Table of Contents
ToggleValence bond theory(VBT) was proposed by two scientists Heitler and London in 1927 to explain the formation of covalent bonds. Later, this theory was improved by Linus Pauling by introducing the concept of hybridization. VBT is also known as the localized bond model. According to valence bond theory, a covalent bond is formed by overlapping of atomic orbitals of combining atoms having unpaired electrons.
Valence bond theory definition
Valence bond theory (VBT) is a localized quantum mechanical approach to describe the bonding in molecules. VBT provides a mathematical justification for the Lewis interpretation of electron pairs making bonds between atoms. The assumption of valence bond theory is that all bonds are localized bonds formed between two atoms by the sharing of an electron from each atom.
Main postulates of valence bond theory
The main features/postulates/principle of valence bond theory are listed below:
- A covalent bond is formed by overlapping of half filled atomic orbitals of combining atoms.
- Atomic orbitals undergoing overlap must be sufficiently close to each other with proper orientation.
- Only valence orbitals of atom overlap each other to form bond by sharing of electrons.
- A pair of electrons with opposite spin is present in overlapping orbitals.
- The strength of bond formed depends on the extend of overlapping. Greater the overlapping of atomic orbitals, stronger the covalent bond formed.
- The energy of the resulting molecule is less than the individual atoms in separation.
- The atoms which unite to form a molecule completely retain their identities in the resulting molecule.
Types of Covalent bond
There are two types of covalent bonds depending upon the type of overlapping of atomic orbitals.
A. Sigma bond(σ-bond)
A covalent bond is formed by the head-on or axial overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals, such bond is called a sigma bond. The overlapping of orbitals takes place along the internuclear axis. The extend of overlapping is large therefore, the strength of the bond is strong. s-s overlapping, s-p overlapping, and px-px overlapping(if x is taken as internuclear axis) form a sigma bond.
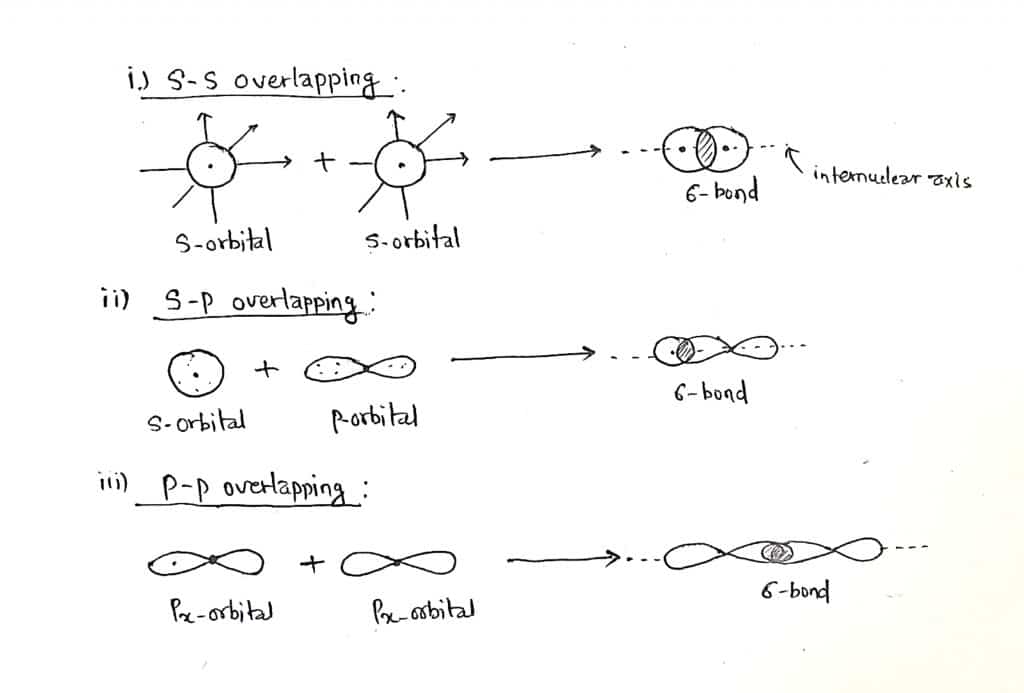
B. Pi bond(π-bond)
A covalent bond is formed by sideways or lateral overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals, such bond is called pi bond. The overlapping takes place perpendicular to the internuclear axis. The extend of overlapping of atomic orbital in such case is small therefore, the strength of the bond is weak. p-p overlapping forms a pi bond.
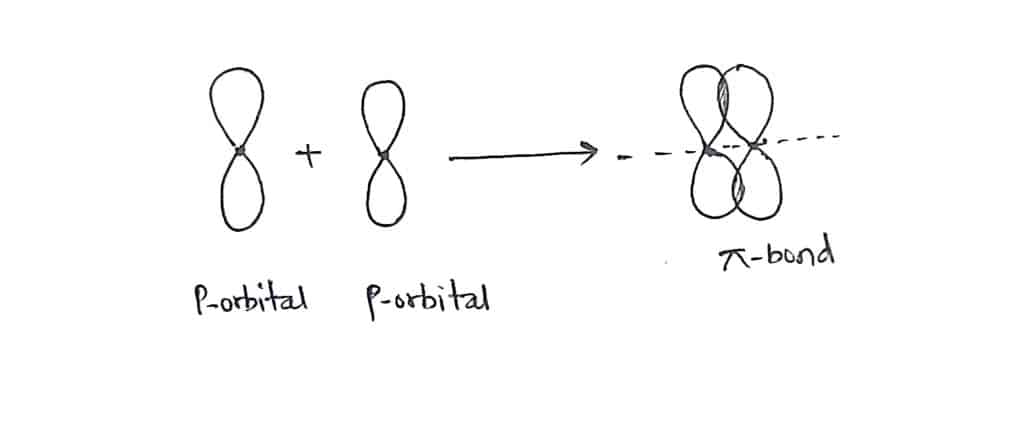
Difference between Sigma bond(σ-bond)and Pi bond(π-bond)
The difference between sigma bond and pi bond is given below:
| σ-bond | π-bond |
| Sigma bond is formed by the head-on overlapping of atomic orbitals. | Pi bond is formed by sideways overlapping of atomic orbitals. |
| Overlapping of atomic orbitals takes place along the internuclear axis. | Overlapping of atomic orbitals takes place along the perpendicular to the internuclear axis. |
| It is stronger than the pi bond. | It is weaker than the sigma bond. |
| Free rotation about the sigma bond is possible. | Free rotation about the pi bond is restricted. |
| It may be present alone or along with pi bonds. | It can’t be formed alone. It is formed after the formation of a sigma bond. |
Limitations of valence bond theory
The drawbacks/defects of valence bond theory are listed below:
- VBT fails to explain the tetravalency of carbon.
- Valence bond theory does not address the issue of the paramagnetic nature of O2 molecule.
- Failure to explain the formation of molecule with odd electron. Example: H2+ like molecule formation.
- No explanation about the bonding in electron deficient compound with incomplete octet such as B2H6.
- It explains only covalent bonding but not co-ordinate covalent bonding.
- No discussion about the energies of the electrons.
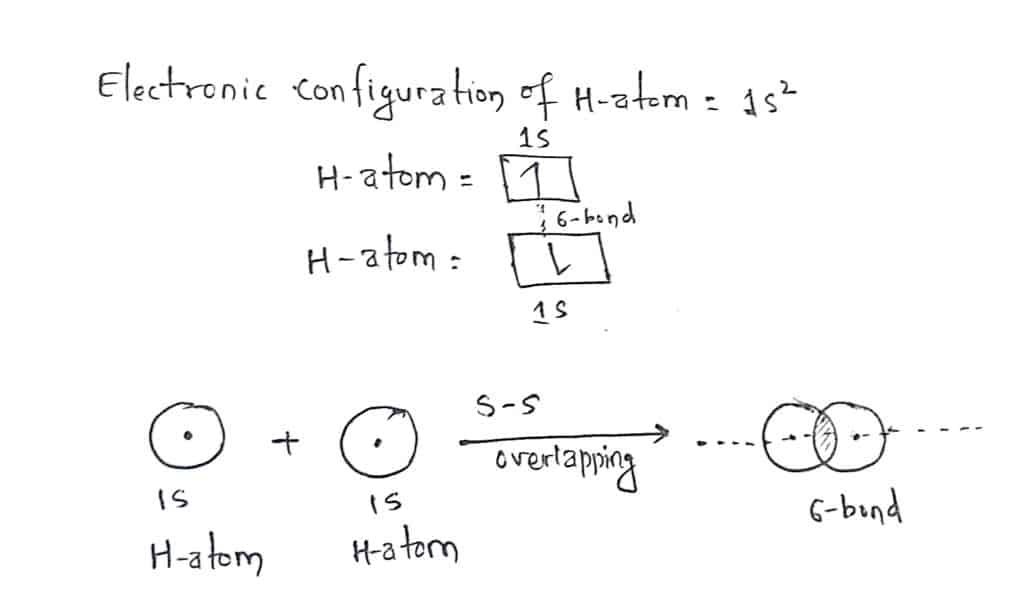
Valence bond theory for hydrogen molecule
We know, a hydrogen atom has only one electron in the s-orbital. The electronic configuration of H-atom is 1s1. In the formation of the hydrogen molecule, the half-filled 1s-orbital of one hydrogen atom overlap with the half-filled 1s orbital of another hydrogen atom forming a sigma bond as shown in the figure.
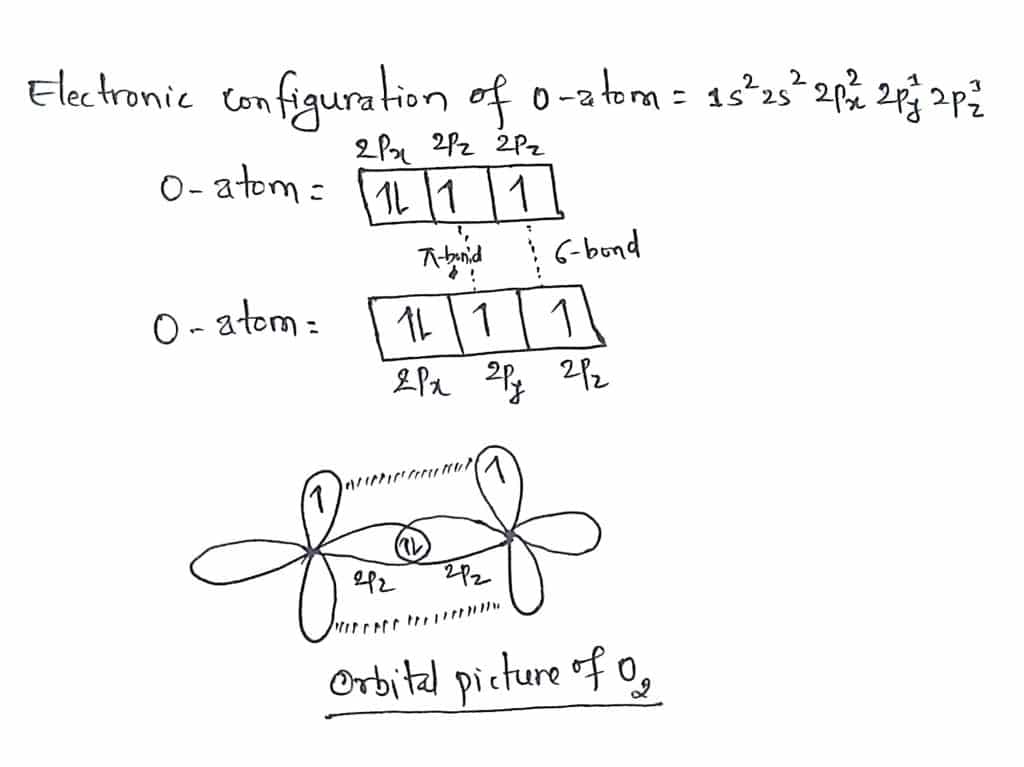
O2 valence bond theory
The electronic configuration of an Oxygen atom= 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py1 2pz1.
An oxygen atom has two half-filled orbitals 2py and 2pz. During the formation of O2 molecules, the half-filled orbital 2py of one oxygen atom overlaps with half-filled orbital 2py of another oxygen atom by head-on overlap to form a sigma bond. Similarly, the remaining orbital 2pz undergo sideways overlap with the 2pz orbital of another oxygen atom to form a pie bond.
valence bond theory vs molecular orbital theory
The difference between valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory is shown below:
| Valence bond theory | Molecular orbital theory |
| In VBT, two half-filled atomic orbitals combine to form a bond between two atoms. | In MOT, atomic orbitals from each atom combine to form molecular orbitals. |
| The atomic orbital of combining atoms retains their identity. | The atomic orbital of combining atoms loss their identity in molecular orbitals. |
| The resonance effect has an important role in VBT. | The resonance effect has no role in MOT. |
| It fails to explain the paramagnetic character of the O2 molecule. | It explains the paramagnetic character of the O2 molecule. |
| It fails to explain the formation and existence of H2+ion. | It explains the formation and existence of H2+ion. |
valence bond theory video lecture
FAQs/MCQs:
what is a valence bond theory?
Valence bond theory (VBT) is a localized quantum mechanical approach to describe the bonding in molecules.
What is a sigma bond?
A covalent bond is formed by the head-on or axial overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals, such bond is called a sigma bond.
What is a pi bond?
A covalent bond is formed by sideways or lateral overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals, such bond is called a pi bond.
Who proposed the Valence bond theory?
Valence bond theory(VBT) was proposed by two scientists Heitler and London in 1927 to explain the formation of covalent bonds.