Table of Contents
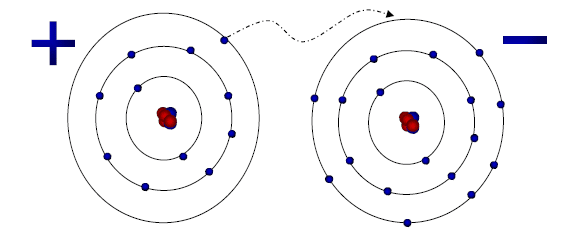
ToggleIonic crystal is a crystalline organic compound/solids having a proper arrangement of ions into a lattice held together by the electrostatic force of attraction. The structural units of these crystals are ions. In such crystals, the lattice is made up of alternating positive and negative ions in equal numbers. It is the coulombic forces of attraction that hold each ion of a given sign to all ions of the opposite sign.
Bond directionality is determined by the lattice structure, which is determined by the arrangement of bonds in the molecule. Ionic bonds are formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another and a positive ion is attracted by a negative ion or vice versa. As a result of the force of attraction occurring from both sides, ionic bonds are non-directional in nature. Anions are mostly packed close together in ionic crystals, with small cations occupying the “holes.”
Ionic Crystal examples
Some of the well-known examples of Ionic crystals are NaCl, CsCl, KCl, KBr, KF, including other alkali halides.
Electrostatic Interaction of NaCl
Properties of Ionic Crystals
The size and magnitude of the charges on the ions that compose the lattice, which determines the physical properties of the crystal, have a large influence on the strength of the attractive forces and the arrangement of ions within the crystal.
Some of the properties of ionic crystals are
- Melting point and Boiling point: Since the ions are strongly bounded to each other by strong electrostatic force of attraction, large amount of energy is required to overcom this attraction. Likewise, the ionic crystals possesses closed-packed structure, and hence large amount of energy is required to makes the ion movable. Thus, Ionic crystals have high melting point and boiling point.
- Electrical Conductivity: There are no free mobile electrons and charged particles to conduct electricity. Each electron is bound tightly to one of the ions, and hence ionic crystal is poor in electrical conductivity. The conductivity increases with increase in conductivity.
- Solubility: Polar solvents have a high dielectric constant, which makes them interact aggressively with ions and lowers the electrostatic attraction between them. Thus, ionic crystals are soluble in polar solvent, and insoluble in non-polar solvent.
- Hardness and Rigidity: Because ions are tightly attached to the lattice and cannot easily move them, surfaces are not easily scratched. Therefore, ionic crystals possesses high rigidity and the hardness.
- Brittleness: Because the ions in ionic solids are bound in a lattice by electrostatic forces of attraction in cations, they are brittle. If a significant enough force is applied along a given plane, ions will shift along that layer, displacing that layer relative to the next, resulting in ionic compound repulsion between like charges. As ions are tightly attached to the lattice and cannot easily displace them, ionic crystals possesses high brittleness.
Ionic Crystal video
FAQs/MCQ
Why ionic crystals are brittle?
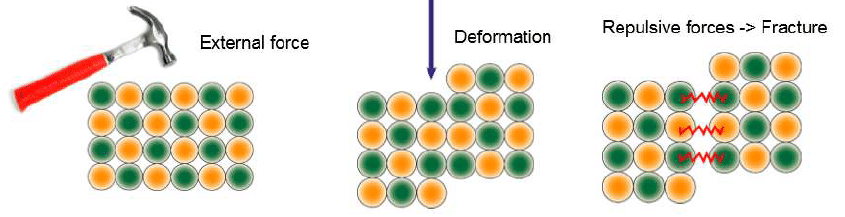
Because the ions in ionic solids are bound in a lattice by electrostatic forces of attraction in cations, they are brittle. If a significant enough force is applied along a given plane, ions will shift along that layer, displacing that layer relative to the next, and hence is brittle
Is diamond an ionic crystal?
No, Diamons is a covalent solid.