Table of Contents
ToggleAllotropes are such forms of an element that exist in two or more than two forms that are physically different but chemically identical in properties. Carbon exhibits various allotropic forms, mainly diamond, graphite, and fullerene. All allotropes of carbon contain the same element of carbon.
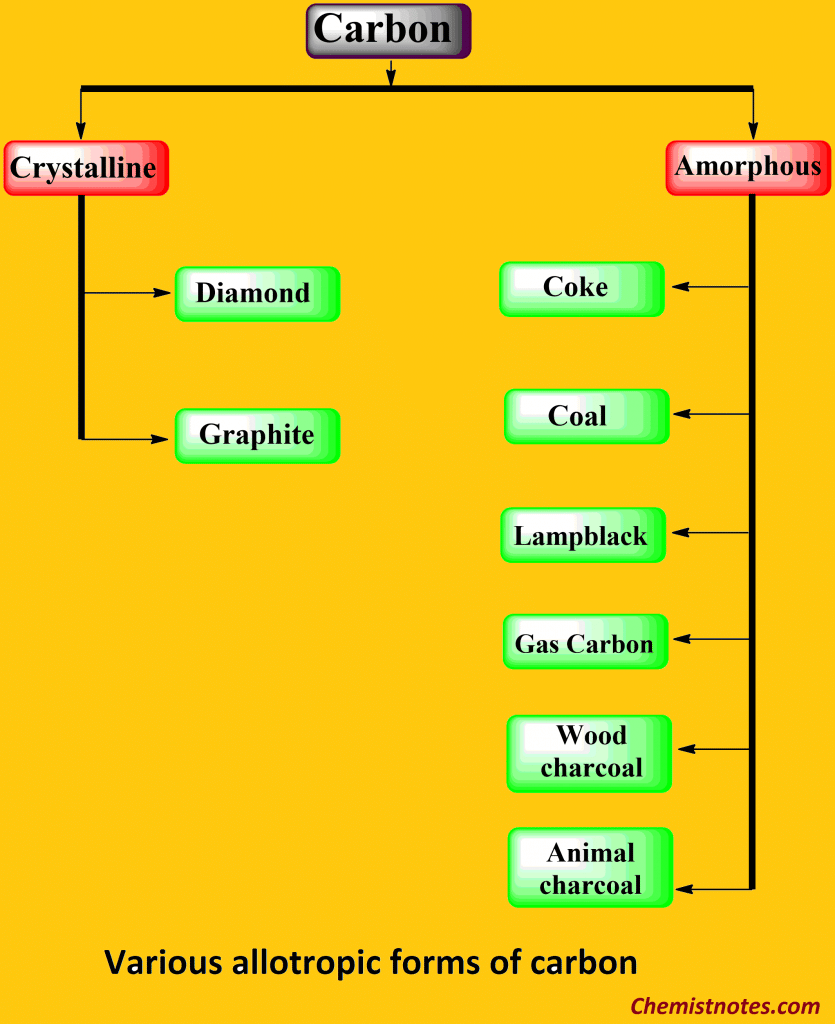
Diamond
- A diamond is the hardest crystalline carbon allotrope.
- It is the purest form of carbon (100% carbon), which is colorless and transparent in X-ray.
- Its density is very high, i.e., 3.5 g/cm3 at 15oC, and it has a very high refractive index (2.417).
- Diamond is known as a bad conductor of heat and electricity for the reason that its electrons are not free to move due to the formation of sp3 hybrid covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
- It is converted to graphite upon prolonged heating above 1800 °C.
- Its melting point is high (3750 oC) because the carbon atoms are tightly held by strong sp3 hybrid covalent bonds.
- In diamond, each carbon atom is sp3 hybridized.
- It is chemically inert with all chemical reagents. But it burns in the air when heated to about 900 °C to give CO2.
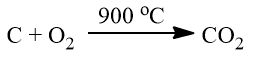
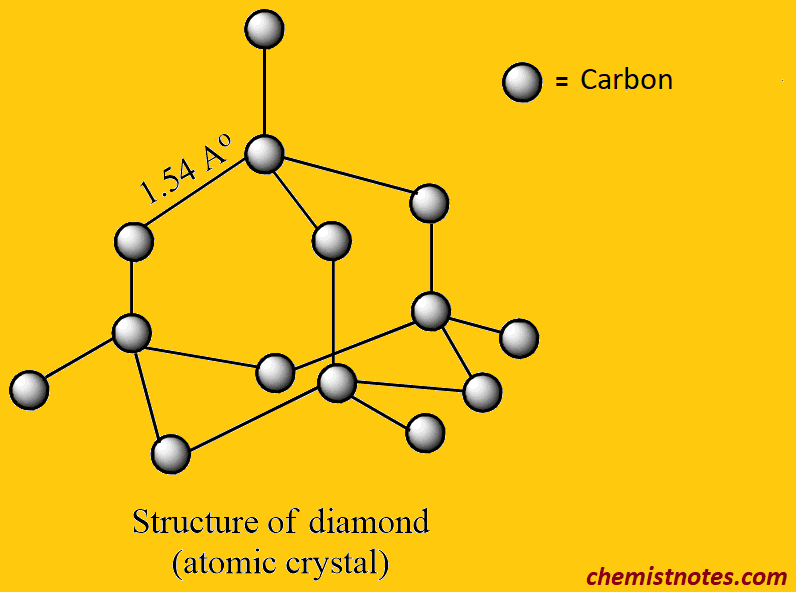
structure of a diamond
Diamond is a big three-dimensional structure in which each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four carbon atoms that lie at the corners of a regular tetrahedron. All carbon atom in a diamond is bound by sp3 covalent bonds to form a number of inter-linked tetrahedron structure (having a carbon atom at the center and four carbon at its corner) resulting in the formation of a 3-D compact atomic crystal. Each carbon-carbon bond angle in tetrahedral structure is 109o28′ and carbon to carbon distance is 1.54 Ao.
Uses of Diamond
- Diamond is used as a precious stone in jewelry as a gem because of its brilliant shine. It is weighed in carat, 1 carat = 0.2 gm.
- It is used for grinding and polishing hard materials as abrasives.
- It is also used in industry, black diamonds are used for cutting glass, and metals borer for rock drilling (colored diamond is due to the presence of slight impurities).
Graphite
It is another crystalline allotrope of carbon. It is known as black lead or plumbago. Diamond slowly changes to graphite millions of years later.
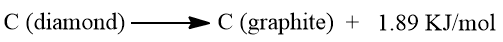
- Graphite is the most stable carbon allotropes.
- It is soft, dark grey in color having metallic luster due to the presence of mobile p- orbital electrons.
- it is slippery and a good conductor of electricity and has a less specific gravity (2.2) than diamond (3.50).
- Graphite is more reactive than diamond because the edge of planes are opened to chemical attack.
- Graphite is stable in all chemical reagents but burns in the air on heating to give CO2.
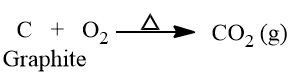
- On heating with Conc. HNO3, yellow mass graphite acid (C11H4O5) is obtained.
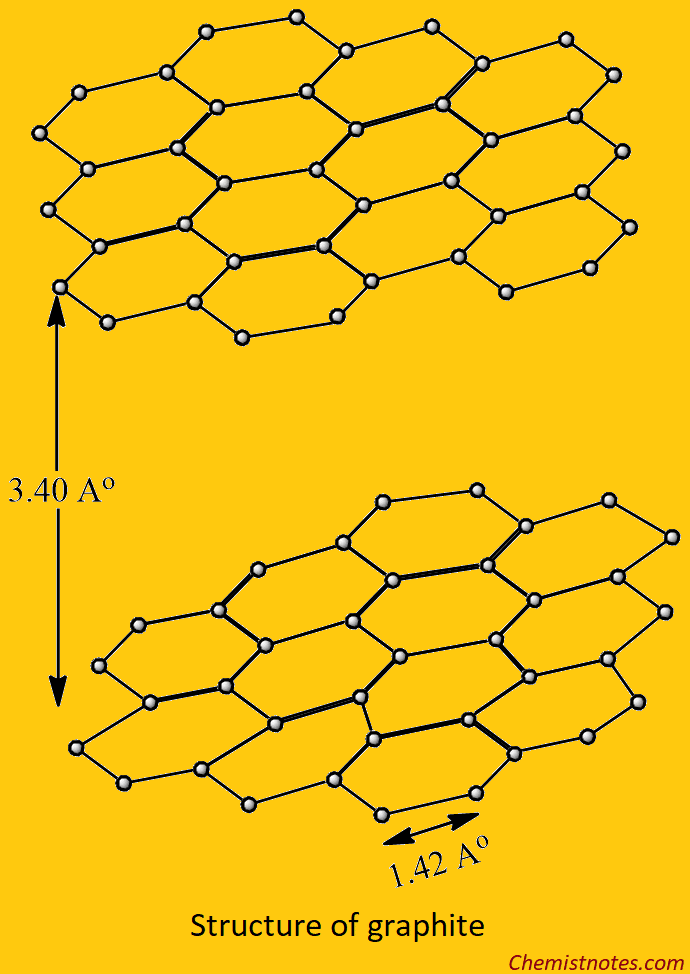
The Structure of Graphite
Graphite consists of the two-dimensional layer structure of carbon atoms. In each layer, the carbon atoms are arranged in regular hexagonal rings. In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other neighboring carbon atoms through trigonal sp2 covalent bonds and forms many hexagonal rings. Each layer is bonded with the adjacent planar layer by weak van der Waal’s forces. In graphite, the central carbon atom is sp2 hybridized. Each carbon atom uses only three valance electrons in sp2 trigonal bonding, the fourth electron is free. These free electrons make graphite a good conductor of electricity.
Uses of Graphite
- As graphite is a good conductor of electricity, it is used for making electrodes in an electric furnace.
- A mixture of graphite and clay is used as a lead in the pencil.
- Used in making graphite crucibles that can withstand high temperatures.
- Used as a lubricant for high-speed machines, and as an additive for motor oil.
- Used for manufacturing paints used in stone polish.
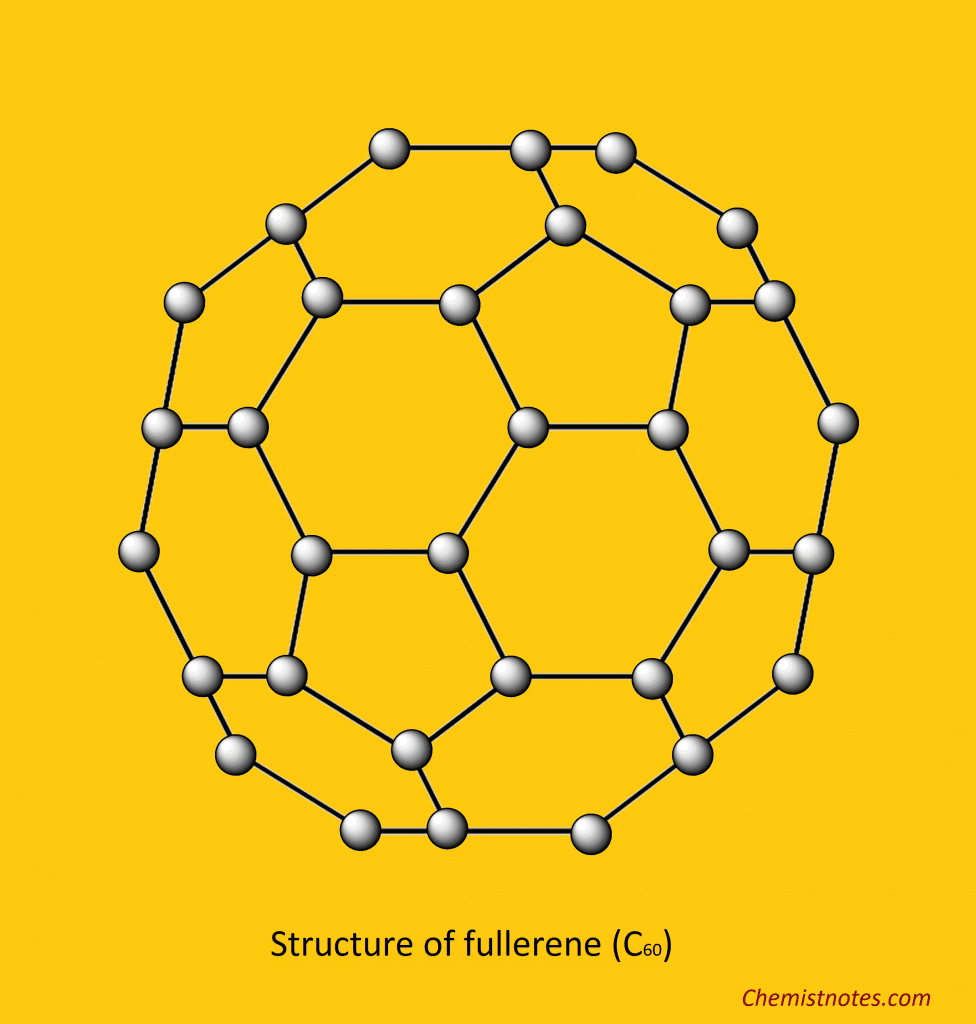
Fullerene
Fullerene is the latest crystalline allotrope of carbon discovered by Korto and Smalley in 1985. It is nearly spherical in shape, containing 60 carbon atoms, and this common form of fullerene is C60. It is named the Buckmsterfullerene after the name of R. Buckminster Fuller. Due to their spherical shape, C60 molecules are called buckyballs. Fullerene (C60) is a molecular substance. The structure of fullerene (C60) is like a soccer ball, which consists of 12 pentagonal and 20 hexagonal faces. On the other hand, they consist of a fused system of five or six-member rings. It is soluble in organic solvents.
Uses of Fullerene
- Fullerene is used as a superconductor due to its reasonable electric conductivity.
- They are useful in trapping certain metal ions such as calcium, gold, etc, inside the carbon clusters so can be used as sieves.
FAQs
Is carbide an allotrope of carbon?
carbide is not an allotrope of carbon.
What are allotropes of carbon?
Carbon exhibits various allotropic forms, mainly diamond, graphite, and fullerene.