Table of Contents
ToggleAcyloin condensation reaction is the formation of acyloin from the ester. This reaction was first reported by Bouveault and Blanc in 1903 but was further extended by Bouveault and Locquine. The symmetrical α-hydroxy ketones are called acyloin, and the formation of α-hydroxy ketones from the esters is simply referred to as acyloin ester condensation.
Acyloin condensation
Esters are treated with active metals like sodium in the absence of any proton donor and the reaction is carried out in an aprotic solvent like xylene. Thus, It involves reductive condensation of esters in an inert solvent with sodium to produce symmetrical α-hydroxy ketones.
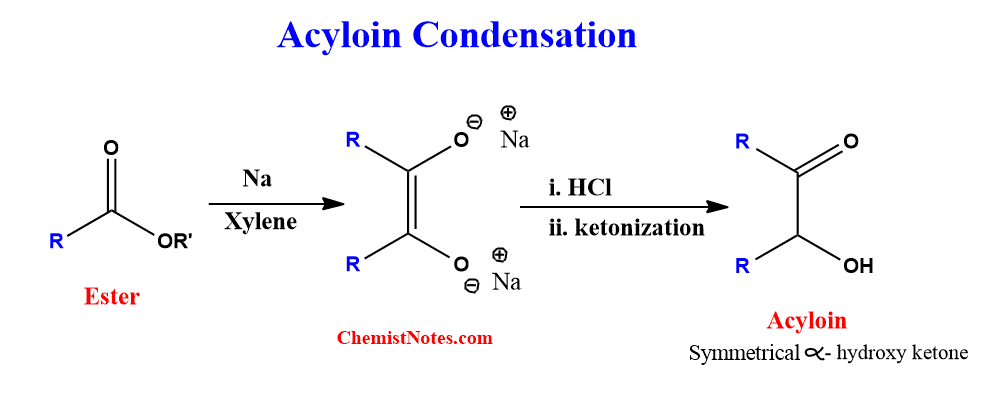
If the ester is treated with sodium in presence of a protic solvent, alcohol is formed as a product instead of symmetrical α-hydroxy ketones. This reaction is known as Bouveault-Blanc reduction. Don’t get confused!!!!.
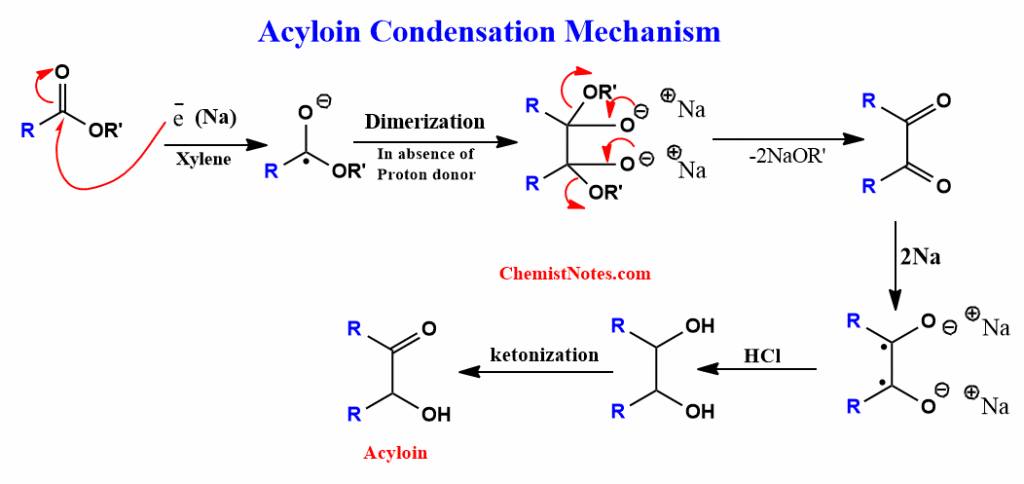
Acyloin condensation mechanism
First of all, sodium reacts with the ester to give radical anion, which further undergoes dimerization to form a dianion. Then two alkoxide ions are released to give diketones. Further, diketones react with sodium to produce dianion, which on acidification gives α-hydroxy ketones. The whole mechanistic pathways are shown below:
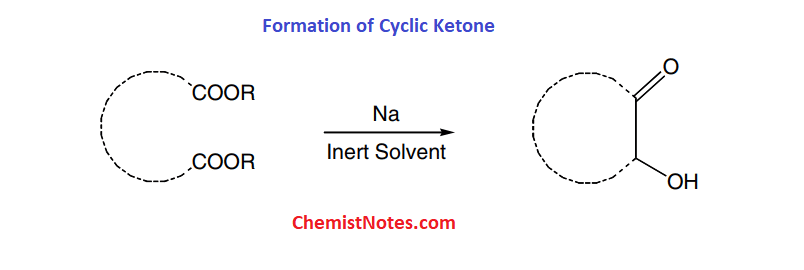
Applications of acyloin condensation
This reaction can be used to synthesize cyclic ketones using diesters with a long hydrocarbon chain between the two ester groups.
References:
- Wang, Z., Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.,2010
- Laue T., Plagens A., Named Organic Reactions, Second edition, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005






