Table of Contents
ToggleClaisen condensation, examples, mechanisms, and applications in organic chemistry have been discussed here:
Claisen condensation reaction definition
Claisen condensation is an aldol condensation reaction that involves a nucleophilic attack of a carbanion on an electron-deficient carbonyl carbon atom followed by the loss of an anion from the reactant, resulting in nucleophilic substitution. The Claisen condensation reaction occurs by the removal of an alpha proton via the action of a strong base, resulting in the production of an enolate ion.
A minimum of one reagent must have an alpha proton and be capable of forming an enolate anion following deprotonation in the Claisen condensation reaction. Sodium ethoxide is mostly used as a base for this reaction.
Claisen ester condensation
Condensation reaction of carboxy ester with an active methylene group of ester aldehyde, acetonitrile in the presence of a strong base, such as sodium ethoxide, yields β-ketoester. This type of reaction is known as claisen ester. Here, the alkoxy part of the ester must act as a good leaving group.

Claisen condensation mechanism
The mechanism of claisen condensation reaction can be carried out into following steps:
Step 1: Abstraction of H+ with ethoxide results in the formation of resonance stabilized α-carbanion from one ester molecule.
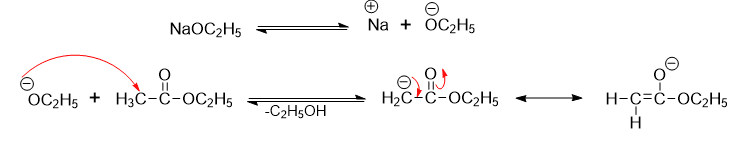
Step 2: α-carbanion attacks the C=O group of the ester nucleophilically, forming an anion that loses the ethoxide ion to generate β-ketoester.
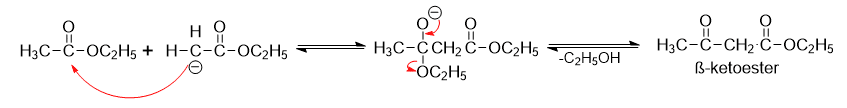
Step 3: Formation of resonance stabilized carbanion that is neutralized by adding acid.
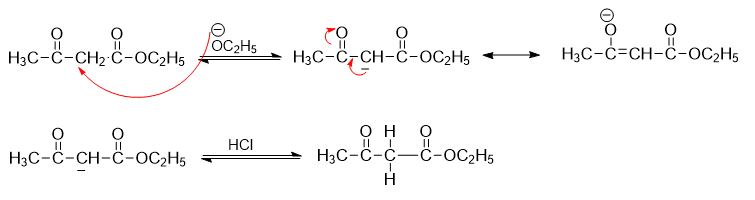
Crossed claisen condensation
Crossed claisen condensation involves the reaction of enolate of one ester and with a different (ideally non-enolizable) ester (ester without α-hydrogen) to give a β-ketoester. The mechanism of the crossed claisen condensation reaction can be described in following steps:

Claisen schmidt condensation applications
- Synthesis of cyclic compounds
- Synthesis of ethylbenzoyl acetate
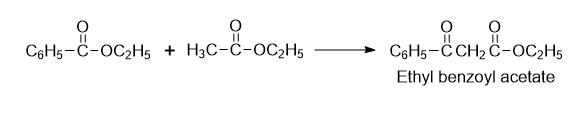
Limitation of crossed chain condensation
If the reaction involves two different esters having -hydrogen, then it yields four different products and hence the reaction becomes unsuitable for synthesis.
Claisen condensation reaction video
FAQs/MCQs
Claisen schmidt condensation
Claisen-Schmidt condensation involves the nucleophilic attack of carbanion on an electron-deficient carbonyl carbon atom followed by loss of an anion.
Intramolecular claisen condensation
Diesters can be converted to cyclic beta-keto esters by an intramolecular reaction known as Dieckmann condensation. In other words, Dieckmann cyclizations are intramolecular Claisen condensations.
Mixed claisen condensation
Mixed claisen condensation, also called cross claisen condensation involves the reaction of enolate of one ester and with an ester having no α-hydrogen to give a β-ketoester.
References
- Morrison, R. T., & Boyd, R. N., Organic chemistry, Allyn and Bacon, Inc. 1987.
- March, J., Advanced Organic Chemistry, Wiley Eastern Limited, 1986.
- Skyes, P., A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Second edition, Orient Longman Ltd., 1988.






