Table of Contents
ToggleAffinity chromatography is a type of chromatographic technique in which separation is based on the various types of specific affinities between a target molecule and a specific ligand coupled to a chromatography medium.
Affinity Chromatography Principle
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating the biochemical mixture on the basis of the special affinity of one of the components with another. The main principle of affinity chromatography is based on the biological interaction of ligand and the target molecules due to the result of electrostatic or hydrophobic or van der Waal’s force or hydrogen bonding.
After the binding of target molecules with affinity medium, the target molecules are eluted from the affinity medium by changing pH, polarity or by using a competitive ligand.
Successful affinity purification requires a bispecific ligand that can be covalently attached to the chromatographic matrix. The coupled ligand must retain its specific binding affinity for the target molecules and, after washing away unbound material, the binding between the ligand and target molecule must be reversible to allow the target molecules to be removed in an active form. Any component can be used as a ligand to purify its respective binding
partner.
Some typical biological interactions, frequently used in affinity chromatography, are listed below:
Enzyme – substrate analogue, inhibitor, cofactor
Antibody – antigen, virus, cell.
Lectin – polysaccharide, glycoprotein, cell surface receptor, cell.
Affinity Chromatography Procedure
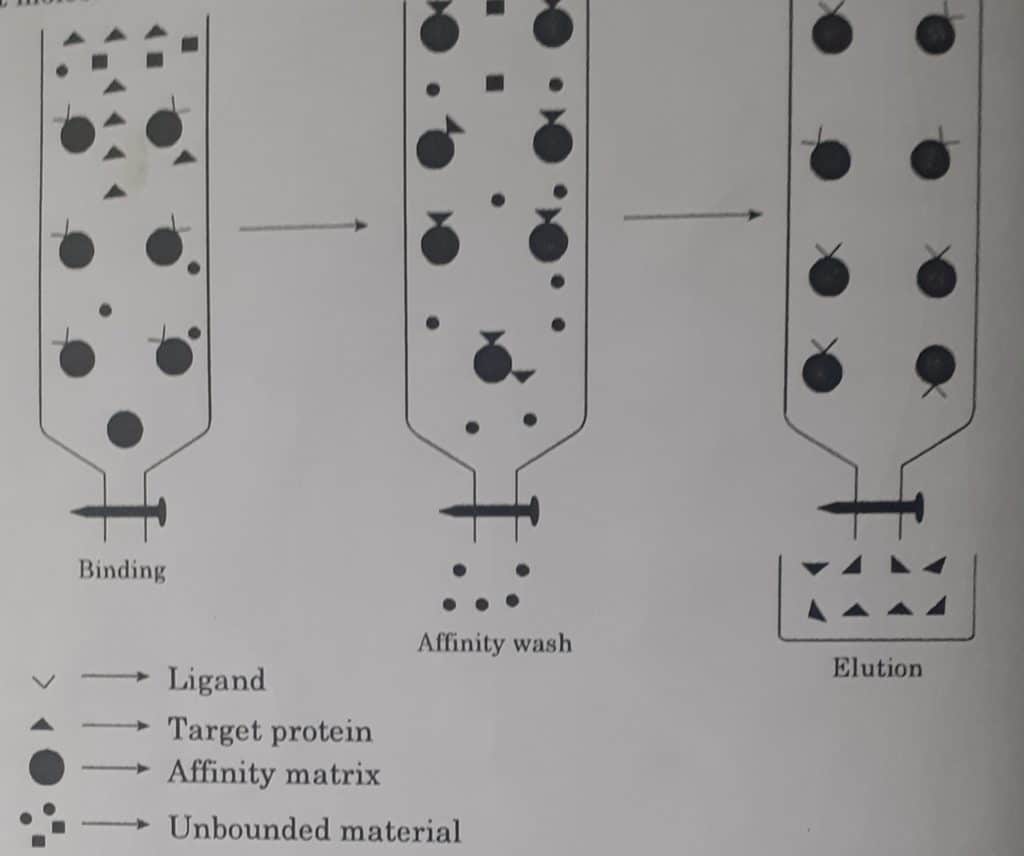
The procedure of affinity chromatography is explained below:
- Affinity medium is equilibrated in binding buffer.
- Sample is applied under conditions that favour specific binding of the target molecule(s) to a complementary binding substance (the ligand). Target substances bind specifically but reversibly, to the ligand and unbound material washes through the column.
- Target protein is recovered by changing conditions to favour elution of the bound molecules. Elution is performed specifically, using a competitive ligand, or non-specifically, by changing the pH, ionic strength or polarity. Target protein is collected in a purified, concentrated form
- Affinity medium is re-equilibrated with binding buffer.
Application of Affinity Chromatography
Some of the important applications of Affinity chromatography are listed below:
- Proteins can be purified by using recombinant tagged proteins
- It is used in immunoglobulin purification.
- It is used in analysis of chiral compounds
- It is also used in the characterization of drug and hormone proteins interactions.
FAQs
What is Affinity chromatography?
Affinity chromatography is a type of chromatographic technique in which separation is based on the various types of specific affinities between a target molecule and a specific ligand coupled to a chromatography medium.






