Table of Contents
ToggleBouveault blanc reduction is a chemical reaction in which ester is reduced to corresponding alcohol using sodium and ethanol as reagents. This reaction was first reported by Bouveault and Blanc in 1903, thus known as the Bouveault-Blanc reaction. In absence of alcohol, the reduction of esters with sodium results in the formation of acyloin, which is known as acyloin condensation.
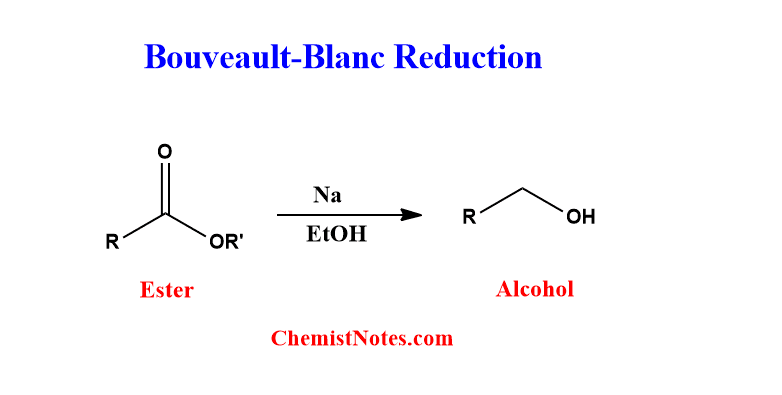
Bouveault blanc reduction
It is, in fact, the reduction of esters into alcohols using sodium in ethanol, where sodium serves as a single electron reducing agent and ethanol serves as a proton donor. Besides ethanol, other alcohols can be applied as a proton donor. The metal donates a single electron to the carbonyl carbon, resulting in the formation of an ion-radical intermediate.
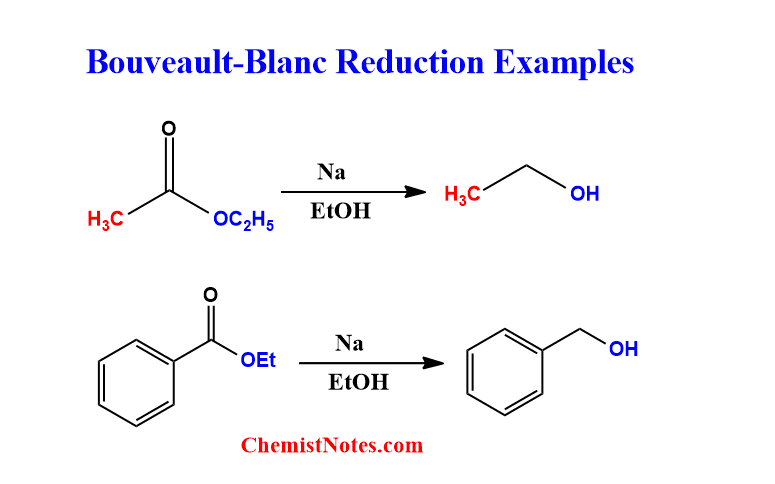
Bouveault Blanc reduction examples
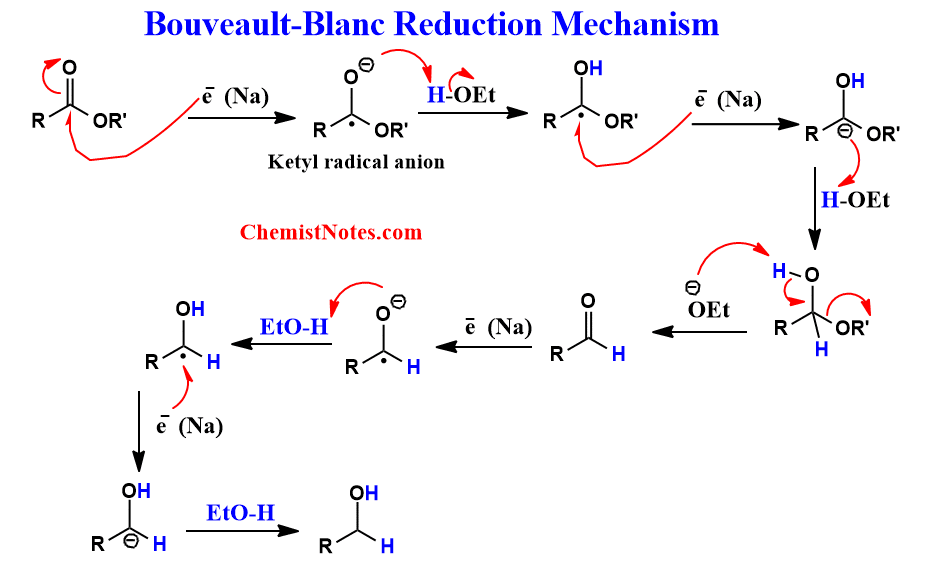
Bouveault blanc reduction mechanism
It has been confirmed that this reaction proceeds via a free radical mechanism in which the ester is first reduced to ketyl radical. Later, ketyl radical is further reduced to an alcohol. The radical mechanism of this reaction has been illustrated as shown below:
Application of Bouveault-Blanc reduction
This reaction is used to reduce, not only esters but also the aldehyde and ketones to the corresponding alcohols. Moreover, if there is a double bond in the appropriate position in the ester, cyclic or spirocyclic alcohol is formed.
Bouveault-Blanc reduction video
References:
- Wang, Z., Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.,2010.
- J.J. Li, Name Reactions, 4th ed.,© Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2009.






