Table of Contents
ToggleHalogens are the non-metallic elements (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and tennessine) belonging to group VIIA or 17 of the periodic table. They are collectively called “halogens” as their salts are present in the seawater(Greek “halo”: sea salts and gen: producer). Astatine is an expectation, which is a radioactive element and unstable, so its chemistry is little known. Among halogens, fluorine is the most reactive and is called a “super halogen.”
| Element | Symbol | Atomic number | Atomic mass | Physical state | Colour | Electronic Configuration |
| Fluorine | F | 9 | 19 | gas | light yellow | [He]2s22p5 |
| Chlorine | Cl | 17 | 35 | gas | greenish yellow | [Ne]3s23p5 |
| Bromine | Br | 35 | 80 | liquid | reddish brown | [Ar]3d104s24p5 |
| Iodine | I | 53 | 127 | solid | violet | [Kr]4d105s25p5 |
| Astatine | At | 85 | 210 | – | – | [Xe]5d106s26p5 |
| Tennessine | Ts | 117 | 294.211 | Solid | – | [Rn] 5f146d107s27p5 |
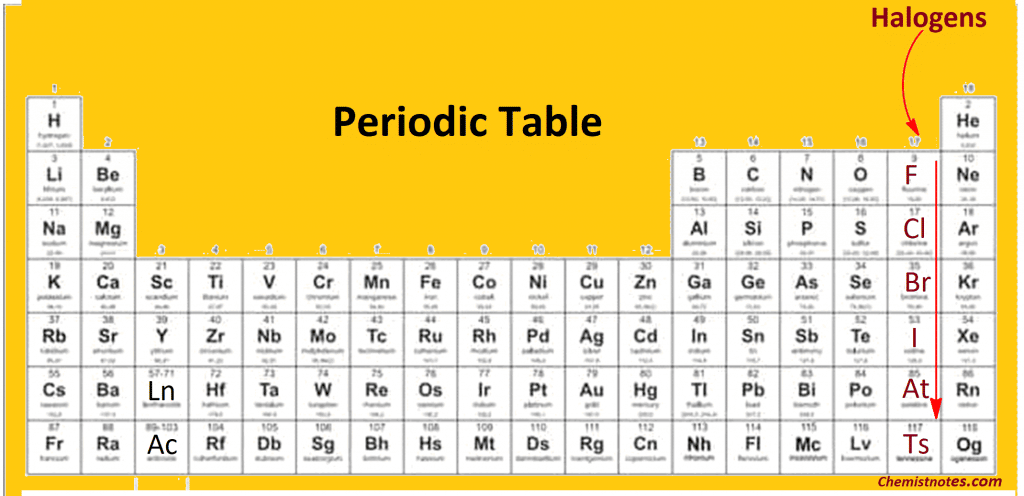
Position of Halogens in the Periodic Table
The halogens constitute group VIIA of the periodic table. Each halogen has seven valence electrons. The outermost electronic configuration of halogen is represented by the general formula ns2np5. All elements, with the last electron being added to one of the orbitals of their p-subshell, therefore find their place in the p-block of the periodic table. Hence, elements are kept at the extreme right of the periodic table, before noble gases.
General Characteristics
The element of group VIIA exhibits similarity in the following properties:
- Electronic configuration: all elements have seven electronic (ns2np5) in their outermost shell. According to Hund’s rule, the five p-electrons are arranged in orbitals as px2, py2, and pz1.
- Fluorine and chlorine gases exist as gases. Bromine is a corrosive liquid, while iodine is a volatile solid at room temperature.
- They exist as diatomic molecules (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) containing covalent bonds.
- The melting point and boiling point both increase in atomic number due to the increase of Vander Waal’s forces.
- Electronic configuration: all elements have seven electrons (ns2np5) in their outermost shell. According to Hund’s rule, the five p-electrons are arranged in orbitals as px2, py2, and pz1.
- Fluorine and chlorine gases exist as gases. Bromine is a corrosive liquid, while iodine is a volatile solid at room temperature.
- They exist as diatomic molecules (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) containing covalent bonds.
- The melting point and boiling point: The m.p and b.p increase in atomic number due to the increase of Vander Waal’s forces F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2.
- Fluorine is the most electronegative element (E.N. = 4) Of the periodic table. The electronegativity value decreases across the group as F > Cl > Br > I.
- Electron Affinity: Electron affinity decreases as we move down the group. The order of electron affinity is Cl > F > Br > I. The lower E.A. The higher value of fluorine than chlorine is due to the small size repulsion between the electrons added and the electrons of the fluorine atom.
- Bond length: As the size of the halogen atom increases, the bond length of the X-X bond in the X2 molecule increases as F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2.
- Reactivity: All halogens are chemically reactive and reactivity decreases from fluorine to iodine: F > Cl > Br > I. The high reactivity of fluorine is due to its high electronegativity, small size, low bond dissociation energy, and high oxidizing power.
- Formation of halides: They combine with metals and non-metals to form ionic and covalent halides, respectively.
The Physical Properties of Halogens
| Property | Fluorine | Chlorine | Bromine | Iodine |
| Molecular Formula | F2 | Cl2 | Br2 | I2 |
| Atomic radius Ao | 0.72 | 0.99 | 1.14 | 1.33 |
| Electronegativity | 4 | 3 | 2.8 | 2.5 |
| Electron affinity (KJ/mol) | 333 | 348 | 340 | 297 |
| M.P. (oC) | -220 | -101 | -7.2 | 144 |
| M.P. (oC) | -188 | -35 | 59 | 184 |
| Bond energy(KJ/mol) | 158 | 253 | 192 | 151 |
| Bond length | 1.43 | 1.99 | 2.28 | 2.66 |
| Odour | Strong pungent | sharp irritating fatal in high dose | irritating poisonous and corrosive | odourless |
The high electronegativity of halogens makes them very reactivity, so they aren’t found in a free state. They occur in nature only in combined states.
FAQs
What are halogens?
The non-metallic element fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine and tennessine belonging to group VIIA or 17 of the periodic table are called halogens.
Where are halogens on the periodic table?
The halogens constitute the group VIIA of the periodic table.
How many valence electrons do halogens have?
Halogens atom has 7 valence electrons in its outermost electron shell.
What elements are halogens?
F, Cl, Br, I, At, Ts elements are halogens.