Table of Contents
ToggleHalf life of zero order reaction is used to represent the rate of reaction. The definition of the half-life period and the half-life period of zero-order reaction has discussed here.
Half life of a chemical reaction
Half life period of a chemical reaction is defined as the time required to decrease the concentration of reactant to half of its initial concentration. Half-lifetime is the time required for one-half of the reaction to be completed. It is denoted by t1/2.
Half life of zero order reaction/how to find half life of zero order reaction?
The half-life of zero-order reaction can be derived by using integrated rate law expression of zero-order reaction.
Consider a general zero-order reaction
A → Product
The rate law expression is given by,
Rate=dx/dt=k[A]o
dx/dt=k
dx=kdt…………………………………………………………….(1)
on integration this equation (1), we get the integrated rate law expression as:
x=kt …………………………………………………..(2)
This is integrated rate law expression for zero order reaction.
Now, At half-life time, t becomes t1/2 and the concentration of reactant becomes half of its original value. Therefore,
t=t1/2 and x=a/2. Putting these values, equation (2) becomes,
a/2= k t1/2
t1/2= a/2k ……………………………………………………………….(3)
This is the expression of the halflife period of zero-order reaction. This equation indicates that the half-life period of the zero-order reaction is directly proportional to the initial concentration of the reactant. On increasing the concentration of reactant twofold, the half-life period will be doubled. In general,
t1/2 ∝ a ……………………………………………………………………..(4).
where a= initial concentration of reactant.
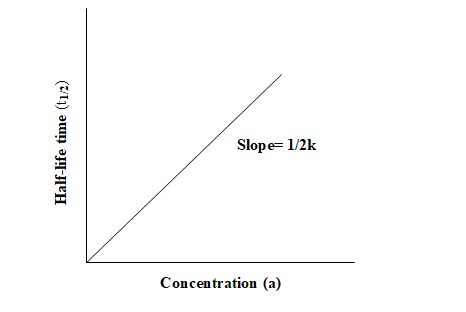
Graphical representation of half life time vs concentration
For zero-order reaction, the half-life time can be plotted against the concentration of reactant, a straight line passing through the origin and having a slope equal to 1/2k is obtained as shown in the figure.
Numerical problems related to Zero-order reaction
Question No.1: If a zero-order reaction completed 50% in 30 minutes, how much time will take it to complete 90%?
Let a=100 mole L-1
First case: Reaction is 50% completed which means x=50 mole L-1 so, for zero-order reaction,
x=kt
k=x/t = 50/30= 5/3
Second case: Reaction is 90% completed which means x=90 mol L-1 so,
k=90/t
Putting the value of k,
5/3=90/t
t= 54 min
Hence, it takes 54 minutes to complete the 90% reaction.
Question No. 2: If a zero-order reaction completes 50% in 20 minutes, how much time will it take to complete a 75% reaction?
Solve yours.
FAQs:
what is half-life of a chemical reaction?
Half-life period of a chemical reaction is defined as the time required to decrease the concentration of reactant to half of its initial concentration