Table of Contents
ToggleSpectrochemical series is defined as the experimentally determined series on the basis of the strength of ligand field for the splitting of d-orbital of metal ion of complexes.
Spectrochemical series definition
Crystal field splitting is greatly influenced by the nature of ligands. Different ligand causes different degrees of splitting of d-orbital of metal ion in the complexes. Ligands that cause larger crystal field splitting are called strong field ligands. Similarly, those ligands which cause smaller crystal field splitting are called weak field ligands.
The experimental observation of spectra of a series of complexes of the same metal ion with different ligands shows that the values of crystal field splitting energy varies depending on the nature of ligands. The arrangement of ligands in a series in the order of increasing crystal field splitting is called spectrochemical series.
Although it is not possible to form a complete series of all ligands with a single metal ion, but from the overlapping sequences following series results.
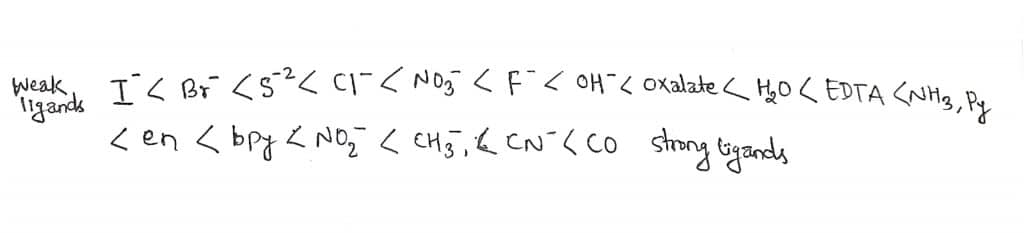
where, py=pyridine, en=ethylenediammine, bpy=2,2-bipyridine.
Factor affecting position of Ligands in series
- The series is experimentally determined but it is difficult to explain theoritically. However, the relative position is based on their increasing σ donation.
- The ligands with high negative charge and small size and having good σ donor and π-acceptor property gives large crystal field splitting and occupy top position of series as strong ligand. In contrast, ligands which acts as π-donor occupy bottom position as weak field ligand.
Significance of Spectrochemical series
Spectrochemical series can be used to predict the relative d-orbital splitting of two complexes containing the same metal ion with the different ligands. Similarly, the relative frequency of the absorption band can be predicted.
Limitation of Spectrochemical series
The spectrochemical series presents serious difficulty in the interpretation of pure crystal field theory. Some of the limitations are listed below.
- The anionic ligands would exert greatest effect but they are at low end.
- OH– should lie above neutral H2O but the order is reverse.
- NH3 produces a greater splitting than H2O although their dipole moments are in reverse order (μNH3 = 4.90 × 10-30 cm; μH2O = 6.17 × 10-30 cm)
- The model is also unable to account for the fact that with certain strong field ligands (such as CN-) , Δo varies only slightly for the analogous complexes within a group.
FAQs:
what is spectrochemical series?
Spectrochemical series is defined as the experimentally determined series on the basis of the strength of ligand field for the splitting of d-orbital of metal ion of complexes.
define spectrochemical series
The arrangement of ligands in a series in the order of increasing crystal field splitting is called spectrochemical series.




One Response
Thanks for awesome notes. How can i download its pdf version?