Table of Contents
ToggleThere are two types of electrified interfaces on the basis of their ability to pass charge across the double layer.
- Polarizable interface
- Non-polarizable interface
Polarizable interface
An ideal polarizable interface is an electrified interface in which, when the potential on the metal is changed from either a positive or negative direction, there is a change of potential across the interfacial region but no passage of charge across the interface takes place. It means, the potential across the double layer changes but no current flows across the double layer.
Non-polarizable interface
A non-polarizable interface is one in which, when the potential on the metal is changed, there are flows of charge(electrons) across the double layers but the potential across the interface remains constant. Therefore, a non-polarizable interface is distinguished by the fact that the potential difference across it remains virtually constant when the potential applied to a cell change.
Difference between polarizable and non-polarizable interface
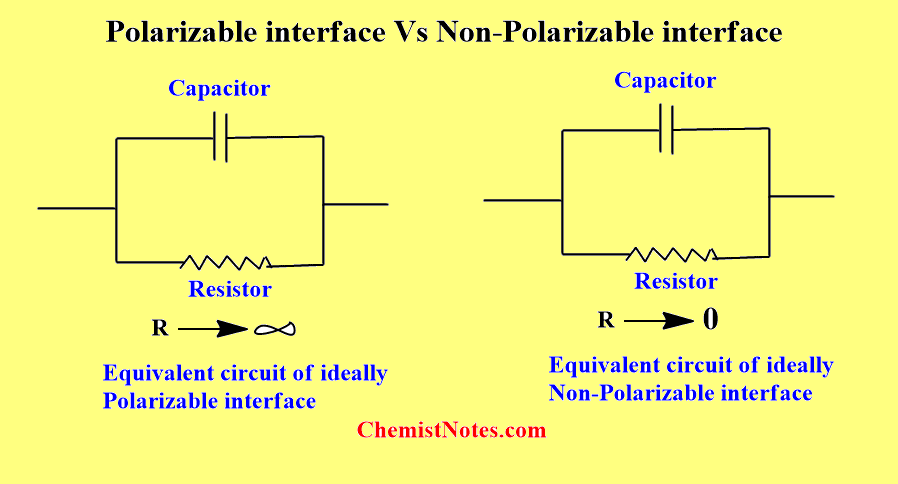
The difference between polarizable and non-polarizable interfaces can be understood in terms of a model consisting of a capacitor and resistor connected in parallel.
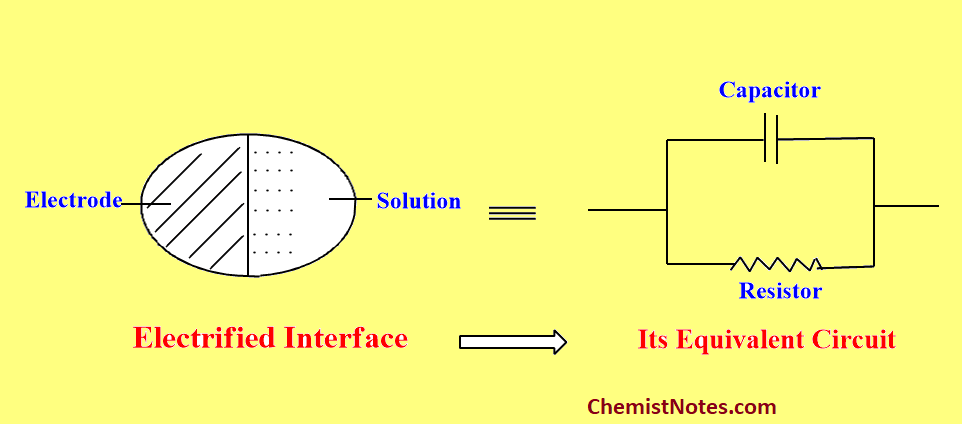
If the resistance is very high, then the capacitor charges up to the value of the potential difference put out by the source. This is the behavior of a polarizable interface.
If on the other hand, the resistance is low then any attempt to change the difference across the capacitor is compensated by the charges leaking through the low resistance path. This is the behavior of a non-polarizable interface.