Table of Contents
ToggleCope rearrangement reaction, examples, mechanism, and its variations along with stereochemistry have been discussed here. Cope rearrangement is quite similar to claisen rearrangement, both are [3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement reactions.
Cope rearrangement reaction
Cope rearrangement is a thermal isomerization of a 1,5-diene through [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement giving a more stable 1,5-diene as a product. Let’s see an example of a cope rearrangement reaction.
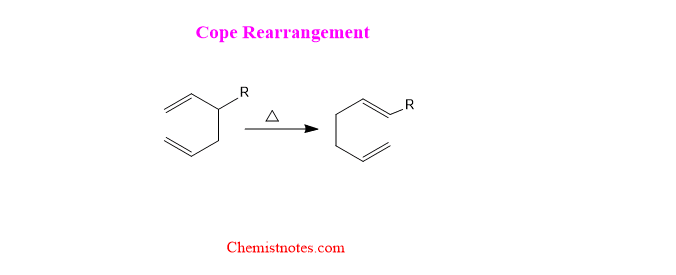
Various types of cope rearrangement reactions have been reported such as oxy-cope rearrangement, aza-cope rearrangement, anionic oxy cope rearrangement reaction, etc.
Some properties of Cope rearrangements are given as:
- These reactions can be induced thermally or photochemically.
- These reactions proceeds via the concerted mechanisms.
- Reactions takes place in solution as well as in vapour phases.
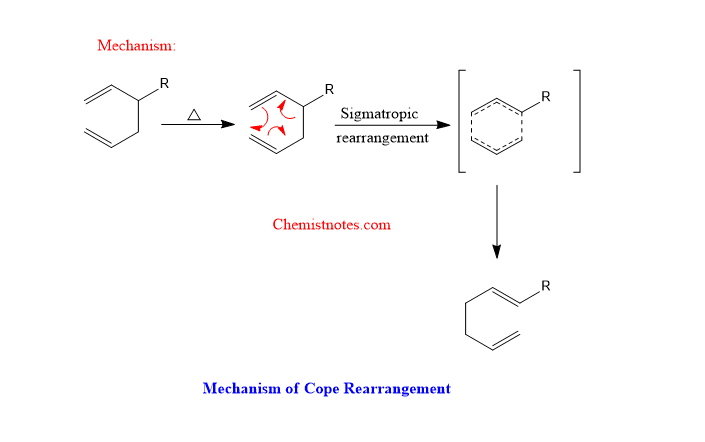
cope rearrangement mechanism
The mechanism of cope rearrangement involves a concerted mechanism as represented below:
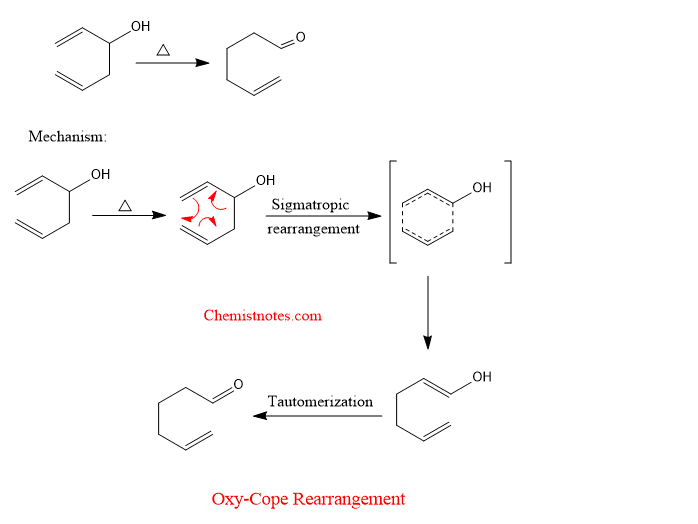
oxy cope rearrangement
When a hydroxyl group is present at position-3 of the 1,5-diene, the rate of rearrangement is increased rapidly when treated with a strong base like potassium hydride (KH). Such a reaction is called oxy-cope rearrangement.
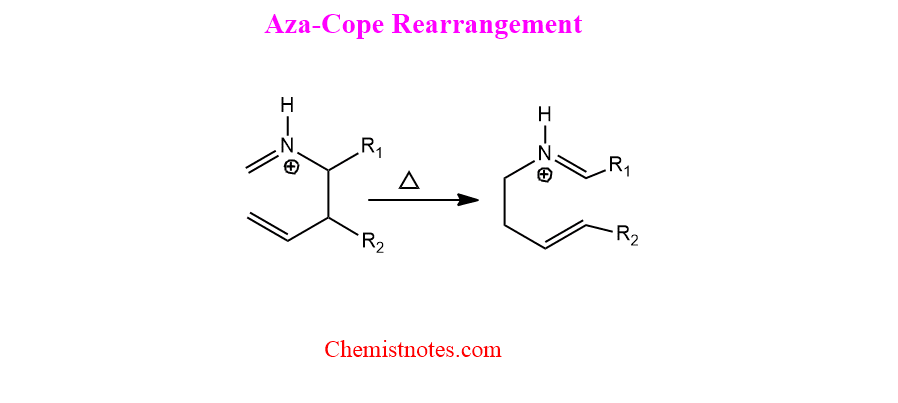
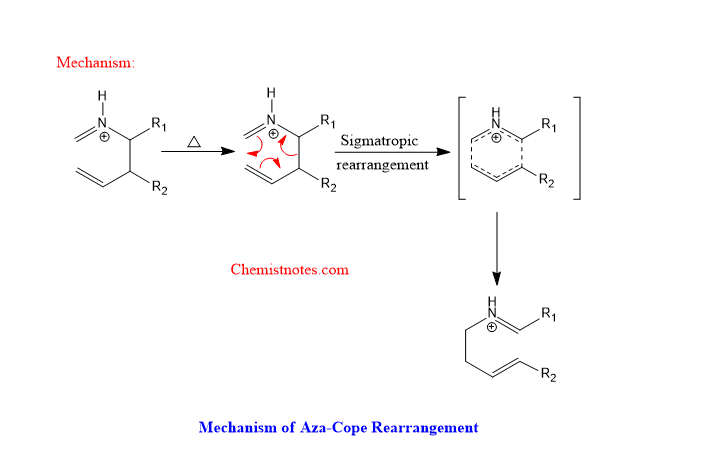
aza cope rearrangement
Let’s see an example of aza cope rearrangement.
aza cope rearrangement mechanism
The mechanism of aza cope rearrangement is shown below:
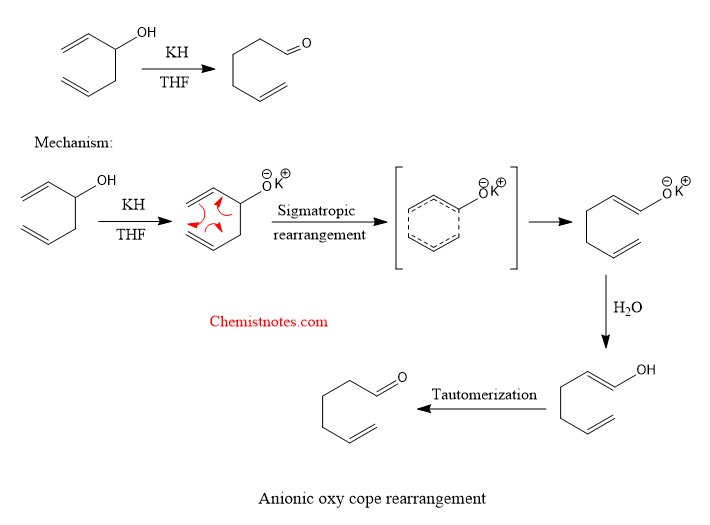
Anionic oxy cope rearrangement
An example of oxy cope rearrangement is given below with its mechanism.
Cope Rearrangement Video
References:
- Wang, Z., Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.,2010
- J.J. Li, Name Reactions, 4th ed.,© Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2009
- Skyes, P., A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Second edition, Orient Longman Ltd., 1988
- March, J., Advanced Organic Chemistry, Wiley Eastern Limited, 1986.
- Morrison, R. T., & Boyd, R. N., Organic chemistry, Allyn and Bacon, Inc. 1987
If you have any problems related to this topic, please comment without hesitation. Thank you.






