Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is standard hydrogen electrode?
Standard hydrogen electrode, also known as Normal Hydrogen Electrode, consists of hydrogen gas in equilibrium with hydrogen ion concentration(H+ ion) in a solution. The electrical contact of this electrode is provided by an inert metal like Platinum(Pt).
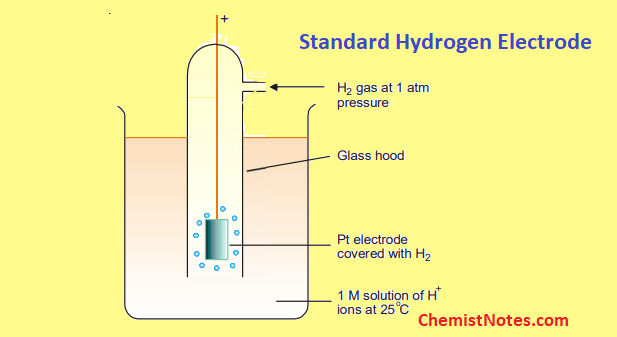
Gaseous hydrogen at a pressure of 1 atm is bubbled over the platinum electrode, which is coated with a very finely divided platinum that causes the electrode reaction to occur rapidly. The electrode is surrounded by a solution whose temperature is 25-degree celsius and in which the H+ ion concentration is 1M.
The half-cell reaction that occurs at the platinum surface is shown below:
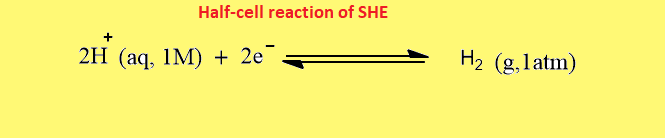
Standard hydrogen electrode equation
The standard electrode potential of any other electrode is obtained by combining the electrode with SHE. Since the standard potential of the hydrogen electrode is zero, the measured potential is the standard potential of the other electrode.
If we constructed a galvanic cell using SHE where SHE acts as cathode then, the cell notation can be expressed as:
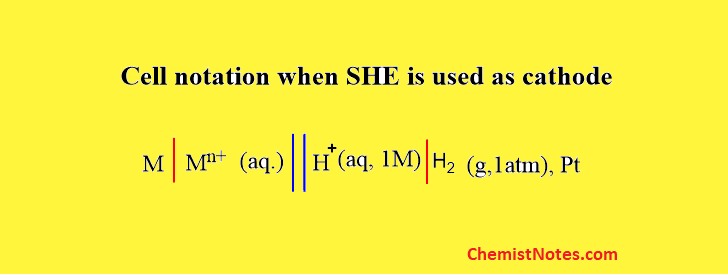
Here, oxidation takes at M/Mn+ electrode, and reduction takes place at SHE.
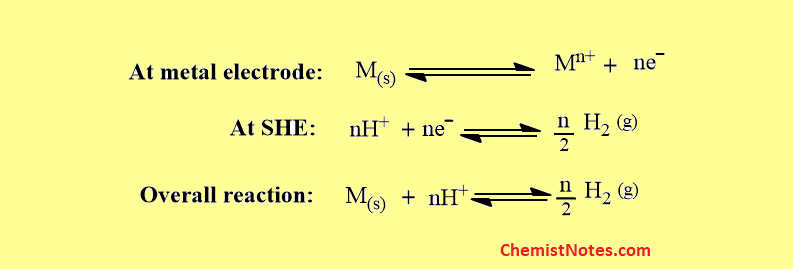
Similarly, if a galvanic cell is constructed using SHE where it acts as an anode then, the cell notation can be expressed as:
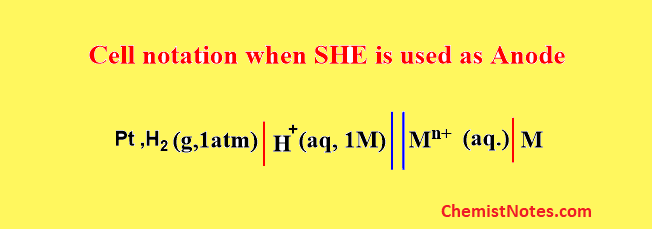
Here, oxidation takes place at SHE, and reduction takes place at M/Mn+ electrode.
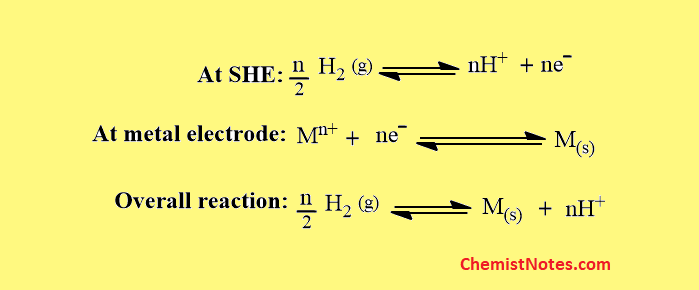
Application of Standard hydrogen electrode
This electrode can be used in the determination of standard electrode potential. By convention, the standard electrode potential is always taken as the standard reduction potential.
Let us take an example of the determination of the standard electrode potential of the Zn++/Zn electrode.
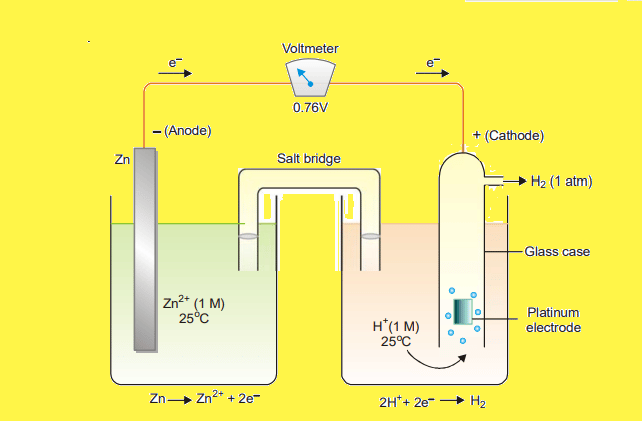
In this case, electrons flow from Zn-electrode to the hydrogen electrode. Therefore, Zn-electrode acts as an anode and SHE acts as a cathode. The cell may be represented as,
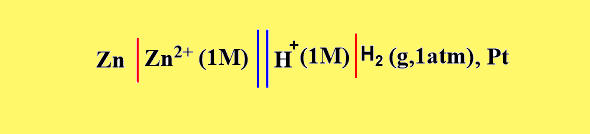
The emf of the cell is found to be 0.76V. Now, the emf of a cell is given by the following expression:
Eocell=EoRight– EoLeft
0.76=Eo H+/H2 – Eo Zn++/Zn
0.76=0 – Eo Zn++/Zn
Eo Zn++/Zn= – 0.76 V
Thus, by combining with SHE, the standard electrode potential of the Zn++/Zn electrode is found to be -0.76 V.
Disadvantages of Standard hydrogen electrode
It is always not convenient to use standard hydrogen electrodes as reference electrodes because of the following experimental difficulties in its preparation and use.
- It is difficult to maintain the unit concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
- The platinum is poisoned by the absorbed impurities from the solution and it makes its use difficult because it stops the reversibility of the reaction.
- It is difficult to maintain the 1 atm pressure of hydrogen gas uniformly for a long time.