Table of Contents
ToggleDarzens condensation, examples, mechanisms, and applications in organic chemistry have been discussed here:
Darzens Condensation Definition
The condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with α -hydrogen esters in the presence of sodium ethoxide or sodamide results in the formation of α, β-epoxy ester. Such a reaction is called the Darzen condensation reaction. Generally, sodium ethoxide is used as an efficient condensing agent. Aliphatic aldehyde yields are low, most likely due to the production of aldol compounds while aromatic aldehydes and ketones or α, β-unsaturated ketones give good yields of glycidic esters.
Some of the examples of perkin condensation reactions are:
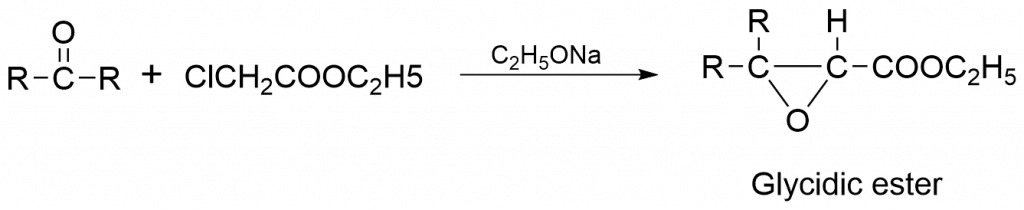
Darzens condensation reaction mechanism
The Darzens Reaction is the condensation reaction of a carbonyl compound with an α-halo ester in the presence of a base to form an α, β-epoxy ester. The mechanism proceeds by multiple steps. Here, the base deprotonates the α-halo ester leading to the formation of carbanion which attacks the carbonyl group (R2CO). The intermediate Halohydrin undergoes SN1 reaction to form the epoxide ring. Mostly the darzens condensation reaction occurs in the favour of the formation of trans glycidic derivatives.

Applications of Darzens Condensation
1. Synthesis of α-pinene
2. Synthesis of one of the reactions of Vitamin A1 Synthesis
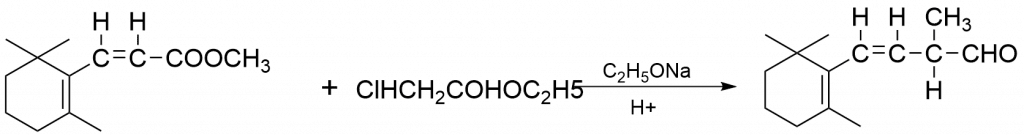
Darzens Condensation Video
FAQs/MCQs
Darzens condensation
Darzens condensation is the condensation reaction of a carbonyl compound with an α-halo ester in the presence of a base to form an α, β-epoxy ester.
References
- Morrison, R. T., & Boyd, R. N., Organic chemistry, Allyn and Bacon, Inc. 1987.
- March, J., Advanced Organic Chemistry, Wiley Eastern Limited, 1986.
- Skyes, P., A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Second edition, Orient Longman Ltd., 1988.