group includes the elements beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
The term “alkaline” refers to the fact that when these elements combine with oxygen, they produce basic compounds. Also, the name “earth” refers to that group 2 metals, like calcium and magnesium, are among the prevalent elements of the planet’s crust.
Alkaline earth metals properties
These elements have the general electrical configuration: ns2
Alkaline earth metals have full s-orbital in their respective valence shells, so they quickly can lose two electrons to create +2 cations. Ultimately, each element in alkaline earth metals is in a +2-oxidation state.
Some of the common properties of Group 2 elements are:
- weak affinity for electrons
- Low electronegativity
- densities are relatively modest
- relatively low melting and boiling points.
Atomic Properties of Alkaline earth metals
| Elements | Be | Mg | Ca | Sr | Ba | Ra |
| Electronic Configuration | 1s22s2 | 1s22s22p63s2 | 1s22s22p63s2 3p64s2 | 1s22s22p63s2 3p64s2 | 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d105s25p66s2 | 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d105s25p6 4f145d106s26p67s2 |
| Atomic Number (Z) | 4 | 12 | 20 | 38 | 56 | 88 |
| Atomic mass | 9.012 | 24.31 | 40.08 | 87.62 | 137.3 | 226.0 |
| Atomic Radius (pm) | 105 | 150 | 180 | 200 | 215 | 215 |
| Ionic Radius (pm) | 34 | 78 | 106 | 127 | 143 | 152 |
Physical Properties of Alkaline earth metals
| Elements | Be | Mg | Ca | Sr | Ba | Ra |
| Colour | Gray | Silvery white | Silvery white | Silvery white | Silvery white | White |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.85 | 1.74 | 1.55 | 2.63 | 3.65 | 5.50 |
| Boiling Point (°C) | 2471 | 1090 | 1484 | 1384 | 1805 | About 1100-1700 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 1287 | 650 | 842 | 769 | 727 | About 700 |
| Flame Colour | None | None | Brick Red | Crimson Red | Apple green | Crimson |
| Ionization Energy ( KJ/mol) | 899.5 | 737.7 | 569.8 | 549.5 | 502.9 | 509.3 |
| Electronegativity (Pauling) | 1.57 | 1.31 | 1 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.9 |
| Hydration Enthalpy (KJ/mol) | -506 | -406 | -330 | -310 | -276 | – |
Chemical Properties of Alkaline earth metal
The chemical behavior of alkaline earth metals is characterized by their great reducing power, which allows them to produce bivalent cations (M2+) extremely quickly. On descending within the group, the elements in group 2 become more electropositive.
Calcium, strontium, and barium react similarly to sodium but are somewhat less reactive.
Except for beryllium, all metals create oxides in the air at ambient temperature.
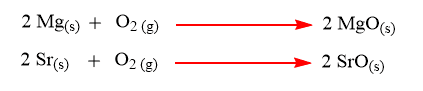
Reaction of alkaline earth metals with Oxygen
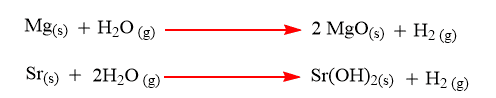
Reaction of alkaline earth metals with water
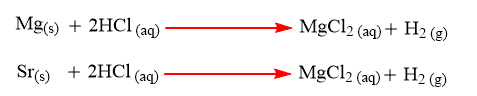
Reaction of alkaline earth metals with dilute HCl
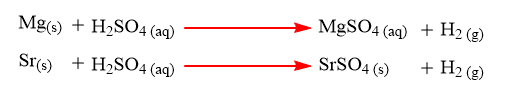
Reaction of alkaline earth metals with dilute H2SO4
Reaction of alkaline earth metals with Halogen

Reaction of alkaline earth metals with liquid ammonia
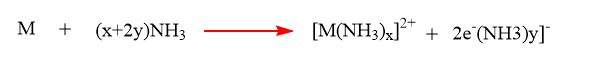
Uses of Alkaline earth metals
- Magnesium, an important constituent of chlorophyll in green parts of plants takes part in photosynthesis.
- Ca2+ ions are essential components for the formation of bones and teeth
- Radium is employed for cancer treatment.
- By using barium, vacuum tubes can be made airless.
- Beryllium is used in the manufacture of alloys.
- The movement of electrical impulses through nerve fibers and the contraction of muscles are both mediated by the ions Ca2+ and Mg2+.
Alkaline Earth Metals Video
[Notes: The data presented in the table may vary from textbooks].